Gross domestic product (GDP): India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content.
|
Historical GDP
LONGSTANDING GIANTS The Times of India Dec 05 2014
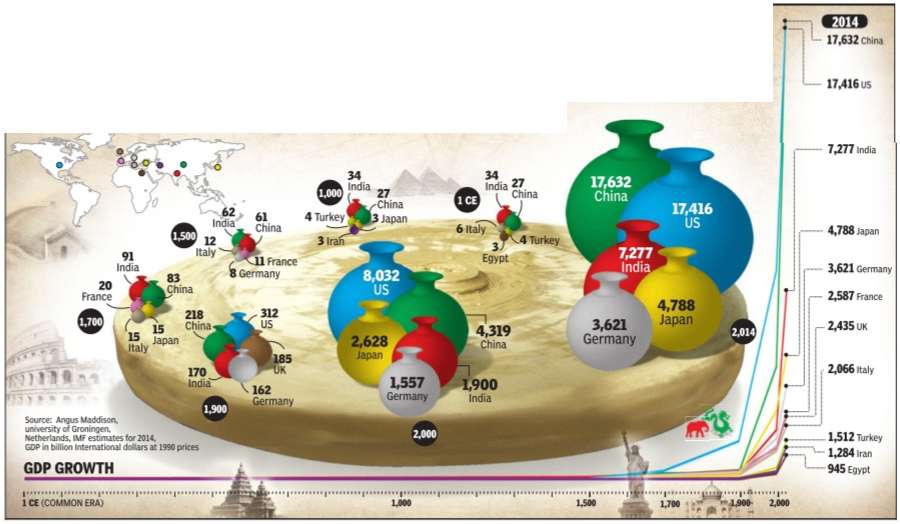
Which will be the world's largest economies in the future? Various studies suggest that it would be either China or India. But what about the largest economies in the past--1CE (Common Era), 1000CE, 1500CE and so on? Interestingly, even these periods were dominated by the Asian giants.For more than 1,700 years, India and China were the world's largest economies. Their dominance ended after the industrial revolution and the subsequent imperialist expansion of European nations which drained the world's wealth to the West. That's what data on historical GDP calculated by the late Angus Maddison, British economist and scholar on quantitative macroeconomic history, shows
Impact of poor monsoons on GDP growth
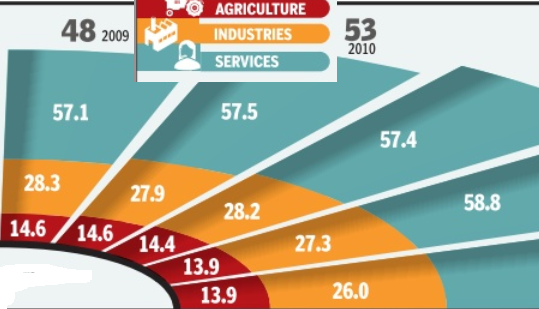
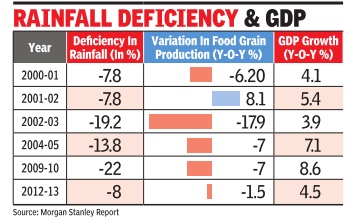
`Poor rains unlikely to impact GDP growth much'
Prabhakar Sinha New Delhi:
TNN [The Times of India Jun 19 2014
Even as country braces for likely deficient monsoon, its impact on GDP may not be very significant.
The decline in farm output as a result of shortfall in rains is unlikely to reduce GDP growth rate in 2014 by more than 0.5 percentage points, says global research firm Morgan Stanley in its latest report
The production of pulses and oil seeds, the report points out, may be worst affected, leading to rise in prices of these items and to bridge the demand-supply gap, the country will have to depend on imports.
Trends in monsoon rainfall will be critical for the overall inflation outlook. While food inflation has softened over the last few months, a poor monsoon may reverse the trend. Monsoon rains have an important bearing on inflation with primary and manufactured articles contributing 24.3% weight in overall wholesale price index and 47.6% in the new Consumer price Index. While the countrywide shortfall in rains is expected to be around 7%, the spatial (region-wise) distribution forecast shows that monsoon deficiency in North-West India may be 8% with a 71% probability . But being the most irrigated region in the country , it currently boasts of full reservoirs. So, according to the report, the region that comprises of Punjab, Haryana and Western UP and produces most of the Kharif crops should see a near-normal production.
If El Nino fears were to come true, the report says, there will be downside risks to Morgan Stanley's estimate of agricultural growth at 2.4% in 2014-15. With agriculture accounting for only 15% of GDP, one percentage point reduction in agricultural growth rate will lead to 15 basis points (100 basis points make one percentage point) decline in GDP growth.
Therefore, even if there is no growth in the agricultural sector, the direct impact on GDP growth will not be of more than 0.5 percentage point, predicts report.