Rapes in India: court verdicts
This is a collection of newspaper articles selected for the excellence of their content. |
The legal aspect: What constitutes a rape?
The nature of the consent
'Nailing rapist hinges on nature of consent'
Shibu Thomas, TNN | Jul 15, 2013
MUMBAI: In recent rulings in rape cases filed after a relationship went awry, courts considered three key aspects —consent, how that consent was obtained and whether or not the accused had mala fide intention in promising marriage before getting into a physical relationship with the victim.
Court has to believe victim on consent
If a victim deposes that she did not give her consent, then the court has to presume that she did not give her consent
India has one of the toughest laws with regards to rape, where if a victim deposes that she did not give her consent, then the court has to presume that she did not give her consent (Section 114-A of the Indian Evidence Act). Section 90 of the IPC stipulates that a consent given under a misconception of fact is not valid.
In cases where love affairs have failed, the law states that if the victim, under a misconception of fact that the accused was likely to marry her, submits to his lust, then such an act is not consensual. Courts have taken a nuanced look at such cases.
Marital rape
The Times of India, Apr 30 2015
Can't criminalize marital rape as marriage sacred in India: Govt
Amid raging debate over the demand to criminalize marital rape, the government on Wednesday told Parliament there is no proposal to make it a criminal offence as the concept cannot be applied in the country where marriage is treated as a `sacrament or sacred'. “It is considered that the concept of marital rape, as understood internationally , cannot be suitably applied in the Indian context due to various factors, including level of education, illiteracy, poverty, myriad social customs and values, religious beliefs, mindset of he society to treat the mar riage as a sacrament,“ minister of state for home affairs Haribhai Parathibhai Chaud hary said in a written reply in Rajya Sabha.
The minister's reply came in reponse to a question by DMK's Kanimozhi who asked he home ministry whether the government will bring a bill to amend the Indian Penal Code to remove the exception of marital rape from the definition of rape; and whether UN Committee on Elimination of Discrimination Against Women had recommended to India to criminalize marital rape.
She cited a UN report that says 75% of married women in India were subjected to marital rape and asked whether the government had taken cognizance of it.
Chaudhary replied that the MEA and ministry of women and child development have reported that the UN panel has recommended to criminalize marital rape.
Sex offences against minors
Child rapists must be castrated: Madras HC
The Times of India, Oct 26 2015
Child rapists must be castrated: Madras HC
A Subramani
The Madras high court, in a landmark order on Friday, a copy of which was made available on Sunday, suggested castration of offenders as a deterrent for curbing spiralling sex offences against children. “Traditional laws are not stringent enough to yield any desired positive result. Suggestion of castration looks barbaric, but barbaric crimes should definitely attract barbaric model of punishment.
Many may not agree... Still, everyone needs to understand the stark reality,” said Justice N Kirubakaran, rejecting a plea from a foreigner facing paedophilia charges to quash the case. The immediate provocation for the Madras high court to suggest castration of those guilty of sexual crimes against children was the brutal gangrape of children in Delhi last week.Calling it a “blood-curdling“ and “horrific“ incident, Justice N Kirubakaran said castration must be an additional punishment for child abusers, especially child rapists.
The judge pointed out that the conviction rate in sex offences against children is a mere 2.4% and between 2008 and 2014, crimes against children had increased by 400%.“This court is sure that additional punishment of castration of child rapists would fetch magical results in preventing and containing child abuses,“ he said.
Is sex on promise of marriage rape?
Every breach of promise to marry is not rape
Pre-marital sex not shocking; all cases not rape: Bombay HC / Shibu Thomas The Times of India Dec 28 2014
In one of the most significant verdicts delivered in 2014 on an issue that reveals a society in transition, the Bombay high court has ruled that every breach of promise to marry is not rape and premarital sex is no longer shocking, at least in India's big cities.
The observations came earlier this year during the hearing of an anticipatory bail plea filed by Rahul Patil of Nashik who was booked on charges of cheating and rape following a complaint filed by his former girlfriend, Seema Deshmukh (both names changed).
Seema, who claimed she was pregnant with Rahul's child, said despite promising to marry her, he had married another girl. Rahul claimed the relationship was consensual and they could not marry as they were from different religions. Rahul and Seema knew each other since 1999 and had a physical relationship since 2006.
“Nowadays keeping (a) sexual relationship...before marriage is not shocking,“ said Justice Mridula Bhatkar, adding that just because a relationship had soured over time, previous physical relations could not be called rape. Though unlike western countries, we have social taboo and are hesitant to accept free sexual relationship between unmarried couples or youngsters as their basic biological need; the court cannot be oblivious to a fact of changing behavioural norms and patterns between man and woman relationship in society ,“ Justice Mridula Bhatkar of Bombay high court said.
The court said a major and educated girl was expected to know the demands of her body and the consequences of sexual relationships, and in a case it would have to be tested independently if her decision to have sex with a man was a conscious one or not.
“Today the law acknowledges live-in relationship(s). The law also acknowledges a woman's right to have sex, a woman's right to be a mother or a woman's right to say no to motherhood.Thus, having sexual relationship with a man whether is her conscious decision or not is to be tested independently depending on the facts and circumstances of each and every case and no straightjacket formula or any kind of labelling can be adopted,“ the judge said.
The HC gave examples of what could be an offence under Section 376 of Indian Penal Code relating to rape -an uneducated poor girl being induced into a sexual relationship after promise of marriage or a man suppressing his first marriage to have sexual relations with a girl. The court also pointed out that a couple may fall out of love and questioned if the physical relationship they had before could be termed as rape.
(Names of the couple have been changed to protect identity) For the full report, log on to http:www.timesofindia.com
Did the accused make a false promise of marriage?
"There is a clear distinction between rape and consensual sex and in a case like this, the court must very carefully examine whether the accused had actually wanted to marry the victim, or had mala fide motives, and had made a false promise to this effect only to satisfy his lust, as the latter falls within the ambit of cheating or deception," the Supreme Court said in a ruling in May. "There is a distinction between the mere breach of a promise and not fulfilling a false promise."
The apex court held that an accused can be convicted of rape only if the court reaches a conclusion that his intention was mala fide and he had clandestine motives.
"... There must be adequate evidence to show that at the relevant time, which is at an initial stage itself, the accused had no intention whatsoever of keeping his promise to marry the victim," the court had ruled. "There may... be circumstances when a person having the best of intentions is unable to marry the victim owing to various unavoidable circumstances. The failure to keep a promise made with respect to a future uncertain date due to reasons that are not very clear from the evidence available does not always amount to misconception of fact."
The Bombay high court in its ruling acquitting a Borivli resident man of rape charges (see on this page 'Affair gone bad no ground for rape charge: Bombay HC') had taken a similar view. The court ruled that the consent was not forced as the victim had admitted to accompanying the accused to a hotel in Gorai. She had not cried out for help. The court held that the accused had "not committed sexual intercourse on false promise of marriage". "He was willing to marry her. The impediment was the proceedings filed by his first wife. Even according to the complainant, the (accused) had assured her that he would get married to her after obtaining divorce from his first wife."
Sex after false promise of marriage is rape
Sex after false promise of marriage is rape, says HC
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Times of India 2010-02-02
New Delhi: Declining bail to a man who allegedly raped his fiancee and later refused to marry her, Delhi High Court said courts need to take a strict view of such cases.
Justice V K Jain refused to grant bail to the man, Nishant (name changed), who had filed a petition for anticipatory bail in a case where he is accused of raping a girl who was approved by his family and had even got engaged to him.
‘‘If a girl surrenders herself to a boy who comes in contact with her for the first time only in connection with a proposal for her marriage and then enters into a formal ceremony of engagement..she does it not because she loves him or wants to have pleasure with him, but because she doesn’t want to disappoint her future husband,’’ the HC held, rejecting the argument of the accused that it was consensual sex.
The HC said if a view was taken that persuading a girl to have physical relations on the false promise of marriage, despite having no such intention, does not constitute rape, ‘‘this will amount to putting premium on a conduct which is not only highly reprehensible and abhorable but also criminal in nature.’’
Sexual intercourse on assurance of marriage not rape if assurance not fulfilled
Premarital sex 'immoral', no religion permits it: Court
PTI [1] | Jan 5, 2014
NEW DELHI: Additional sessions judge Virender Bhat held that a woman, especially grown up, educated and office-going, who has sexual intercourse on the assurance of marriage does so "at her own peril".
"In my opinion, every act of sexual intercourse between two adults on the assurance of promise of marriage does not become rape, if the assurance or promise is not fulfilled later on by the boy," the judge said.
"When a grown up, educated and office-going woman subjects herself to sexual intercourse with a friend or colleague on the latter's promise that he would marry her, she does so at her own peril. She must be taken to understand the consequences of her act and must know that there is no guarantee that the boy would fulfil his promise, the court held while acquitting an employee of a multinational company of the charges of rape.
The 29-year-old man, a resident of Punjab, was arrested when a woman, doing a secretarial and administrative job at a private company in Delhi, lodged a complaint of rape against him in May 2011.
In her complaint, the woman had alleged that the man, whom she had met through a chat website in July 2006, used to have physical relations with her on several occasions by promising to marry her.
Re-examination of rape survivor
The Times of India, Aug 14 2015
AmitAnand Choudhary
Mindless re-examination of cab rape survivor angers SC
The Supreme Court expressed strong resentment against the mindless re-examination of a rape survivor by the counsel of a former Uber cab driver accused of assaulting the woman on December 5 last year. After a daylong hearing, a bench of Justices J S Khehar and Adarsh Goel criticized the high court order allowing the request of accused Shiv Kumar Yadav to re-examine the survivor despite finding no fault with the trial court's decision to disallow the request.
Before the Supreme Court stayed the HC order on March 10, the counsel for the accused had already examined the rape survivor for three days on the basis of the HC decision allowing the accused to summon her and other witnesses back for re-examination after closure of evidence in the trial.
Counsel for the accused, D K Mishra, said the incompetence of the previous counsel had many loopholes in the de fence case and virtually supported the prosecution. For this reason and to give a fair trial to the accused, the witnesses needed to be re-examined, he said.
Going through the records of the survivor's re-examination, the bench said, “We feel all this is a misuse of the process at your hand. That is the reason we were asking you repeatedly to show us a single relevant question which you had asked the girl in the three days of re-examination. Not a single relevant question has been asked and it appears the nonsensical questions were put to her only to humiliate the girl who has made a serious charge against you.“
Highlighting the general plight of rape survivors who face questions aimed at embarrassing and harassing them, the bench asked, “Is it that simple for a girl to come to court again and again to repeatedly face humiliating questions?“ Mishra argued that the incompetence of the earlier advocate and non-asking of vital questions had left many fronts unattended, leaving the accused vulnerable in the trial, and it was the duty of the court to permit re-examination of the rape survivor and witnesses in the interest of justice and fair trial.
The bench's response was caustic. “If we agree with you (the counsel for the accused), the criminal justice system will be finished. According to you, if a person is a criminal, he should be allowed to sit on society's head and he should be honoured because he has committed a crime.
“If we agree with you, then no trial will ever get completed. At every juncture, the accused will engage a new counsel who will seek recall of the witnesses for re-examination on the pretext that the previous counsel had failed to ask questions of vital importance. It will be impossible for the trial court to return a finding on the guilt and no one accused of crime will ever be punished,“ the bench said.
It agreed with attorney general Mukul Rohatgi that it was a strange case where the HC rejected every ground raised by the accused seeking reexamination yet allowed him to recall witnesses for fresh questioning in the trial court.The bench reserved its verdict on the petition filed by the woman and Delhi Police challenging the Delhi HC verdict.
According to the prosecution, the incident occurred on the night of December 5, 2014 when the woman, an executive working in a company based in Gurgaon, was heading back home.
Rape cases, like murder, cannot be compounded
Can’t nix rape case even after compromise: SC
Dhananjay.Mahapatra @timesgroup.com New Delhi:
The Times of India Jul 29 2014
Dowry harassment cases are personal in nature and can be quashed if the estranged couple reach a “genuine” compromise, the Supreme Court has ruled.
A bench of Justice Ranjana Desai and N V Ramana drew a contrast between offences under Section 498A IPC and heinous crimes like rape and murder, though all three are non-compoundable.
It said Section 320 of the Criminal Procedure Code provided the list of offences that could be compounded after parties reached a compromise and the courts have to strictly follow that.
Justice Desai said: “It is, therefore, not possible to permit compounding of offences under Section 498A of the IPC and Section 4 of the Dowry Prohibition Act. However, if there is a genuine compromise between husband and wife, criminal complaints arising out of matrimonial discord can be quashed, even if the offences alleged therein are noncompoundable, because such offences are personal in nature and do not have repercussion on society, unlike heinous offences like murder, rape etc.“
The judgment came in a case related to a complaint under Section 498A and Section 4 of Dowry Prohibition Act by a woman against her husband and parents-in-law. Though the Madhya Pradesh HC ac upheld the husband’s conviction. However, it reduced his term to six months imprisonment from a two-year sentence imposed by the trial court.
In SC, the couple reached a compromise, with the husband agreeing to pay Rs 2.5 lakh in addition to bearing the cost of litigation. The woman pleaded for quashing of the case against her estranged husband, which was opposed by the standing counsel for MP. But the bench rejected the state’s objection.
Reduction of punishment on compromise or marriage with rape convict
No reduction of punishment on compromise or marriage between rape survivor and rape convict
SC warns courts against showing leniency towards rape convicts
Dhananjay Mahapatra, TNN | Aug 27, 2013
NEW DELHI: The Supreme Court on Tuesday ruled that compromise between rape survivor and rape convict cannot be a ground to reduce sentence of imprisonment.
Even offer of marriage by the accused to rape survivor cannot persuade courts to reduce sentence of rape convicts, the top court said.
The apex court said law permits the court to reduce sentence even in rape cases under exceptional circumstances but compromise between the assaulted woman and the rapist cannot be a ground for that exception.
The top court said allowing compromise between rape survivor and convict for reduction of sentence would allow the accused to exert every kind of pressure on the rape survivor to settle for a compromise.
Long delay in trial and the fact that rape survivor has settled in life were also no grounds to reduce sentence of rapists, the SC ruled. Religion, caste or status of accused too should not make any difference to the case trial and imposition of sentence when convicted, the court said. Justifying harsh punishment in rape cases, the court said rape is not only a physical and mental assault of a woman but also a crime against society requiring courts not to show leniency to rape convicts when it came to imposing sentence.
Warning the high courts and trial courts against leniency towards rape convicts, SC said orders imposing sentence less than prescribed or releasing accused on the grounds that period of sentence has already been undergone would reflect insensitivity of court towards rape survivor and society.
Rape: conviction even if victim does not testify
‘Rape conviction even if victim won’t testify’
Shibu Thomas | TNN
Mumbai: A man can be convicted of rape even if the victim does not testify in court during the trial, the Bombay High Court has ruled. The court’s ruling came in the infamous case of 2002 when a mentally challenged minor girl was raped by a youth in a Borivli-bound suburban train.
‘‘Non-examination of the girl in the given circumstances will not be fatal for the prosecution case,’’ said justice J H Bhatia. The judge observed the victim girl was mentally challenged and was unable to express herself. The victim’s evidence was therefore not recorded by the trial court. ‘‘In such circumstances, merely because her evidence could not be recorded, the evidence of two eye-witnesses and other circumstantial evidence corroborating them could not be simply brushed aside or thrown away,’’ said the judge while finding Jogeshwari resident Salim Shaikh guilty of the charge of rape.
The court, however, reduced Shaikh’s jail term from 10 years to seven years, after defence advocate Arfan Sait argued there was no justification to award a harsh prison term than the minimum prescribed by law. ‘‘Merely because the victim in this case was mentally retarded cannot be a reason to award the sentence of imprisonment for 10 years,’’ agreed Justice Bhatia. Shaikh who has been in jail since his arrest in August 2002, has been ordered to be released by the court if he has completed his sentence.
The incident that shocked the city occurred on August 14, 2002 around 1.50 am in a Borivli-bound local train. The victim was travelling by train, when the accused raped her between Malad and Borivli. When other commuters tried to come to the aid of the victim, Shaikh reportedly threatened them. Shaikh jumped out of the train as soon as it reached Borivli station. Two of the commuters, who were the prime witnesses in the case, approached the police to register a complaint. Shaikh was nabbed, while the victim was sent to a shelter.
A medical examination confirmed rape. The trial court sentenced Shaikh to 10 years rigorous imprisonment. He then filed an appeal in the HC. Advocate Sait, who was appointed from the legal aid panel to represent Shaikh, pointed to drawbacks in the prosecution story. Sait argued the victim had not been examined to prove the offence of rape.
No leniency for rapists:SC
The Times of India, Jul 02 2015
Dhananjay Mahapatra
SC: No leniency to rapist even if case is `settled'
`Compromise Under No Circumstance'
Tired of the lenience high courts continue to show to rapists in defiance of its rulings, the Supreme Court firmly told HCs not to go soft on a rape convict even if he wins over the survivor by promising marriage or striking a compromise. “...In a case of rape or attempt of rape, the conception of compromise under no circumstances can really be thought of,“ a bench of Justices Dipak Misra and P C Pant said. It reversed a Madhya Pradesh high court order allowing a rapist to walk after serving a sentence for little over a year as he had struck a compromise with the parents of the survivor, a minor. A Guna court had sent the man to five years in jail. The bench asked the HC to hear the case afresh on sentence and asked cops to re-arrest the rapist. The Madhya Pradesh HC judgment and the recent Madras HC order granting bail to a rape accused to allow him to meet the survivor to explore the possibility of a compromise appeared to have hurt the judicial conscience of the SC, which had just last year warned courts not to show leniency towards rapists. In 2014, the apex court in Shimbhu and Another vs Haryana had categorically ruled, “Rape is a non-compoundable offence and it is an offence against society and is not a matter to be left for the parties to compromise and settle... a compromise entered into between the parties cannot be construed as a leading factor based on which lesser punishment can be awarded.“
The rulings from the two high courts, despite this judgment, appeared to have a disconcerting effect on the SC bench of Justices Dipak Mishra and P C Pant as counsel for MP, C D Singh, pointed out that the HC had dealt with the case in a “laconic“ manner.
Writing the judgment for the bench, Justice Misra said, “Sometimes, solace is given that the perpetrator of the crime has acceded to enter into wedlock with her which is nothing but putting pressure in an adroit manner; and we say with emphasis that the courts are to remain absolutely away from this subterfuge to adopt a soft approach to the case, for any kind of liberal approach has to be put in the compartment of spectacular error. Or to put it differently , it would be in the realm of a sanctuary of error.
“We are compelled to say so as such an attitude reflects lack of sensibility towards the dignity , the `elan vital', of a woman. Any kind of liberal approach or thought of mediation in this regard is thoroughly and completely sans legal permissibility .“
The bench said sexual assault on a woman suffocated her breath and tarnished her reputation, the “richest jewel one could conceive... When a human frame is defiled, the `purest treasure' is lost,“ it said.
Compromise with rapist
Madras HC reverses order
Jul 12 2015
A Subramani
HC nixes rape `compromise' order
Madras court takes cue from SC's July 1 order, cancels convict's bail
The Madras high court, which had outraged activists by granting bail to a convict in a rape case and asking the survivor and offender to try out a compromise' through mediation, has recalled the order and cancelled interim bail given to the convict. The court has now also stopped the ongoing `mediation' process, and asked the convict, V Mohan, to surrender on July 13.
Justice P Devadass passed the order in view of a Supreme Court order dated July 1 in the State of Madhya Pradesh vs Madanlal case wherein the apex court had held that mediation and compromise should not be an option in rape cases.
“This court by its order dated June 18, directed the parties to go for mediation.In view of the judgment of the Supreme Court in state of Madhya Pradesh vs Madanlal, dated July 1, the said order of this court directing the parties to go for mediation is recalled. Consequently , the interim bail granted to Mohan is cancelled. The officer-in-charge, mediation centre attached to this court shall stop the par ties from attending the mediation. Registrar (Judicial) of this court shall ensure compliance of this order,“ the judge said in his order.
On June 18, Justice Devadass, hearing a criminal appeal by Mohan, highlighted the plight of the rape survivor's child and said the girl child was a bigger victim than the teen-mother. The girl was raped in 2008 by Mohan, her neighbour, when she was just 15. She delivered the child the next year.
A mahila court in Cudda lore had found Mohan guilty of rape in its verdict on July 22, 2014 and sentenced him to seven-year jail, besides a fine of Rs 2 lakh. It was while admitting his appeal in the HC against the conviction that Justice Devadass ordered `me diated settlement'. He even cited an earlier case, which too involved a minor rape survivor, and said he had referred it for mediation. The case was `approaching a happy conclusion' as the offender had agreed to marry the victim, the judge said.
The judgment triggered debate and widespread condemnation. The July 1 judgment of the apex court was, under the circumstances, seen as a message to the Madras high court as well.
Noting that Mohan shall surrender before the mahila court in Cuddalore on July 13, Justice Devadass said that in default the trial court shall issue warrant to secure the petitioneraccused and commit him to Central Prison at Cuddalore.
Life term only if rape is brutal
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
Life term only if rape is brutal, else 10 yrs: HC
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
New Delhi: The Delhi High Court has said that the offence of rape should be accompanied with acts of brutality to merit maximum penalty of life imprisonment for the guilty. Reducing the punishment awarded to a tutor from life imprisonment to 10 years, a bench of justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Suresh Kait said the act of rape should be brutal to attract maximum punishment. The accused had raped his minor student in August 2004.
According to the FIR that was lodged on the complaint of the victim’s mother, she was shocked to witness the crime on returning from market as her daughter took tuitions from the accused.
Interestingly, with solid medical evidence and the testimony of the mother against him, the accused Arun Kumar sought leniency in his sentencing. Kumar pleaded for a lighter prison term saying life sentence was too harsh a verdict.
HC noted that there were no aggravating circumstances in the case and reduced Kumar’s term.
‘‘Counsel for the accused concedes that in view of the evidence, even excluding the DNA report, there is tell tale evidence of the appellant being the tormentor of the young girl,’’ HC observed pointing out just because the victim was a minor, it doesn’t mean the accused be given life term.
‘‘Brutality at the time of rape has to be factored in. If the rape is accompanied by acts of brutality, higher sentence should be imposed,’’ HC said.
Child born of rape
Children born in rape cases are not "property" in the crime
Kids born in rape cases can't be 'property' in crime: HC
PTI | Aug 15, 2013
MUMBAI: In a significant order, the Bombay high court has observed that children, born to minor unwed mothers in rape cases, cannot be treated as "property" in the crime while considering requests from Child Welfare Committees to declare such children free for adoption.
Accordingly, Justices R M Borde and R V Ghuge quashed orders of a Child Welfare Committee which asked an adoption agency to seek NOC from court and permission from police to allow adoption of children born to unwed mothers who had been raped.
The high court was hearing two separate petitions filed by Snehalaya Snehankur Adoption Centre which had applied to the Child Welfare Committee to give a declaration that such children, born to unwed mothers, were free for adoption.
Assistant government pleader told the court that the Child Welfare Committee had asked police to inform whether they would need the presence of children since they are born out of sexual violence, in respect of which act, an offence has been registered with the police. Besides, it was also awaiting a report from a probation officer.
The judges said, "Merely because children are born out of sexual violence to minor unwed mothers, it does not mandate calling of report from police as to whether they would need the children for investigation or for calling upon the adoption agency to produce a 'no objection certificate' from the competent court dealing with trial of offence."
"It must be understood that the police are concerned with the investigation of crime which is in the nature of sexual violence meted to a minor girl. Also, the court in a trial is concerned with the offence of sexual violence alleged against the accused," the judges said recently.
Considering the applications, tendered by adoption agency seeking a declaration from the committee that the children are free for adoption, those children, who are born to unwed minor mother out of sexual violence, cannot be treated as "property" involved in the crime," the bench said.
"There is no role of police or court in a criminal trial relating to sexual violence, in the matter of grant of declaration by the committee that the children are free for adoption. We are of the opinion that the committee has not exhibited sensitivity, as contemplated by the government in its policy on children in 2003," they said.
Right to assaulter/ father's property: HC
The Times of India, Nov 04 2015
Court leaves decision to Legislature
The Lucknow bench of the Allahabad high court ruled that a child born of rape has inheritance rights to the biological father's property . The right will, however, be subject to the personal law concerned. “The child will be treated as an illegitimate child of the biological father,“ the court said, “However, if heshe is given away for adoption, the child will not have the right to inheritance.“
The direction came as the court delivered the judgment in a rape case involving a 13year-old victim. A division bench of Justices Shabihul Hasnain and Devendra Kumar Upadhyaya told the government to pay the child Rs 10 lakh as maintenance. It also asked the government to ensure that the girl gets a job once she attains adulthood.
The victim belongs to a poor family , and got pregnant after she was raped earlier this year. The family got to know about the pregnancy after the legal deadline of 20 weeks for abortion expired.They moved the HC seeking permission for abortion, but a panel of doctors appointed by the court deemed it too dangerous for the teenager. The court appointed a panel of senior lawyers to assist it on the issue of inheritance for a child born of rape. “The matter relating to inheritance, the manner of birth...is irrelevant; the rights of inheritance of a person are governed by the personal law to which the person is subject, irrespective of the manner of birth,“ the court said.
It clarified that it was not giving any specific direction for inheritance of property in the case because it may have grave consequences if the father starts claiming some special reproach privileges over the child, like rights of visitation or custody, which is “undesirable“.
The court added, “The rights of inheritance in the property of a biological parent is a complex personal law right which is guided by either legislation or custom.“
“It may not be possible to judicially lay down any norm or principle for inheritance by a minor who is born as a result of rape. Such attempt by the court would amount to legislation by judicial pronouncement and would operate as precedent in times to come. It would not therefore be desirable to venture into this field and accordingly we leave it open for the appropriate legislature to deal with this complex social issue.“
The court said that in the present case there are two victims: the girl who was raped and the child born of rape.
Changing mindset
Gang rape by Badaun cops a reminder of 1970s mindset
Dhananjay Mahapatra The Times of India Jan 05 2015
Cries of sexual assault victims seldom got heard in a male chauvinistic society till 1970s. The lawyers for the accused mostly succeeded in portraying the victim as a woman of loose character. The accused got acquitted or was awarded lenient sentence.
The coloured judicial mindset reached its crest on September 15, 1978, when the Supreme Court acquitted two Maharashtra policemen, who were convicted by the Bombay HC for sexually assaulting a minor girl Mathura who had allegedly eloped with her lover [1979 (1) SCR 810].
The SC had based the acquittal because medical report showed Mathura to be habituated to sex and that she did not raise an alarm when being sexually assaulted.
Many cringed at the insensitive `Mathura' judgment. The course correction was done by Justice Krishna Iyer on August 14, 1980 in Rafiq Vs State of UP [1981 (1) SCR 402]. Since then, barring a few exceptions, the judiciary had been stringent in its approach towards accused facing rape charges.
The age-old weapon to demolish victim's charge had been to seek corroborating evidence for her allegations. The lawyers for the accused know that rapes are committed in seclusion and independent witness seldom exist. Iyer had said: “Corroboration as a condition for judicial reliance on the testimony of a prosecutrix (victim) is not a matter of law, but a guidance of prudence under given circumstances.
Talking about the mindset, Justice Iyer had said: “There are several `sacred cows' of the criminal law in Indo-Anglian jurisprudence which are superstitious survivals and need to be re-examined. When rapists are reveling in their promiscuous pursuits and half of humankind -womankind is protesting against its hapless lot, when no woman of hon our will accuse another of rape since she sacrifices thereby what is dearest to her, we cannot cling to a fossil formula and insist on corroborative testimony , even if taken as a whole, the case spoken to by the victim strikes a judicial mind as probable.“
He had also advised against knee-jerk reaction of making the punishment for rape more stringent. Better course would be to sensitize and professionalize the machinery responsible for probe and prosecution, he had said.
Lack of sensitivity towards rape victims among Judges lead to devastating results. In 2007, Oxford Country court judge Julian Hall doubted a 10-year-old girl's age and blamed her provocative sense of dressing to award a friendly 9-month prison term to the man who violated her. Hall forgot rape was a heinous offence which gets severest punishment world over when the victim is a minor. Did it matter how she dressed or how old she appeared to be? Hall probably subscribed to the mindset of another Judge -Betrand Richards of Ipswich Crown Court -who had in 1982 created a sensation by his judgment in another rape case.
A young lady on a lonely stretch stuck out her thumb for a hitch. A young man driving a car gave her a lift. He took advantage of the lonely stretch and raped her. He was convicted for the offence. But Judge Richards let him off with a fine of 2,000 pounds saying the girl was guilty of “contributory negligence“ by knowingly taking the risk of hitchhiking at a lonely hour on a lonely stretch.
The judge did not see the other side -the girl was trying to get away from the lonely stretch and had reposed trust in the young man.
In India, Justice Narain Singh Azad of Madhya Pradesh HC could qualify to be counted in the category of Halls and Richards. Eight years ago, Justice Azad had awarded cursory punishments to convicts in nearly a hundred rape cases on the ground that offenders were illiterate tribals. Fortunately, the SC saw the fallacy in the approach and sent back all the cases to the HC for a fresh hearing.
What the SC laid down in its judgment in the case State of Maharashtra Vs Madhukar Narayan Mardikar [1991 (1) SCC 57] needs to be kept in sight for a change in mindset.
It had said: “The unchastity of a woman does not make her open to any and every person to violate her person as and when he wishes.She is entitled to protect herself if there is an attempt to violate her person against her wish. She is equally entitled to protection of law.Therefore, merely because she is of easy virtue, her evidence cannot be thrown out.“
Disposal of rape cases by Indian courts
Pendency of rape cases falls in 5 HCs
Karnataka Disposed Of Over 4.5k Rape Cases In 3 Yrs, Delhi HC 2nd Best
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Times of India 2013/08/13
New Delhi: The high courts of Calcutta, J&K, Gauhati, Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh are among the high courts with the lowest pendency of rape cases despite the fact that some of these states have seen a high number of sexual harassment cases coming up for trial every year in their lower courts.
The pendency of rape cases in these HCs range from 26 to 177, while some others such as the HCs of Allahabad, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab & Haryana, Chhattisgarh and Orissa had pendency ranging from 1,000 to 8,200 as of September 2012.
Delhi has 924 rape cases pending in its high court even after disposal of more than 1,100 cases between 2009 and 2012. Delhi HC, after Karnataka, remains the best performer in the last three years in clearing backlog. Karnataka, which had 243 cases pending in its HC, disposed of over 4,500 rape cases during this period, according to the law ministry.
But as far as rape cases coming up for trial are concerned, West Bengal ranks at the top with 15,197 cases reported in 2012. Maharashtra is second with 14,400 cases, followed by Madhya Pradesh with 11,200.
Even in Uttar Pradesh, which has the highest pendency in its HC, the cases reported for trial are way below at 5,790.
Bihar, notorious for its crime graph earlier, reported 4,100 cases for trial, above Gujarat at 3,373 cases.
Section 309 of the Code of Criminal Procedure
Releasing the data in Lok Sabha in response to a question last week, law minister Kapil Sibal said, “To expedite the trial of criminal cases and for certain serious offences relating to crime against women, Section 309 of the Code of Criminal Procedure provides that in every enquiry or trial, proceedings shall be held as expeditiously as possible and in particular, when examination of witnesses has once begun, the same shall be continued from day-today until all witnesses in attendance have been examined.”
Section 309 also provides that when the inquiry or trial relates to an offence under Sections 376 to 376D of the IPC, the inquiry or trial shall, as far as possible, be completed within a period of two months from the date of commencement of examination of witnesses.
“Not only that, several legislations enacted for protection of women and children against violence and sexual offences contain provisions for speedy trial of such cases,” Sibal said.
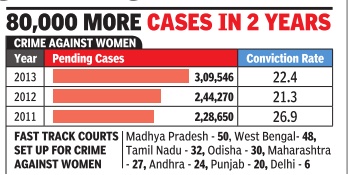
Pending rape cases
Over 31,000 rape cases pending in High Courts
December 17 2014
Crimes against women are on the rise, and so is the pendency of such cases in the subordinate and high courts across the country. In the last three years, number of cases relating to sexual harassment, kidnapping and abduction including rape has gone up from 2.28 lakh to 3.09 lakh. Over 31,000 rape cases are pending in high courts alone.
Concerned at increasing pendency of cases of crime against women and children, the law ministry has written to the state governments and the chief justices of HCs to constitute fast track courts for speedy trial of such cases. The conviction rate in these cases, however, came down from 27% to 22% between 2011 and 2013.
After the December 2012 Delhi rape case, the government had asked the state gov ernments to allocateTOTAL (ALL S additional funds for setting up of fast track courts (FTCs) for trials related to crime against women and children.
This has resulted in at least 318 FTCs being set up by various HCs, designating them exclusively for trials of cases related to crime against women. Madhya Pradesh has set up highest FTCs for women and children (50), followed by West Bengal (48).
There are 310 cases of sexual harassment pending in the Supreme Court while it has L STATES) 318 disposed of 1,455 since 2009. In the HCs, the pendency of rape r cases is as high as 31,386 while e 15,453 have been disposed of in the last three years.
Pending rape cases: 2011–2013
Sex offence cases up after reforms
Somreet Bhattacharya, December 16, 2014
The “police reforms“ that followed the Nirbhaya case led to a free and easy registration of crimes against women. As a result, now the police have to note down a woman's complaint verbatim. Earlier, the police used to modify the complaints. The new system has also done away with medical tests and inquiries prior to the registration of the case.
Police officers admit that this has increased the number of rape cases registered by nearly 150% of what it used to be. At the same time, it has also led to a lot of frivolous rape cases being filed to settle personal scores as well.
Officers say that the free registration has increased the number of FIRs getting registered per year from 680 in 2012 to 1,559 cases in 2013 and 1,925 cases till November this year. The number of molestation cases has also gone up from 615 in 2012 to 3,347 last year and 3,932 cases till November 2014.
According to a police officer, once a woman registers a complaint, the police have to treat it as a statement and arrest the accused within a week. Even activists agree that now women don't have to run from pillar to post to register an FIR. “Once a case is registered, the general perception of the public, including the family members of the victim, tends to question the character of the woman. People start judging the woman first and then the accused,“ said Manisha Goel, an MBA aspirant and an activist.
The police also admit that the increase in the number of cases has resulted in the piling up of cases at each police station, affecting the investigations. Now, in a rape case, the investigating officer has to submit a chargesheet within 20 days of it being registered, which forces them to complete the probe in a hurry . The problem is compounded by the shortage of women staff at police stations as well, police officers claim.
Conviction rate
2016/ Delhi: Rate lowest in 5 years
The Times of India, Aug 24 2016
Ambika Pandit
Rape conviction rate at 5-yr low
An alarmingly low rate of conviction for rape continues to remain a cause of concern. According to Delhi Police data, it stood at an abysmally low 29.37% in 2015. Between 2011 and 2015, the conviction rate touched a high of 49.25% in 2012 the year the infamous Nirbhaya ca se took place. At a review meeting, led by the department of women and child development, the police shared data related to conviction in various crimes against women from 2011 to 2015. These included rape, dowry deat h, molestation, sexual harassment and cruelty by husband. Sources said serious con cern was raised at the meeting over the data on rape conviction, with the rate having shown a consistent decline from 2012 onwards (see box).With the chief secretary likely to review the women safety schemes later this month, Delhi Police have been asked to submit a detailed analysis on the decline in the conviction rate. They have also been asked to report the number of FIRs filed related to such crimes during the five-year period.
The police are learnt to have pointed that amendments to the law after the December 16 gang rape resulted in a significant rise in the number of cases registered, but not all of them stood the test of court.Also, case load on the judiciary has increased. A senior police official said one of the reasons for the data reflecting a decline in conviction rate is that a case takes four to five years on average to be decided and hence the conviction status for most cases that happened during the said period would take time to come.
The review also sought a status check from the Public Works Department on putting up streetlights in dark spots. As many as 7,304 dark spots were identified in the areas under the jurisdiction of the north corporation and another 124 under the east corporation. The Delhi Urban Shelter Improvement Board identified 1,108 such spots.PWD submitted that surveys have been completed in areas under the north and east corporations and the DUSIB.
LED streetlighting is estimated to cost Rs 19.92 crore and Rs 47.3 lakh in the north and east corporation areas, respectively . While the two civic bodies have given PWD the go-ahead to put up the lights, the South Corporation has decided to undertake the work on its own.
Concerns were also raised at the meeting about the wide gap in the number of dark spots identified by the PWD in the areas under the north and east corporations.
See also
Age of consent Crimes against women: India Juveniles, benefits and privileges of Juvenile delinquency in India Especially the section 'Rape by juveniles' Premarital sex
Other articles about rapes in India
Rapes in India<> Rapes in India: court verdicts<> Rape definitions unique to India<> Rapes in India: the legal position after 2013 <>Rapes in India: Compensation and help for survivors
<>Rapes in India: annual statistics