Public Distribution System (PDS): India
m (Pdewan moved page Public Distribution System: Universal to Public Distribution System (PDS): India without leaving a redirect) |
Revision as of 14:20, 5 February 2016
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Public Distribution System: Universal
Universal PDS only way to beat hunger, tackle price spiral? Contrary To Fears, Cost Of Such An Exercise Is Not Prohibitive: Study
Galloping food prices have shattered family budgets across the country, with latest inflation data showing that prices rose at nearly 18% in the week ending February 6. Many essentials of Indian kitchens are almost beyond reach; sugar is up by nearly 60%, pulses by 46% and potatoes by 53% over a year. In a country already suffering from chronic malnutrition and low incomes, this trend is a killer.
President Pratibha Patil in her speech to the Parliament last year had promised to provide at least 25 kilograms of rice/wheat at Rs 3 per kg to all families below the poverty line (BPL). Finance minister Pranab Mukherjee had confirmed this in his Budget speech. The National Food Security Bill, introduced in Parliament last year, includes this provision. Yet, the government appears to be dragging its feet on this vital policy issue.
Centre for Budget and Governance Accountability (CBGA) points out that if food security is to be really achieved, restricting the provision of subsidized grain to the BPL category is unlikely to do the trick. What would dramatically improve availability of food grains and bring down their prices is channelling cheap foodgrains through a universal public distribution system.
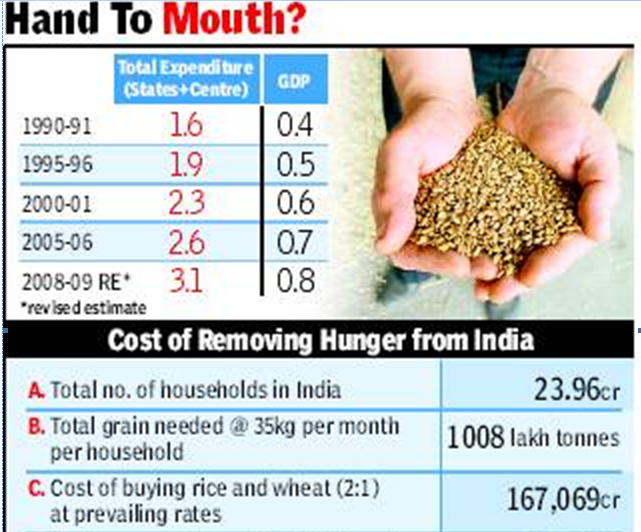
Contrary to fears, the cost of providing subsidized food grains to all Indians is not prohibitive, according to analysis done by the CBGA, even if the amount of grain provided per family per month is raised to 35kg, the amount now given to BPL families under the targeted PDS. They show that additional expenditure of just Rs 84,399 crore is needed for this. This is less than a fifth of the revenue foregone by the government through tax exemptions in 2008-9, which stood at a whopping Rs 418,096 crore.
The total food subsidy currently provided by the government is less than 1% of the country’s gross domestic product (GDP), and about 3% of the total expenditure incurred by the central and state governments together, according to data compiled by CBGA. It has hovered around this mark for nearly two decades. In 2009-10, the food subsidy given by central government was Rs 52,490 crore. This amount is transferred to the Food Corporation of India (FCI) to compensate the difference between the cost FCI incurs in buying from farmers, storing and transporting and the lower prices at which it sells to public distribution system.
If food grain were to be sold at Rs 3 per kg to the estimated 24 crore households in India, the government would have to shell out Rs 136,829 crore, CBGA calculates. This is based on the assumption that procurement, storage and distribution will cost about Rs 18 per kg for rice and about Rs 14 per kg for wheat. Deducting the current food subsidy of Rs 52,490 from this gives an estimate of Rs 84,399 as additional expenditure. The amount of subsidy will get increased to Rs 94,419 crore if grain is sold at Rs 2 per kg.
This expenditure is justified, says CBGA, because over 50% of children in India are underweight and nearly 75% of women are anaemic, as per the third National Family and Health Survey. Despite record harvests every year, the amount of cereals and pulses available per person has been steadily declining from 186kg per annum in 1991 to 166kg in 2000 and further down to 160kg per annum in 2007.
Whether government has the political will to tackle hunger in the country will become clear next week when the annual Budget is presented to Parliament.