Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG): India
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| − | + | =YEAR WISE DEVELOPMENTS= | |
| − | =2014= | + | ==2014== |
John Sarkar & Shubham Mukherjee | John Sarkar & Shubham Mukherjee | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
From the highs of Q3 of 2018, the FMCG sector is staring at a slowdown with the value growth dropping to 10%. In this quarter, demand has dropped across segments with salty snacks, biscuits, spices and packaged tea leading slowdown. | From the highs of Q3 of 2018, the FMCG sector is staring at a slowdown with the value growth dropping to 10%. In this quarter, demand has dropped across segments with salty snacks, biscuits, spices and packaged tea leading slowdown. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===2018> 19=== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/more-exits-fewer-openings-hit-fmcg/articleshow/73506438.cms January 22, 2020: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | [[File: FMCG growth in urban and rural markets, 2018 and 2019..jpg|FMCG growth in urban and rural markets, 2018 and 2019. <br/> From: [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/more-exits-fewer-openings-hit-fmcg/articleshow/73506438.cms January 22, 2020: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | NEW DELHI: Around half of the slowdown in growth in the FMCG segment was led by small players, with more than 5,000 businesses shutting shop in 2019, a report showed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | While these small businesses (turnover less than Rs 100 crore) accounted for 20% of the FMCG business in India, their contribution to the slowdown in consumption was pegged at 45%, followed by 32% for large companies (turnover greater than Rs 600 crore) and 24% for medium-sized companies (turnover between Rs 100 crore and Rs 600 crore), according to the latest study by market research company Nielsen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The slowdown was driven by fewer new manufacturers entering the FMCG space and declining distribution. While the total number of FMCG manufacturers increased from 36,600 in 2017 to 40,100 in 2018, the number remained stagnant at 40,600 in 2019, due to more exits by the smaller companies. Growth in distribution, too, plunged into the negative for smaller players from 7.8% in 2018 to -4.2% in 2019. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This led to companies spending less on innovations, which resulted in a steep 25% dip in new launches in 2019 over the previous year. “2019 has been a tough year for the FMCG industry with over four-point decline, but we do see it stabilising in the last quarter of the year,” said Prasun Basu, South Asia Zone president at Nielsen Global Connect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “A mix of macro-economic factors, and channel and zone factors driven by manufacturers, coupled with consolidation of smaller players have been instrumental in the slowdown. However, 2020 offers a stable outlook for the industry arresting the 2019 decline,” he said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The last quarter of 2019 saw the FMCG industry grow at 6.6% (7.3% with e-commerce), compared to 15.7% in Q4 2018, indicating an arrest as against the sharp slowdown witnessed in the previous quarters. After two years of double-digit growth, FMCG witnessed 9.2% growth (excluding e-commerce) in the calendar year 2019, down from 13.5% in the previous calendar year. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For 2019, the slow growth was led by the rural market, which accounts for 75% of India’s population and contributes 36% to overall FMCG spends. Traditionally, rural India has grown around 3-5% points faster than urban. But in the last quarter, its growth dropped below that of urban India for the first time in seven years. | ||
| + | Nielsen expects Q1 (Jan-Mar 2020) FMCG growth to be in the range of 8-9%, marginally higher than Q4 2019. The full year 2020 forecast, however, is expected to be stable at 9-10%. | ||
| + | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
| Line 57: | Line 77: | ||
[[Category:India|C FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA | [[Category:India|C FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA | ||
FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA]] | FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA]] | + | |
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|C FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIAFAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA | ||
| + | FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|C FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIAFAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA | ||
| + | FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA | ||
| + | FAST MOVING CONSUMER GOODS (FMCG): INDIA]] | ||
Revision as of 20:02, 30 August 2022
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
YEAR WISE DEVELOPMENTS
2014
John Sarkar & Shubham Mukherjee
Dec 27 2014
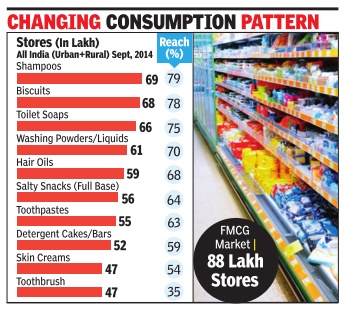
Personal care drives FMCG biz on rural push. Biscuits only food item among top 5 categories
For decades, food items have been the most widely distributed FMCG products in the country. But that rule of thumb is changing. Indians are more likely to find more personal care products than food in a shop these days—a result of consumer goods players pushing the distribution of an entire range of their products in the face of wary consumer spending.
Latest data from market research firm Nielsen reveals that on the list of the top five FMCG product categories, only one food product—biscuits— finds place. The category with the maximum reach, or penetration as it’s called in market parlance, is shampoos at 79%, followed closely by biscuits at 78%.
Distribution of categories has undergone a dramatic transformation in the last 15 years. FMCG is available in 8.8 million outlets and shampoo is available in 80% of those outlets, says D Shivakumar, chairman and CEO, PepsiCo India.
“Skin creams have got into the top 10 distributed list and packaged tea, which was the most distributed category a few decades ago, is now out of the top 10. Daily-use, lowunit price, easy-to-sell via wholesale are the key lessons for categories in the last 10 years.” Data suggests that most of this evolution is due to a lot of un-branded consumption shifting to branded consumption. For instance, in utensil cleaners and edible oils penetration has increased to 36% from 33% and 21% to 17% from 2012 to 2014, respectively. “Earlier, people would turn up at shops with bottles to buy loose mustard oil. That’s changing with rising affluence levels and lower packaging costs. In future, we will see more un-branded-tobranded consumption in nonmature categories such as, hair oils and hair conditioners,” says Vijay Udasi, executive director, Nielsen India.
The findings also reveal a drop in penetration levels of detergents cakes and bars from 60% in 2012 to 59% in 2014 as more consumers shift to washing machines to do their laundry . Similarly, skin creams have also seen a drop of 2% due to changes in consumer behaviour. “The segments within the skin creams category have also changed.More people are buying emerging products like face washes, anti-ageing and under-eye creams,“ says Udasi.
For HUL, next step now is to make its brands accessible using pack sizes and price points tailored to win across the country . “We have been able to maintain our leadership position in a growing market by following a market development approach. One of the most successful attempts on this front has been the Dove `twin sachet', which offers a shampoo and conditioner together at a Rs 5 price point to induce trials,“ says Srirup Mitra, category head – Hair Care, HUL.
But the dominance of nonfood categories on the top could change. There are ominous signs. Take the salty snacks category for instance.
Penetration has risen from 58% to 64%. Even a category like noodles, which has still not broken into the top-ten list, has seen an increase in penetration from 38% to 42%.
“The next level of growth lies within branded foods,” says Udasi. “There is an emergence of new food categories in bread spreads, including peanut butter and branded spices. As affluence levels rise, rural consumers will spend more on grocery items and food.” Although FMCG growth has been slowing for some time now, sliding by 8.1% from 2010 to 2013, Nielsen predicts that India’s FMCG industry will grow from $37 billion in 2013 to $49 billion in 2016. Distribution growth and innovations around sachet offerings will play major roles in fuelling growth, which had slowed down in the last few years. While the rise of e-commerce is being keenly watched, several new models may evolve over the next few years.
2018> 2019: The slowdown
July 24, 2019: The Times of India
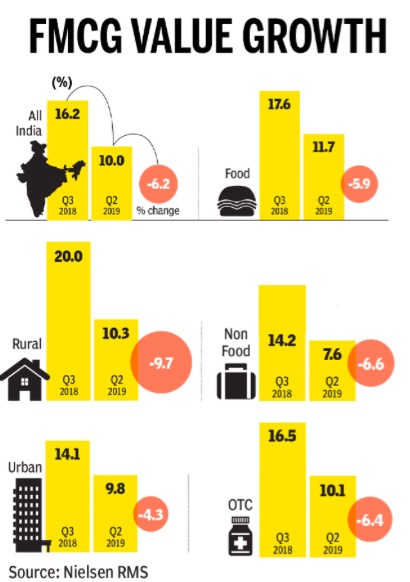
From: July 24, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic:
2018> 2019: FMCGs and the slowdown
From the highs of Q3 of 2018, the FMCG sector is staring at a slowdown with the value growth dropping to 10%. In this quarter, demand has dropped across segments with salty snacks, biscuits, spices and packaged tea leading slowdown.
2018> 19
January 22, 2020: The Times of India
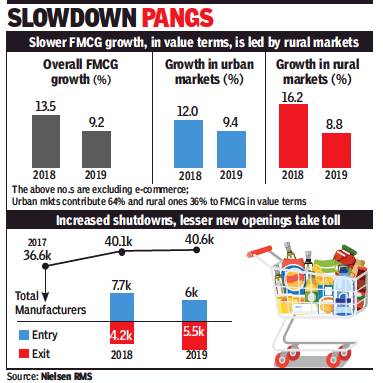
From: January 22, 2020: The Times of India
NEW DELHI: Around half of the slowdown in growth in the FMCG segment was led by small players, with more than 5,000 businesses shutting shop in 2019, a report showed.
While these small businesses (turnover less than Rs 100 crore) accounted for 20% of the FMCG business in India, their contribution to the slowdown in consumption was pegged at 45%, followed by 32% for large companies (turnover greater than Rs 600 crore) and 24% for medium-sized companies (turnover between Rs 100 crore and Rs 600 crore), according to the latest study by market research company Nielsen.
The slowdown was driven by fewer new manufacturers entering the FMCG space and declining distribution. While the total number of FMCG manufacturers increased from 36,600 in 2017 to 40,100 in 2018, the number remained stagnant at 40,600 in 2019, due to more exits by the smaller companies. Growth in distribution, too, plunged into the negative for smaller players from 7.8% in 2018 to -4.2% in 2019.
This led to companies spending less on innovations, which resulted in a steep 25% dip in new launches in 2019 over the previous year. “2019 has been a tough year for the FMCG industry with over four-point decline, but we do see it stabilising in the last quarter of the year,” said Prasun Basu, South Asia Zone president at Nielsen Global Connect.
“A mix of macro-economic factors, and channel and zone factors driven by manufacturers, coupled with consolidation of smaller players have been instrumental in the slowdown. However, 2020 offers a stable outlook for the industry arresting the 2019 decline,” he said.
The last quarter of 2019 saw the FMCG industry grow at 6.6% (7.3% with e-commerce), compared to 15.7% in Q4 2018, indicating an arrest as against the sharp slowdown witnessed in the previous quarters. After two years of double-digit growth, FMCG witnessed 9.2% growth (excluding e-commerce) in the calendar year 2019, down from 13.5% in the previous calendar year.
For 2019, the slow growth was led by the rural market, which accounts for 75% of India’s population and contributes 36% to overall FMCG spends. Traditionally, rural India has grown around 3-5% points faster than urban. But in the last quarter, its growth dropped below that of urban India for the first time in seven years. Nielsen expects Q1 (Jan-Mar 2020) FMCG growth to be in the range of 8-9%, marginally higher than Q4 2019. The full year 2020 forecast, however, is expected to be stable at 9-10%.
See also
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG): India