Air Quality Index: India
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
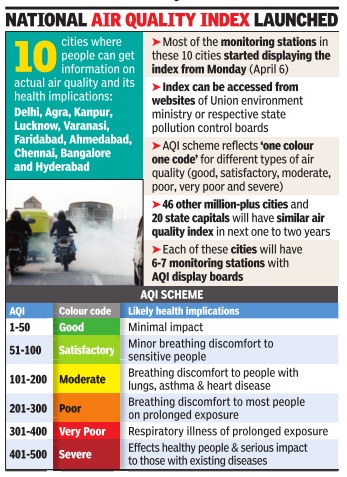
2015: National Air Quality Index (AQI)
The Times of India, Apr 07 2015
Vishwa Mohan
Choking India gets Air Quality Index
With Prime Minister Narendra Modi launching a national air quality index (AQI), India on Monday joined a global club which includes the US, France, China and Mexico that have implemented such an alert system.The system will give details of air quality and information on its likely health implications for city dwellers. India's AQI will initially be available to people in 10 cities -Delhi, Faridabad, Agra, Kanpur, Lucknow, Varanasi, Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Chennai and Hyderabad. It will help people in these cities take precautions on days when the air quality is particularly poor.
Other cities, including Mumbai, Kolkata and Chandigarh, will come under the national indexing network in a couple of months when their pollution control boards are ready with the new and updated round-the-clock monitoring stations. All metropolitan cities and state capitals that do not get access to the Air Quality Index will have a similar facility made available to them within a year or two.
The central agencies have taken into account eight pollutants: PM2.5, PM10, nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide, ozone, carbon monoxide, ammonia and lead while calculating and releasing the AQI.The index, using continuous 24-hour average data, will be made available daily from various monitoring stations in those cities.
The move, which will not only enhance public awareness but also create a competitive environment among cities to mitigate air pollution, was welcomed by environmentalists and think-tanks.
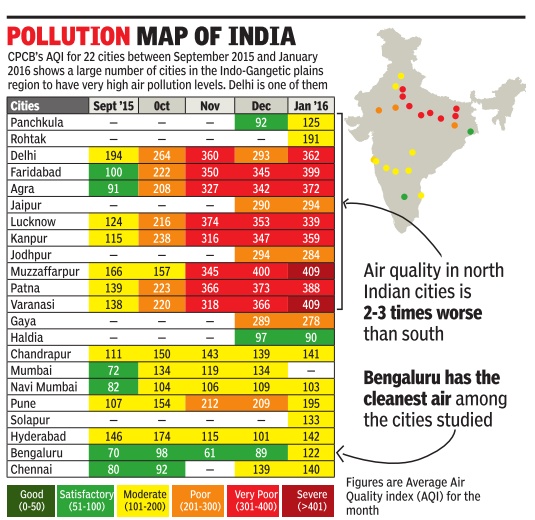
2015-16: AQI for 24 cities
The Times of India, Feb 06 2016
Jayashree Nandi
Delhi not the country's pollution capital: CPCB
The capital lost a dubious crown on Friday with the country's pollution watchdog saying it is not India's most polluted city , perhaps not even the second worst. But Central Pollution Control Board's (CPCB) data for the September 2015-January 2016 period clearly shows that Delhi's air is far from healthy . CPCB has published air quality indices (AQI) for 24 cities that help in comparing pollution levels at a glance with a colour code and a numerical value. In India, AQIs are determined based on the concentrations of seven pollutants, including PM2.5 (fine, respirable particles), sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and carbon monoxide (CO). In January , when Varanasi in UP and Muzaffarpur in Bihar had “severe“ AQI values of 409, Delhi scored a “very poor“ with 362. Even neighbouring Faridabad was worse with an AQI of 399. Only three cities--Bengaluru, Haldia and Panchkula--had moderate air quality during the period.
Although the AQIs will draw attention to the problem of air pollution in smaller cities, experts say the indices are at best indicative because in most cities CPCB has very few monitoring stations, and sometimes these are out of order. For instance, Muzaffarpur, Gaya, Faridabad and Varanasi have only one station each.
Centre for Science and En vironment's analysis of Del hi Pollution Control Committee's (DPCC) real-time monitoring data for December shows the capital had 23 severe air quality days although CPCB says there were none.“We have to factor in that many CPCB stations are in background areas or less polluted locations,“ CSE said.
Four key takeaways in the CPCB data:
Delhi is not India's pollution capital
In the past five months, Delhi had 13 “severe“ air quality days while Muzaffarpur had 37, Varanasi 24, Agra and Faridabad 22 each, and Lucknow 18. In a “severe“ AQI episode, most governments declare an air quality emergency as even young and healthy people can develop a variety of symptoms. People are advised to stay indoors. Delhi, however, had more “very poor“ air quality days -AQI of 301-400 -than any other city.It had 69 to Kanpur's 65 and Varanasi's 43. Of the remai ning 71 days, 43 recorded “poor“ air quality in Delhi. The city also had as many as 43 days in the poor category .Delhi's pollution problem seems worrying because while it swings between bad and very bad, the other cities also have moderate air pollution at times.
Jekyll-and-Hyde cities
ome cities manage to have S very bad and very good air days in the rainy months, so their average does not reflect the severity of pollution. In September, Chandrapur in Maharashtra recorded a peak of 420, which is severe, and a minimum of 39, which is good, lowering its average to 111 or inside the moderate category . Agra also had a minimum of 26 in September, as against a peak of 404.
Weather and location influence air quality
ities with the worst AQIs C are mostly in the IndoGangetic plains, indicating that weather and location affect air quality as much as emissions. “There are geographical factors as well as anthropological (human),“ said Gufran Beig, project director at System of Air Qua lity and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR) under the ministry of earth sciences. Winds from the north and south of the plains converge in the zone, increasing the pollution, he explained.“The area is also the second largest alluvial plain, it is very fertile land and so naturally it is the most polluted. It also has more emission sources like industries, vehicles and brick kilns,“ he added.The zone also has a concentration of thermal power plants. Dipankar Saha, additional director, air lab at CPCB, said reducing emissions is the only way to counter the zone's meteorological disadvantage.
Differing fuel standards
Trucks and other heavy vehicles sold in many small cities of north India have BSIII engines although BS IV diesel is available. CSE has called for immediate implementation of BS IV norms across the country . CSE researchers say while places like Chandrapur are highly industrialised, motorisation rates are very high in cities like Kanpur and Lucknow due to rapid urbanisation. “This shows air pollution is a national public health crisis,“ said Anumita Roy Chowdhury , head of CSE's `Clean Air' campaign. “Stronger public opinion has provoked action in Delhi but other cities, especially the second rung cities, are victims of policy neglect.We urgently need a national air quality strategy . National air quality standards should be legally binding.“