Healthcare: India
Contents |
Dengue
Alarming 80% rise in dengue cases in 2013
Durgesh Nandan Jha TNN
The Times of India 2013/08/21
New Delhi: Dengue cases have risen alarmingly across the country this year, with data showing an 80% rise in the disease till July 31 as compared to the same period last year.
India has recorded 15,983 dengue cases so far in 2013 as compared to 8,899 cases in the corresponding months last year, latest health ministry data shows. But the good news is, while the cases have risen sharply, fatalities have actually declined — 56 as compared to 76 last year.
Kerala reported most dengue cases at 5,801, followed by Karnataka (3,775), Tamil Nadu (3079) and Maharashtra (961) till end-July. Delhi witnessed a sharp rise in cases over the last few weeks, with the total this year touching 54. No one has died due to dengue in the capital so far.
‘Several factors for spread of dengue’
“There is no single reason for the increase in dengue cases. It is governed by various man-made and environmental factors including unprecedented growth in population, unplanned and rapid urbanization and inadequate waste management,” union health minister Ghulam Nabi Azad stated in a written reply in the Lok Sabha on Tuesday.
Increasing mobility of the population and poor infrastructure to monitor mosquito breeding were some other reasons cited by the health minister. Azad said guidelines for clinical management of dengue cases have been sent to the states for circulation in hospitals and rapid response teams have been formed.
Dengue, termed by many experts as the world’s most rapidly spreading mosquito-borne viral disease, is caused by four serotypes. While type I and III are milder in nature causing classic dengue fever and fever without shock, respectively, dengue type II and IV are considered deadly. These cause fever, bleeding and a drop in platelet count. Researchers say severe dengue cases, dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome, started showing up in India since 1988.
“A reason behind the increased frequency could be the presence of many strains of the virus. It exposes people already infected to become susceptible to infection as they are not immune to all the subtypes,” said Dr Ekta Gupta, clinical virologist at the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS).
Experts say construction sites are a major area of mosquito-breeding followed by government buildings and water tanks. “In Mumbai, the municipal body, charges heavy fines if mosquitoes are found to be breeding at a site. The building’s completion certificate is stalled till the fine is paid. Similar steps should be taken in cities like Delhi,” said Dr Jagdish Prasad, director general of health services.
Better healthcare still out of bounds
New Delhi: India may be among the fastest growing economies in the world, but the UNDP’s Human Development Report 2006 shows that this growth hasn’t translated into better public healthcare for the citizen, at least not as yet. For instance, there are only seven countries — of the 177 that the HDR looks at — with a lower share of public expenditure in total health expenditure. These seven — Guinea, Congo, Myanmar, Cambodia, Armenia, Tazikistan and Burundi — are not exactly those with whom India would like to be compared, but they are the only ones in which the government accounts for less than a quarter of total health expenditure. For India, the share of public expenditure in the total is exactly one-fourth or 25%.
The low share of public health expenditure is not surprising, given the fact that only 13 countries spend a smaller proportion of the gross domestic product (GDP) on the health sector than India’s level of 1.2%. Apart from six of the seven mentioned above, these include Pakistan and Bangladesh in our neighbourhood as well as Azerbaijan, Georgia, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea and Indonesia. One result of this low level of government spending on healthcare is that people have to spend more from their pockets to keep themselves in good health. Thus, India’s private spending on healthcare at 3.6% of GDP is higher than most. In fact, only 33 of the remaining 176 countries has a higher level on this count.
However, the high private expenditures are clearly unable to bridge the gap when it comes to things like immunisation, which are typically public programmes in most parts of the globe. Not surprisingly, India’s immunisation rate for those who are one-year old against measles is worst in the world, with just 13 countries doing worse. A similar picture emerges if we look at the numbers for full immunisation of one-year olds against tuberculosis. Again, there are a mere 20 of the 176 others who have a lower rate.
What highlights all of this as a glaring failure of our governments is the fact that India’s pool of roughly 6.5 lakh physicians is the third biggest in the world after China, which has about twice as many, and the US, which has only a few tens of thousands of doctors more than India, although for a population that’s only about onethirds the size of India’s.
Doctors, in rural areas
Funds fail to draw docs to villages
Despite 42,000cr Kept Aside For Rural Medical Care, Rs 10,000cr Lying Unspent Subodh Varma TIMES INSIGHT GROUP
As the country awaits another central government Budget, there is a growing demand for more financial muscle on several fronts. But, is throwing money at complex problems really a solution? A look at the progress of a crucial program of the government, the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM), indicates that money can’t buy everything.
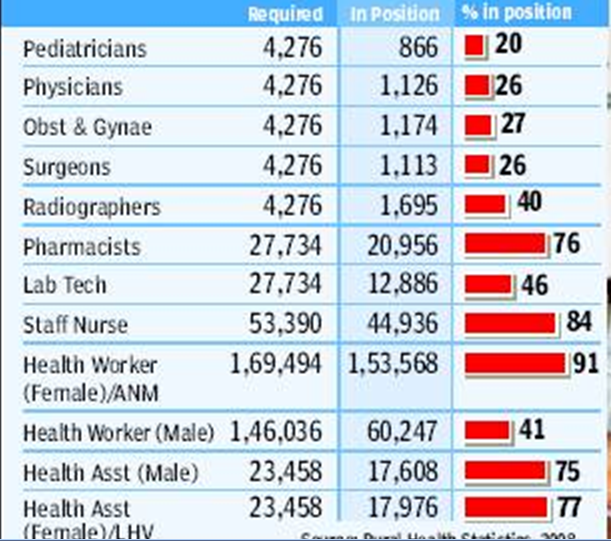
One of the biggest bottlenecks facing policy-makers is that of medical personnel. Recently released data by the ministry of health and family welfare shows a shocking shortfall of doctors, nurses, health assistants, radiographers, pharmacists and other personnel in the rural health delivery structure. This is despite over 82,000 new personnel being appointed under NRHM in the past four years and many villages getting to see a doctor for the first time.
The situation is worse for qualified doctors. Just 20% of required pediatricians and only about 26% of surgeons, obstetricians and gynaecologists, and general physicians are in place. They are needed at the Community Health Centres (CHC), each serving a population of 1.2 lakh. Among technical personnel, only about 40% of the required radiographers and 47% of laboratory technicians are in place to run diagnostic labs. There is a shortfall of about 25% for pharmacists, and 16% for staff nurses.
Even at the lower rungs of the medical service hierarchy, like the health sub-centres and primary health centers, many of the key personnel are not yet appointed. Nearly a quarter of 46,000 male and female health assistants are missing, while over 60% of health workers are not yet in place. The situation is much better for the auxiliary nurse and midwife (ANM) with about 90% appointments having taken place, but that still leaves nearly 16,000 ANM posts vacant. Two ANMs are required at the primary level in order that delivery cases are handled day and night. Just about one third of the PHCs are functioning with two ANMs.
Expenditure data shows that the problem is not of resources. Out of the Rs 42,000 crores released by the central government in the past four years for NRHM, nearly Rs 10,000 crore is lying unspent with state governments. In addition, all state governments together have allocated an eyepopping Rs 1,06,388 crore for health and family welfare in their respective states.
Yet, progress under NRHM, has been uneven, and the country is still far from achieving goals set for various health indicators. “Spending money jazzing up an auto-rickshaw is not going to convert it into a car”, says public health expert Dr Amit Sengupta. A thorough revamp of the infrastructure is needed and the government needs to think afresh about it, he says.
But why are medical personnel not in place? “An indifferent political leadership and bureaucracy, deficient medical education infrastructure, especially for technical and paramedical staff, low salaries for doctors, and frustration among them in rural postings as there are no drugs, no support staff and erratic infrastructure, are some of the problems,” Sengupta said. “Sadly, doctors prefer lucrative private incomes in urban areas or foreign lands, rather than serving people in the villages,” he says.