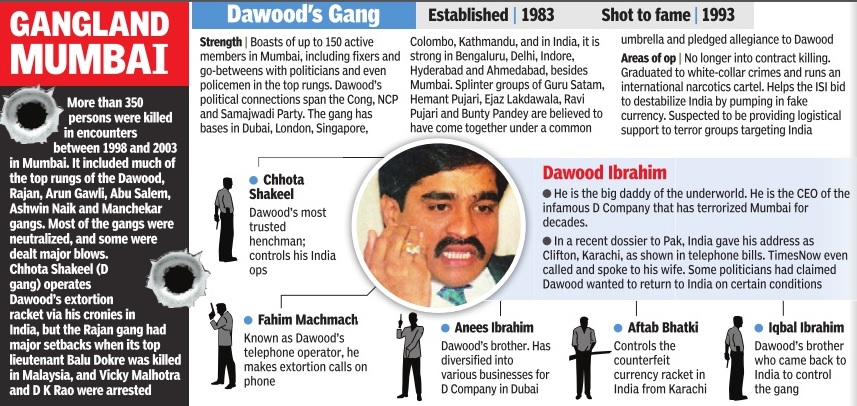
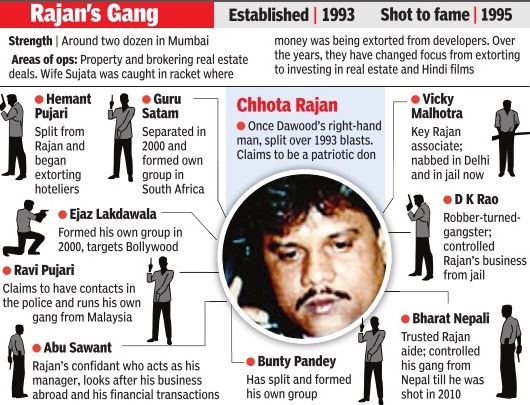
The Gangs of Mumbai
(Created page with "[[File: Gangs of Mumbai1.jpg|The Gangs of Mumbai, 2015; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Gallery.aspx?id=27_10_2015_017_025_002&type=P&artUrl=GANGLAND-MUM...") |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Category:India |M ]] | [[Category:India |M ]] | ||
[[Category:Crime |M ]] | [[Category:Crime |M ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =1960s-90s: Tamil dons, Haji Mastan and Filmistan= | ||
| + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=WHEN-TAMIL-DONS-RULED-BOMBAY-02112015013013 ''The Times of India''], November 2, 2015 | ||
| + | [[File: How much of Mani Rathnam’s ''Nayakan '' was true to Varadaraja Mudaliar’s real life.jpg| How much of Mani Rathnam’s ''Nayakan '' was true to Varadaraja Mudaliar’s real life?; Graphic courtesy: [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=WHEN-TAMIL-DONS-RULED-BOMBAY-02112015013013 ''The Times of India''], November 2, 2015|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | CDS Mani & Abdullah Nurullah | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Chhota Rajan's arrest has thrown spotlight on predecessors Varadaraja Mudaliar, Haji Mastan''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chhota Rajan's arrest in Indonesia has thrown the spotlight on mafia dons, their power and global scale of operations, and their ri valries. Despite their criminal activities, Dawood Ibrahim and Chhota Rajan have sought to portray themselves as leaders protecting members of their community , delivering quick justice and settling local disputes. | ||
| + | Not too long back, Tamil dons ruled the underworld of Bombay , as Mumbai the underworld of Bombay , as Mumbai was known then. Compared to D Company and Rajan, they were smaller. But they too sought the mantle of the leadership of their community poor migrants living in slums like Dharavi. Bombay of 1960s-80s had certain resemblances to the 1920s-30s Chicago and the Italian mafia, with gangsters controlling smuggling, gambling, prostitution and bootlegging. Bollywood also spawned the black market ticket business and later extortion rackets. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Haji Mastan Mirza and Varadarajan Muniswami Mudaliar were also mi grants. Coincidentally enough, they were both born on March 1, 1926, -Mastan in Panaikulam in Ramnathapuram district and Varadarajan in Tuticorin in the Madras presidency . | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chhota Rajan's main mentor was a southern mobster Badda Rajan, nickname of Rajan Mahadev Nair, who was associated with Varadarajan -then among the city's top three gangsters with Mastan and Afghan-origin pathan Karim Lala. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varadarajan sought the help of Badda Rajan to protect his territories and neutralize threats from rivals. This helped Badda Rajan expand his sphere of influence. Gradually , Badda Rajan and his protégé diversified their activities, moving from selling film tickets in black to protection money rackets and settling financial and land disputes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Migrating to Bombay at the tender age of eight, Mastan, with his father, started a small cycle repair shop in the city's bustling Crawford market. In 1944, Mastan landed a porter's job at the Bombay docks where he met Karim Lala and their association in various small businesses and smuggling proved lucrative. Haji Mastan was a major player in the smuggling of precious metals in the 1955-75 period and later became a celebrity in Bollywood, financing directors and studios for film production. Later he ventured into film production. Unlike underworld dons who emerged later and spread terror, he was regarded as a relatively soft mafia lord. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It was reported that Amitabh Bachchan's character in the box office hit `Deewar' was inspired by Mastan's life. Thespian Raj Kapoor was reported to have sought financial assistance from him at a critical period. Mastan is also believed to have shared a good equation with other stars like Dilip Kumar, Dharmendra, Feroz Khan and Sanjeev Kumar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mastan's image also spawned another film, “Once upon a time in Mumbaai“ with Ajay Devgn portraying a Mastan-like character and Emraan Hashmi cast as an equivalent of Dawood Ibrahim. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mastan came into prominence when he was jailed during the Emergency . In jail, he is believed to have picked up Hindi. Much later in 1984, he entered the political arena floating the Dalit Muslim Suraksha Maha Sangh. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varadarajan went to Bombay in the early 1960s and got to work as a porter at the Central Railway's main Victoria Ter minus. He would feed the poor outside a Muslim dargah, winning the support of locals. He got an opportunity to assist in the distribution of illicit liquor. With Mastan who had set up a smuggling op eration at the Bombay port, he was also involved in stealing cargo. Later, he got pulled into contract kill ings, narcotics and land hment. As a Tamil don, he was encroachment. As a Tamil don, he was held in high regard in his community in Matunga, Sion, Dharavi and Koliwada where he was said to have been the judge arbiter in many cases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A Murugan bhakt in Tamil Nadu, the astute Varadarajan turned a Ganpathi bhakt capitalizing on the popularity of the elephant-headed god in Bombay and put up a pandal during Ganeshotsav festival. But his hugely popular Ganpathi pandal was served an eviction notice at the behest of the police in the mid-1980s. This was also the time when most members of his gang were jailed or eliminated in encounters forcing him to flee Mumbai for Chennai where he led a retired life till his demise in January 1988 following a heart attack. His body was taken to Mumbai in a chartered flight by Haji Mastan as per Mudaliar's wishes. People paid homage to him. Mastan passed away in Mumbai in 1994. | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 9 November 2015
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
1960s-90s: Tamil dons, Haji Mastan and Filmistan
The Times of India, November 2, 2015

CDS Mani & Abdullah Nurullah
Chhota Rajan's arrest has thrown spotlight on predecessors Varadaraja Mudaliar, Haji Mastan
Chhota Rajan's arrest in Indonesia has thrown the spotlight on mafia dons, their power and global scale of operations, and their ri valries. Despite their criminal activities, Dawood Ibrahim and Chhota Rajan have sought to portray themselves as leaders protecting members of their community , delivering quick justice and settling local disputes. Not too long back, Tamil dons ruled the underworld of Bombay , as Mumbai the underworld of Bombay , as Mumbai was known then. Compared to D Company and Rajan, they were smaller. But they too sought the mantle of the leadership of their community poor migrants living in slums like Dharavi. Bombay of 1960s-80s had certain resemblances to the 1920s-30s Chicago and the Italian mafia, with gangsters controlling smuggling, gambling, prostitution and bootlegging. Bollywood also spawned the black market ticket business and later extortion rackets.
Haji Mastan Mirza and Varadarajan Muniswami Mudaliar were also mi grants. Coincidentally enough, they were both born on March 1, 1926, -Mastan in Panaikulam in Ramnathapuram district and Varadarajan in Tuticorin in the Madras presidency .
Chhota Rajan's main mentor was a southern mobster Badda Rajan, nickname of Rajan Mahadev Nair, who was associated with Varadarajan -then among the city's top three gangsters with Mastan and Afghan-origin pathan Karim Lala.
Varadarajan sought the help of Badda Rajan to protect his territories and neutralize threats from rivals. This helped Badda Rajan expand his sphere of influence. Gradually , Badda Rajan and his protégé diversified their activities, moving from selling film tickets in black to protection money rackets and settling financial and land disputes.
Migrating to Bombay at the tender age of eight, Mastan, with his father, started a small cycle repair shop in the city's bustling Crawford market. In 1944, Mastan landed a porter's job at the Bombay docks where he met Karim Lala and their association in various small businesses and smuggling proved lucrative. Haji Mastan was a major player in the smuggling of precious metals in the 1955-75 period and later became a celebrity in Bollywood, financing directors and studios for film production. Later he ventured into film production. Unlike underworld dons who emerged later and spread terror, he was regarded as a relatively soft mafia lord.
It was reported that Amitabh Bachchan's character in the box office hit `Deewar' was inspired by Mastan's life. Thespian Raj Kapoor was reported to have sought financial assistance from him at a critical period. Mastan is also believed to have shared a good equation with other stars like Dilip Kumar, Dharmendra, Feroz Khan and Sanjeev Kumar.
Mastan's image also spawned another film, “Once upon a time in Mumbaai“ with Ajay Devgn portraying a Mastan-like character and Emraan Hashmi cast as an equivalent of Dawood Ibrahim.
Mastan came into prominence when he was jailed during the Emergency . In jail, he is believed to have picked up Hindi. Much later in 1984, he entered the political arena floating the Dalit Muslim Suraksha Maha Sangh.
Varadarajan went to Bombay in the early 1960s and got to work as a porter at the Central Railway's main Victoria Ter minus. He would feed the poor outside a Muslim dargah, winning the support of locals. He got an opportunity to assist in the distribution of illicit liquor. With Mastan who had set up a smuggling op eration at the Bombay port, he was also involved in stealing cargo. Later, he got pulled into contract kill ings, narcotics and land hment. As a Tamil don, he was encroachment. As a Tamil don, he was held in high regard in his community in Matunga, Sion, Dharavi and Koliwada where he was said to have been the judge arbiter in many cases.
A Murugan bhakt in Tamil Nadu, the astute Varadarajan turned a Ganpathi bhakt capitalizing on the popularity of the elephant-headed god in Bombay and put up a pandal during Ganeshotsav festival. But his hugely popular Ganpathi pandal was served an eviction notice at the behest of the police in the mid-1980s. This was also the time when most members of his gang were jailed or eliminated in encounters forcing him to flee Mumbai for Chennai where he led a retired life till his demise in January 1988 following a heart attack. His body was taken to Mumbai in a chartered flight by Haji Mastan as per Mudaliar's wishes. People paid homage to him. Mastan passed away in Mumbai in 1994.