Divorce: India
(→Alimony for wives) |
(→Hindu Marriage Act) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 672: | Line 672: | ||
In the judgment, the HC dimissed the writ petition submitted by man who said his former wife’s application seeking maintenance be dismissed since she had waived her right to it in the consent terms for divorce. The woman had moved the maintenance plea before a magistrate court in 2010. The man sought a dimissal of the plea and cited the consent terms. On October 13, 2011, the court rejected the man’s application. He then challenged it before sessions court which too rejected his plea. In 2016, the man submitted writ petition before the HC. | In the judgment, the HC dimissed the writ petition submitted by man who said his former wife’s application seeking maintenance be dismissed since she had waived her right to it in the consent terms for divorce. The woman had moved the maintenance plea before a magistrate court in 2010. The man sought a dimissal of the plea and cited the consent terms. On October 13, 2011, the court rejected the man’s application. He then challenged it before sessions court which too rejected his plea. In 2016, the man submitted writ petition before the HC. | ||
| + | ==Maintenance can be sought under different laws== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/bengaluru/can-seek-maintenance-under-different-laws-karnataka-hc/articleshow/96157962.cms Vasantha Kumar, Dec 12, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | BENGALURU: There is no bar on an aggrieved woman seeking maintenance under the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act as well as under Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code or under the Hindu Marriage Act or even under the Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956, the Karnataka HC has observed in a recent judgement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The only rider would be that the amount to be paid to the wife will be inclusive of the maintenance awarded under each of the four jurisdictions and not exclusive, justice M Nagaprasanna noted in his order, while upholding the Rs 30,000 per month interim maintenance granted to a woman from Mangaluru. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the Rajneesh vs Neha (2021) case, the Supreme Court has observed that in the light of overlapping of jurisdictions, the grant of maintenance under section 20(1)(d) of DV Act would be in addition to the maintenance granted under section 125 of CrPC, and also held that there is no bar on seeking maintenance under the DV Act and section 125 of CrPC or the Hindu Marriage Act, or Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956," the judge noted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dismissing the petition filed by the man, the court said the SC has held that if the husband is an able-bodied man, it is his duty to maintain his wife. The petitioner from Belthangady taluk in DK district got married on December 31, 2018 and the couple has no children. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On December 11, 2020, the wife alleged harassment by the husband and his family and registered a case against them. on February 22, 2021, she filed a petition under the DV Act before a court in Moodabidri, seeking interim maintenance. She was awarded Rs 20,000 per month as maintenance. The husband challenged the proceedings under the DV Act and the high court granted a stay on the same. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
== Maintenance is not a blanket liability== | == Maintenance is not a blanket liability== | ||
| Line 785: | Line 805: | ||
=Cruelty: applicability= | =Cruelty: applicability= | ||
| + | ==Relatives, distant, can also be booked: HC== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/nagpur/hc-kin-not-sharing-roof-can-be-booked-for-mental-cruelty/articleshow/97147921.cms Vaibhav Ganjapure, Jan 20, 2023: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | NAGPUR: Bringing relatives not staying under one roof under the purview of Section 498-A regarding cruelty to married women, the Nagpur bench of Bombay high court has held that even such kin could be booked and their physical presence is not necessary in the household. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “Such being the nature of mental cruelty, it is not necessary that it must take place in the physical presence of persons. It (mental cruelty) can be handed out even from a distant place,” a division bench comprising justices Sunil Shukre and Manohar Chandwani ruled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rejecting plea by relatives of a complainant-woman’s husband hailing from Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi, the bench also imposed Rs10,000 fine on them for abusing the process of law. They were told to deposit the amount within three weeks with the High Court Bar Association (HCBA) here for developing its library. In case of failure, the HC registry was asked to recover the amount from them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “For meting out mental cruelty to the complainant-woman, in a prima facie way, petitioners seem to have employed modern means of communication, i.e. telephone. On many occasions, they have also remained present in her company. Therefore, this is not a case where the petitioners, by virtue of their separate residence, could be presumed to not have treated her in a cruel manner,” the bench said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The petitioners had moved HC for quashing FIR against them filed by the woman under sections 498-A, 323, 524 read with 34 of IPC and sections 3 and 4 of Dowry Prohibition Act. The police have filed a charge sheet before the judicial magistrate first class (JMFC) court in the city based on the FIR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contending that there were no specific allegations against them, the petitioners pointed out that there was no proof that they had resided together with the woman and her husband. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The justices said though the petitioners appear to be residing away from the woman’s matrimonial home, the allegations in FIR and witnesses’ statements do indicate that there used to be several occasions when all or some of them, on one or other occasion, had resided with her. “They also had opportunities to talk personally or on telephone with the complainant. During their such encounters, they subjected her to humiliation, harassment and cruelty,” the bench noted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pointing out that cruelty as envisaged under Section 498-A is not only physical, the judges said it also takes within its fold several other forms, including mental. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “Mental cruelty is an abstract concept, and it is a matter of experience for a person who is subjected to it. Many times, certain taunts are made but it all depends upon the way the person takes those remarks or responds to them. Sometimes, the taunts might be seen to be innocuous by one person, while they may not be necessarily so perceived by another. There are also certain derogatory remarks, which have been held by the Supreme Court to be presumptively constituting cruelty, as for example consistently suspecting the wife’s fidelity,” they said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==SC: Woman can file plaint for cruelty after divorce== | ==SC: Woman can file plaint for cruelty after divorce== | ||
[https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/?olv-cache-ver=20180427052502 The Times of India ] | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/?olv-cache-ver=20180427052502 The Times of India ] | ||
A woman can lodge a complaint under the domestic violence law against the excesses committed by her ex-husband even after the dissolution of marriage, the Supreme Court has said. The top court refused to interfere with the order of the Rajasthan high court which held that the absence of subsisting domestic relationship in no manner prevents a court from granting relief to the aggrieved woman. | A woman can lodge a complaint under the domestic violence law against the excesses committed by her ex-husband even after the dissolution of marriage, the Supreme Court has said. The top court refused to interfere with the order of the Rajasthan high court which held that the absence of subsisting domestic relationship in no manner prevents a court from granting relief to the aggrieved woman. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
=Cruelty: definition= | =Cruelty: definition= | ||
| Line 1,005: | Line 1,055: | ||
“Carrying a foetus in the womb she would obviously be inconvenienced by sex and assuming she totally shunned sex with the petitioner (husband) as her pregnancy grew would not constitute cruelty ,“ Justice Pradeep Nandrajog and Justice Pratibha Rani said. | “Carrying a foetus in the womb she would obviously be inconvenienced by sex and assuming she totally shunned sex with the petitioner (husband) as her pregnancy grew would not constitute cruelty ,“ Justice Pradeep Nandrajog and Justice Pratibha Rani said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Derogatory words, the use of== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=17_02_2023_006_009_cap_TOI Feb 17, 2023: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | New Delhi : Delhi High Court has observed that repeated use of derogatory and humiliating words by a woman against her husband and his family amounts to cruelty. | ||
| + | |||
| + |
The division bench of Justices Sanjeev Sachdeva and Vikas Mahajan said every person is entitled to live with dignity and honour and no one can be expected to live with constant abuse being hurled at him. “In the present case, the conduct of the appellant-wife, which has been proved on record, is of such quality, magnitude and impact as would have caused mental agony, pain, anger and suffering to the respondent-husband on a regular and continuous basis and, thus, clearly amounting to cruelty,” said the bench. | ||
| + | |||
| + |
The high court dismissed the wife’s appeal challenging the divorce order passed by the family court, which allowed the husband’s petition under Section 13(1)(i-a) of Hindu Marriage Act, 1956 seeking dissolution of marriage on the ground of cruelty. | ||
| + | |||
| + |
Referrring to the comments attributed to the wife, the high court said “repeated use of the words of the nature as extracted herein are clearly humiliating and would certainly amount to cruelty”. The bench upheld the findings of the family court, which had observed that the husband was treated with cruelty by the wife and that she used to abuse him and his parents in filthy language. | ||
| + | |||
| + |
The high court was satisfied that cruelty, which was proved on record, was sufficient and constituted cruelty as required under Section 13(1)(i-a) of Hindu Marriage Act. “Consequently, we find no infirmity in the judgment allowing the petition and granting divorce on the ground of cruelty. We, accordingly, find no merit in the appeal. The appeal is consequently dismissed,” the bench noted. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
==Extra-marital affair, false allegation of / HC== | ==Extra-marital affair, false allegation of / HC== | ||
| Line 1,137: | Line 1,208: | ||
The court said there was no clear picture as to what prompted Priyanka to die by suicide. | The court said there was no clear picture as to what prompted Priyanka to die by suicide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Household work by married woman is not cruelty== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/mumbai/hc-not-cruel-to-ask-married-woman-to-do-household-work/articleshow/95133186.cms PTI, Oct 28, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | MUMBAI: If a married woman is asked to do household work for the family, the same cannot be equated to the work of a maid servant and would not amount to cruelty, the Aurangabad bench of the Bombay High Court said while quashing a case lodged by a woman against her estranged husband and his parents for domestic violence and cruelty. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A division bench of Justices Vibha Kankanwadi and Rajesh Patil, on October 21, quashed the FIR lodged against the man and his parents. | ||
| + | The woman, in her complaint, had alleged she was was treated properly for a month after marriage, but thereafter, they began treating her like a maid servant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | She also claimed her husband and his parents, a month after the marriage, started demanding Rs 4 lakh to buy a four-wheeler. In her complaint, the woman said she was then subjected to mental and physical harassment by her husband over this demand. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The HC, in its order, noted the woman had merely stated she was harassed but had not specified any such act in her complaint. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “If a married lady is asked to do household work definitely for the purpose of the family, it cannot be said it is like a maid servant. If she had no wish to do her household activities, then she ought to have told it either prior to the marriage so that the bridegroom can rethink about the marriage itself or if it is after marriage, then such problem ought to have been sorted out earlier,” the court said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It further said mere use of the words harassment ‘mentally and physically’ is not sufficient to attract Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code unless such acts are described. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “Unless those acts are described, it cannot be concluded whether those acts amounted to harassment or subjecting a person to cruelty,” the HC order stated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The omnibus allegations the wife made against the husband would not attract the offence under the provision, the court said, and allowed the petition filed by the husband and his parents seeking to quash the case. | ||
[[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| Line 1,142: | Line 1,233: | ||
[[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
DIVORCE: INDIA]] | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIA | + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA |
DIVORCE: INDIA]] | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| Line 1,425: | Line 1,516: | ||
The court added that Geeta’s behaviour even before she lodged criminal complaints against her husband would amount to cruelty. ‘‘(Geeta’s conduct) shows that she had made Jitesh and his family’s lives miserable. The manner in which she used to lodge criminal complaints one after another against Jitesh undoubtedly would constitute mental cruelty,’’ said the HC. | The court added that Geeta’s behaviour even before she lodged criminal complaints against her husband would amount to cruelty. ‘‘(Geeta’s conduct) shows that she had made Jitesh and his family’s lives miserable. The manner in which she used to lodge criminal complaints one after another against Jitesh undoubtedly would constitute mental cruelty,’’ said the HC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Womaniser, calling husband one== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/mumbai/labelling-hubby-womaniser-is-cruelty-hc/articleshow/95087632.cms Rosy Sequeira, Oct 26, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | MUMBAI: Observing that a wife's labelling of her husband as a womaniser and alcoholic had shredded his reputation in society, the Bombay High Court upheld a family court's order that dissolved their marriage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Justices Nitin Jamdar and Sharmila Deshmukh on October 12 dismissed the 2006 appeal of the wife against the Pune FC's November 2005 order. While her appeal was pending, the husband died and his legal heir was brought on record in his place. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The judges noted that the FC's order was based on the wife's "unsubstantiated" allegations - that he was constantly under influence of liquor, out late at night and on some pretext visited her sister. Her sister only deposed that he drank liquor. "The evidence on record produced by the petitioner fails to prove the allegations made by her in pleadings," they said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In his evidence before FC, the husband stated she separated him from his children and grandchildren, defamed him and due to her conduct "his marital and social life has been completely destroyed." | ||
| + | |||
| + | The judges noted that in February 2002, when the husband's divorce plea was dismissed, the same allegations were not held to constitute cruelty as he did not say he suffered mental torture due to them. In the appeal, he made a specific case that she had defamed him by her false and baseless allegation causing him mental agony. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "It is a settled position in law that 'cruelty' can broadly be defined as a conduct which inflicts upon the other party such mental pain and suffering as would make it not possible for that other party to live with the other," the judges said. They noted that the husband was "a retired army major" and the wife's petition said he "belongs to the upper strata of society and has a standing" in society. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "...the petitioner has repeatedly made allegations assassinating his character in both rounds of litigation and failed to prove them. The conduct of the petitioner in continuing to make unwarranted, false and baseless allegations pertaining to the respondent's character labelling him as an alcoholic and womaniser has resulted in shredding his reputation," the judges said. They added that the husband's stand that he could not continue with the matrimonial relationship "cannot be said to be unjustified." They concluded that the wife's "conduct constitutes cruelty" under the Hindu Marriage Act. | ||
[[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| Line 1,430: | Line 1,539: | ||
[[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
DIVORCE: INDIA]] | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIA | + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA |
DIVORCE: INDIA]] | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| Line 1,492: | Line 1,601: | ||
“In the process, what is ignored is that, in spite of the dispute still existing, the academic performance of the children, while in their mother's custody, has gone up tremendously ,“ it added. | “In the process, what is ignored is that, in spite of the dispute still existing, the academic performance of the children, while in their mother's custody, has gone up tremendously ,“ it added. | ||
| + | ==Indian courts can decide custody cases despite foreign court’s verdict== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=23_12_2022_030_005_cap_TOI Dec 23, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Kolkata : Indian courts had the power to decide on child custody cases irrespective of what aforeign court had ordered, the Calcutta HC said, granting interim custody of a six-year-old child — a US citizen by birth — to his Rourkela-based mother, while allowing his US-based father visitation rights, reportsSaibal Sen. | ||
| + | |||
| + |
A California court had directed that the child be repatriated to his father’s sole custody. The fatherthen filed a habeas corpus petition for his child, so that they could return to California. The HC held that the “principle of comity of courts” required “consideration of an order passed by a foreign court”, and not “its enforcement”. | ||
| + | |||
| + |
The father had argued that his financial position allowed him to provide his child the best educationin the US. The child had s pent more time with his mother in India than in the US and repatriating him would mean he would have to spend a lot of time a lone, g iven his father’s busy schedule, the HC said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
==Parent denied custody must be allowed to talk to child daily: SC== | ==Parent denied custody must be allowed to talk to child daily: SC== | ||
| Line 1,781: | Line 1,906: | ||
It further said, “It is not a common practice or desirable culture for a Hindu son in India to get separated from his parents on getting married at the instance of the wife, especially when the son is the only earning member in the family .A son, brought up and given education by his parents, has a moral and legal obligation to take care and maintain the parents. | It further said, “It is not a common practice or desirable culture for a Hindu son in India to get separated from his parents on getting married at the instance of the wife, especially when the son is the only earning member in the family .A son, brought up and given education by his parents, has a moral and legal obligation to take care and maintain the parents. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Wife forcing husband to live away from parents== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/kolkata/wife-forcing-man-to-leave-parents-without-reason-is-cruelty-calcutta-hc/articleshow/99366020.cms Aheli Banerjee, April 10, 2023: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | KOLKATA: The Calcutta High Court has recently ruled that a husband has the right to file for divorce on grounds of mental cruelty if his wife tried to compel him to separate from his parents without justifiable reason. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The court added it was the "pious obligation of the son to live and maintain the parents", adding a son living with his parents was "absolutely normal in Indian culture and ethos". Saying this, the division bench of justices Soumen Sen and Uday Kumar on March 31 turned down a woman's plea challenging a fam-ily court's decision to grant her husband divorce. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The case dates back to 2009, when a family court in West Midnapore granted Prashant Kumar Mandal div-orce from his wife, Jharna, on grounds of cruelty. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The high court bench was hearing the wife's plea, challenging this order. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The family court had bas-ed its order on the premise that since their 2001 marriage, Jharna had publicly insulted Prashant, calling him "unemployed" and a "cow-ard". He was then teaching part-time in schools and giv-ing private tuitions, and his income was insufficient to support the family. To make ends meet, he would occasionally ask Jharna - who was earning Rs 1,400 a month - to help out with the finances. Even as Prashant was in the process of joining a government job, Jharna filed a criminal case against him and his parents on allegations of "torture", stopping him from getting the job. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =NOT grounds for divorce= | ||
| + | ==Infertility is no ground for divorce; Deserting wife is cruelty: HC== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/kolkata/cant-seek-divorce-on-grounds-of-infertility-amounts-to-cruelty-calcutta-hc/articleshow/97111719.cms Saibal Sen, January 19, 2023: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | KOLKATA: Infertility cannot be a ground for divorce and deserting one's wife who is battling mental and physical health issues due to infertility is "mental cruelty", the Calcutta High Court has ruled. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The HC was hearing an appeal by a man for quashing of criminal charges slapped on him after he filed for divorce citing "persistent mental torment and agony" caused by his wife, who was battling mental health issues due to to primary infertility and premature menopause. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The couple were married for nine years and the wife, a schoolteacher, had also undergone treatment at Bengaluru's National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A month after the husband filed for divorce in June 2017, the wife filed criminal charges against him. The Beliaghata police filed a charge sheet against the husband on December 6, 2017, implicating him for criminal breach of trust (406 IPC), physical and mental cruelty (498A) and voluntarily causing hurt (323 IPC). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The HC refused to interfere in the trial court proceedings. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "The reason of infertility is not a ground for divorce. There are several options to become parents. A spouse has to be understanding in these circumstances as it is the other who can help one to regain her/his mental, physical and emotional strength. To be able to face the world, the society in general, bravely together," Justice Shampa Dutt (Paul) said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' This is cruelty under 498A: HC ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hearing a case in which a husband sought divorce from his wife who developed premature infertility, Justice Shampa Dutt (Paul) took exception to the timing of the divorce plea. "The wife appears to have developed primary infertility with premature menopause, which is a great mental shock for a woman who is yet to become a mother.... further stress was added with the wife losing her mother.... it is the spouse's duty to be the strength which the other has lost," the judge said in order on Tuesday. The HC asked, "If the petitioner/husband had the problem, would he not expect support from his wife...?" | ||
| + | |||
| + | The judge said it was "insensitive of the petitioner to ask the opposite party in such traumatic situation for a divorce by mutual consent, which amounts to mental cruelty..." She said this was 'cruelty' under 498A IPC as it affected one's life & health.The HC said the case diary and the charge sheet "makes out a clear prima facie case of a cognizable offence against the accused/petitioner”. | ||
| + | |||
| Line 1,800: | Line 1,970: | ||
“It is evident that the wife needs money for the treatment of breast cancer. Hence, it cannot be ruled out that in order to save her life by getting money , she agreed for a settlement of dissolution of marriage,“ the bench said. | “It is evident that the wife needs money for the treatment of breast cancer. Hence, it cannot be ruled out that in order to save her life by getting money , she agreed for a settlement of dissolution of marriage,“ the bench said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
==No divorce for falsehood, suppression of crucial information== | ==No divorce for falsehood, suppression of crucial information== | ||
| Line 1,821: | Line 1,998: | ||
The court dismissed a man's plea who demanded divorce contending that his wife often used to remove vermillion and take off her mangalsutra to irk him. She also refused to cover her head with her saree's pallu, as per the tradition in his family, he alleged. The court observed that, “Merely because a woman sometimes removes her mangalsutra and vermilion, a man can't seek the severance of matrimonial ties.A woman can't be expected to cover her head with a pallu in the 21st century. In any case, these can't be the sole grounds for divorce.“ | The court dismissed a man's plea who demanded divorce contending that his wife often used to remove vermillion and take off her mangalsutra to irk him. She also refused to cover her head with her saree's pallu, as per the tradition in his family, he alleged. The court observed that, “Merely because a woman sometimes removes her mangalsutra and vermilion, a man can't seek the severance of matrimonial ties.A woman can't be expected to cover her head with a pallu in the 21st century. In any case, these can't be the sole grounds for divorce.“ | ||
| − | = Hindu Marriage Act= | + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA |
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Hindu Marriage Act= | ||
| + | ==Procedure under HMA; divorce under Article 142== | ||
| + | [https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/supreme-court-divorce-explained-ruling-8585167/ Khadija Khan, May 2, 2023: ''The Indian Express''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | A five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on Monday ruled that it can exercise its plenary power to do “complete justice” under Article 142(1) of the Constitution to dissolve a marriage on the ground that it had broken down irretrievably, without referring the parties to a family court where they must wait 6-18 months for a decree of divorce by mutual consent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Bench led by Justice S K Kaul held that the court could, in the exercise of this power, waive the mandatory six-month waiting period for divorce under The Hindu Marriage Act (HMA), 1955, and allow the dissolution of the marriage on grounds of irretrievable breakdown even if one of the parties was not willing. (Shilpa Sailesh vs Varun Sreenivasan case) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' What is the current procedure for divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act? ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Section 13B of the HMA provides for “divorce by mutual consent”. Both parties to the marriage must together file a petition to the district court “on the ground that they have been living separately for a period of one year or more, that they have not been able to live together and that they have mutually agreed that the marriage should be dissolved”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Under Section 13B(2) of the Act, the parties must move a second motion before the court “not earlier than six months after the date of the presentation of the [first] petition…and not later than eighteen months after the said date, if the petition is not withdrawn in the meantime”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The mandatory six-month wait is intended to give the parties time to withdraw their plea. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thereafter, “the court shall, on being satisfied, after hearing the parties and after making such inquiry as it thinks fit…that the averments in the petition are true, pass a decree of divorce declaring the marriage to be dissolved with effect from the date of the decree”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A petition for divorce by mutual consent can be moved only after a year of the marriage. However, Section 14 of the HMA allows a divorce petition sooner in case of “exceptional hardship to the petitioner or of exceptional depravity on the part of the respondent”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A waiver of the six-month waiting period under Section 13B(2) can be sought in an exemption application filed before the family court. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In its 2021 ruling in Amit Kumar vs Suman Beniwal, the SC said, “Where there is a chance of reconciliation, however slight, the cooling period of six months from the date of filing of the divorce petition should be enforced. However, if there is no possibility of reconciliation, it would be meaningless to prolong the agony of the parties to the marriage.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | The process of obtaining a decree of divorce is often time-consuming and lengthy owing to a large number of similar cases pending before family courts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' And what is Article 142 of the Constitution? ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Under Subsection 1 of Article 142, the Supreme Court “may pass such decree or make such order as is necessary for doing complete justice in any cause or matter…, and any decree so passed or order so made shall be enforceable throughout the territory of India”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | While the power available under Article 142 is sweeping, the SC has defined its scope and extent through its judgments. The majority opinion in Prem Chand Garg (1962) laid down that “an order to do complete justice…must not only be consistent with the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution, but it cannot even be inconsistent with the substantive provisions of the relevant statutory laws”. The seven-judge Bench in A R Antulay (1988) upheld Prem Chand Garg. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the Bhopal gas tragedy case (Union Carbide Corporation vs Union of India, 1991) the SC underlined the wide scope of Article 142(1), which confers power “at an entirely different level and of a different quality”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The present case was originally filed in 2014, where the parties sought a divorce under Article 142. While granting divorce to the parties, the SC said it can depart from procedure as well as existing substantive laws only if the decision to exercise the power under Article 142(1) is “based on considerations of fundamental general and specific public policy”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The fundamental general conditions of public policy refer to the fundamental rights, secularism, federalism, and other basic features of the Constitution; specific public policy was defined by the court to mean “some express pre-eminent prohibition in any substantive law, and not stipulations and requirements to a particular statutory scheme”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' “Irretrievable breakdown” ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | What factors can courts consider while deciding if a marriage has irretrievably broken down? During the pendency of the case last year, the court said that it would determine what rules should be followed while dissolving marriages directly under Article 142 of the Constitution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first and most “obvious” condition is that the court should be fully convinced and satisfied that the marriage is “totally unworkable, emotionally dead and beyond salvation and, therefore, dissolution of marriage is the right solution and the only way forward”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The court laid down the following factors: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *the period of time that the parties had cohabited after marriage; | ||
| + | |||
| + | *when the parties had last cohabited; | ||
| + | |||
| + | *nature of allegations made by the parties against each other and their family members; | ||
| + | |||
| + | *orders passed in the legal proceedings from time to time; | ||
| + | |||
| + | *cumulative impact on the personal relationship; | ||
| + | |||
| + | *whether, and how many attempts were made to settle the disputes by a court or through mediation, and when the last attempt was made. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The court also noted that the period of separation should be sufficiently long, and “anything above six years or more will be a relevant factor”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It emphasised the need to evaluate the factors according to the economic and social status of the parties, including their educational qualifications; whether they have any children; their age; and whether the spouse and children are dependents. | ||
| + | |||
==Divorce for Hindu married to non-Hindu== | ==Divorce for Hindu married to non-Hindu== | ||
''' Hindu married to non-Hindu can't get divorce under Hindu Marriage Act: Bombay high court ''' | ''' Hindu married to non-Hindu can't get divorce under Hindu Marriage Act: Bombay high court ''' | ||
| Line 1,854: | Line 2,105: | ||
It is also an essential condition under the act that at the time of filing a petition for divorce, both the spouses were Hindus by religion, ruled the bench. | It is also an essential condition under the act that at the time of filing a petition for divorce, both the spouses were Hindus by religion, ruled the bench. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
= Incidence of divorce, separation= | = Incidence of divorce, separation= | ||
| Line 1,955: | Line 2,213: | ||
==Divorce granted without couple’s presence in court== | ==Divorce granted without couple’s presence in court== | ||
| + | |||
[https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2021%2F03%2F08&entity=Ar01319&sk=2291D392&mode=text Swati Deshpande, March 8, 2021: ''The Times of India''] | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2021%2F03%2F08&entity=Ar01319&sk=2291D392&mode=text Swati Deshpande, March 8, 2021: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| Line 1,963: | Line 2,222: | ||
The husband had been abroad on a two-month tourist visa. The visa was extended for over 10 months due to the pandemic flight restrictions and unprecedented contingency. | The husband had been abroad on a two-month tourist visa. The visa was extended for over 10 months due to the pandemic flight restrictions and unprecedented contingency. | ||
| + | |||
The Indian Consulate first rejected the husband’s application to attest his documents, but later, after several escalations, it played a role in even aiding the virtual dissolution. | The Indian Consulate first rejected the husband’s application to attest his documents, but later, after several escalations, it played a role in even aiding the virtual dissolution. | ||
| Line 1,970: | Line 2,230: | ||
Since the couple have been separated for over two years and seven months, the waiting period of six months in cases of mutual consent divorce petitions would “only prolong their agony’”. Datta said the consulate may not be able to attest the husband’s documents once again for the final hearing six months later and, citing the new strain of the virus now spreading, she had said that unless the cooling off period was waived the case would be left in the lurch. | Since the couple have been separated for over two years and seven months, the waiting period of six months in cases of mutual consent divorce petitions would “only prolong their agony’”. Datta said the consulate may not be able to attest the husband’s documents once again for the final hearing six months later and, citing the new strain of the virus now spreading, she had said that unless the cooling off period was waived the case would be left in the lurch. | ||
| + | |||
The family court waived the statutory six months and on its second hearing date declared them divorced, said the decree released a few days ago. | The family court waived the statutory six months and on its second hearing date declared them divorced, said the decree released a few days ago. | ||
| − | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | + | |
| + | ==No divorce under Art 142 if one side unwilling: SC== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=14_10_2022_001_001_cap_TOI Oct 14, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | New Delhi:The SC said it would not exercise its omnibus powers under Article 142 to annul an “irretrievably broken down” marriage on the husband’s plea when the wife wants to make the marriage work, reports Dhananjay Mahapatra.
The bench said, “Marriage is not a casual event in India. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We haven’t reached western standards of ‘marriage today and divorce tomorrow’. You both are highly educated… (and) may adopt the western philosophy but powers under Article 142 cannot be exercised to annul the marriage when one party is unwilling. ” | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
DIVORCE: INDIA]] | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA |
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==No divorce under Art 142 if one side unwilling: SC== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=14_10_2022_001_001_cap_TOI Oct 14, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | New Delhi:The SC said it would not exercise its omnibus powers under Article 142 to annul an “irretrievably broken down” marriage on the husband’s plea when the wife wants to make the marriage work, reports Dhananjay Mahapatra.
The bench said, “Marriage is not a casual event in India. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We haven’t reached western standards of ‘marriage today and divorce tomorrow’. You both are highly educated… (and) may adopt the western philosophy but powers under Article 142 cannot be exercised to annul the marriage when one party is unwilling. ” | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:India|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Law,Constitution,Judiciary|DDIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
| + | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|DIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIADIVORCE: INDIA | ||
DIVORCE: INDIA]] | DIVORCE: INDIA]] | ||
Revision as of 14:45, 12 May 2023
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. the Facebook community, Indpaedia.com. All information used will be acknowledged in your name. |
PART I
ALIMONY/ MAINTENANCE
How to determine/ calculate alimony
Alimony not for mere survival: SC
The Times of India Apr 07 2015
Dhananjay Mahapatra
The Supreme Court ruled that courts must direct a man to pay such alimony to his estranged wife so as to allow her to live life with dignity and not just make ends meet. “Be it clarified that sustenance does not mean and can never allow to mean mere survival. A woman, who is constrained to leave marital home, should not be allowed to feel that she has fallen from grace and move hither and thither arranging for sustenance. As per law, she is entitled to lead a life in the similar manner as she would have lived in the house of her husband,“ a bench of Justices Dipak Misra and P C Pant said.
Increasing the maintenance amount from Rs 2,000 per month to Rs 4,000 to a retired Army personnel's estranged wife, the bench said at the time of quantifying maintenance under Section 125 of Criminal Procedure Code, the status of the husband has to be taken into consideration. Writing the judgment for the bench, Justice Misra said, “As long as the wife is held entitled to grant of maintenance under Section 125, it has to be adequate so that she can live with dignity as she would have lived in her matrimonial home. She cannot be compelled to become a destitute or a beggar.“
The court said the husband would have to arrange for payment of maintenance to wife even if he had no job.“Sometimes, a plea is advanced by the husband that he does not have the means to pay , for he does not have a job or his business is not doing well. These are only bald excuses and, in fact, they have no acceptability in law,“ the bench said.
“If the husband is healthy , able bodied and is in a position to support himself, he is under legal obligation to support his wife, for wife's right to receive maintenance under Section 125, unless disqualified, is an absolute right,“ it said.
Loss of matrimonial home and the cohabitation with husband are unfortunate developments for a woman, the bench said, adding “at this stage, the only comfort that the law can impose is that the husband is bound to give monetary comfort“.
Cannot be awarded mechanically
HC: Don't award maintenance mechanicallyJul 28 2017 : The Times of India (Delhi)
Do not treat husbands like “armless soldiers“ and order them to pay maintenance to wives in a “mechanical manner“, the Madras high court told family courts on Thursday , reports A Subramani. A man has to take care of his aged parents as well, the HC said, adding that family courts should not brush this aspect aside lightly.
The HC ruling came in a case where a family court had ordered a man earning Rs 10,500 a month to pay Rs 7,000 to his wife and child, leaving Rs 3,500 for the man and his father. Slamming the attitude of the family court, Justice RMT Teekaraman of the HC said such an order needed to be deprecated.
Childcare to be factored in
Dhananjay Mahapatra, November 5, 2020: The Times of India
SC: Maintenance to estranged wife to factor in childcare too
The Supreme Court said if an estranged wife gave up her job to take care of children and the elderly in the family, then this will have to be taken into consideration by the family court while quantifying monthly interim maintenance payable to her by the husband.
The court also found that pleas for grant of interim maintenance were pending in courts for years even though the law stipulated a 60-day window, from the date of issuance of notice by the court to a husband on the estranged wife’s application, for grant of maintenance. It considered overlapping laws regarding grant of maintenance and laid down guidelines for all trial courts and high courts.
This is the first time that the highest court has considered the sacrifices made by career women in taking care of children and ruled that this would be an added component for enhancing the grant of interim compensation to her, so that she could lead a life almost akin to what she was used to when all was well in the matrimonial home.
A bench of Justices Indu Malhotra and R S Reddy said, “In a marriage of long duration, where parties have endured the relationship for several years, it would be a relevant factor to be taken into consideration. On termination of the relationship, if the wife is educated and professionally qualified, but had to give up her employment opportunities to look after the needs of the family, being the primary caregiver to minor children and elder members of the family, this factor would be required to be given due importance.
“This is of particular relevance in contemporary society, given the highly competitive industry standards, the separated wife would be required to undergo fresh training to acquire marketable skills and retrain herself to secure a job in the paid workforce to rehabilitate herself. With advancement of age, it would be difficult for a dependent wife to get an easy entry into the workforce after a break of several years.”
The SC said the family court must also take into consideration the educational expenses of children staying with the estranged wife in computing maintenance as “education expenses of the children must be normally borne by the father”. If the wife was working and earning sufficiently, education expenses of the children, including fees for coaching classes and extracurricular activities, may be shared proportionately between the parties, it said.
Writing the 56-page judgment, Justice Malhotra said, “Serious disability or ill health of a spouse, child/children from the marriage/dependant relative who require constant care , would also be a relevant consideration.”
Finding that neither the Hindu Marriage Act nor the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act specified the date from which interim maintenance was to be granted, leading to exercise of discretion by family courts, the SC said interim maintenance had to be granted from the day the estranged woman filed an application in court.
The SC also said non-payment of maintenance could lead to arrest of the delinquent husband and may even lead to confiscation of his assets and their auction to make good the dues to the estranged wife.
Alimony to be 25% of ex-hubby’s salary: SC, 2017
`Just Amount To Ensure Dignified Life For Ex-Wife'
The Supreme Court has set a benchmark for maintenance to be paid by a husband to his estranged wife, stating that 25% of his net salary might constitute a “just and proper“ amount as alimony .
However, the court reduced the quantum of alimony in a particular case it was hearing to a shade under 21%, reasoning that the man remarried and had to support his new family . The court said the amount of maintenance or permanent alimony must be sufficient to ensure that a woman lived with dignity after separating from her husband.
A bench of Justices R Ba numathi and M M Santanagoudar made the observation while directing a resident of West Bengal's Hooghly , earning Rs 95,527 a month, to set aside Rs 20,000 as maintenance for his former wife and the ir son, turning down the man's plea that the amount was excessive.
Its order came on the man's plea challenging a Calcutta high court order directing him to pay her Rs 23,000 per month.Though the apex court said there was nothing amiss in the high court order, it reduced the amount by Rs 3,000 on the ground of the man's remarriage.
The couple has been figh ting a legal battle over maintenance since 2003 when the district judge fixed the amount at Rs 4,500. The high court, however, awarded Rs 16,000 per month in 2015 and increased it to Rs 23,000 in 2016 as the husband's salary went up from Rs 63,842 to Rs 95,527. The apex court's ruling follows its inclination to protect claims of women in matrimonial disputes affecting their financial status.
“Twenty-five percent of the husband's net salary would be just and proper to be awarded as maintenance to the (former) wife. The amount of permanent alimony awarded to her must be befitting the status of the parties and the capacity of the spouse to pay maintenance, which is always dependant on the factual situation of the case... and the court would be justified in moulding the claim for maintenance passed on various factors,“ the SC bench said.
While stating that the high court was justified in enhancing the maintenance on the basis of the husband's salary , the SC bench noted : “However, since the appellant has also got married a second time and has a child from the second marriage, we think it proper to reduce the amount of maintenance of Rs 23,000 to Rs 20,000 per month as maintenance to his (former) wife and son,“ the court said.
The apex court had said in a judgment it had delivered in 2016, “A Hindu woman's right to maintenance is a personal obligation so far as the husband is concerned, and it is his duty to maintain her even if he has no property ... . It is well settled that under the Hindu Law, the husband has got a personal obligation to maintain his wife and if he is possessed of properties then his wife is entitled to a right to be maintained out of such properties.“
Cannot be based on husband’s I-T returns:
Alimony can’t be based on hubby’s I-T returns: Guj HC
Saeed Khan | TNN
Ahmedabad: Asking a doctor to pay a monthly maintenance of Rs 15,000 to his estranged wife, Gujarat high court on Monday said an alimony cannot be decided on the basis of a husband’s income tax returns because these papers are not the gospel truth.
Rani Tahelramani had filed a case under Domestic Violence Act against her husband, Anup Vidhani, a Vadodara-based eye surgeon. She had also sought maintenance from her husband but a lower court turned down her plea saying a decision on her complaint would be taken soon. When the proceedings dragged on, she appealed in the sessions court seeking alimony.
The wife argued in the sessions court that her husband had a flourishing private practice and runs an eye hospital and has a monthly income of over Rs 1 lakh. Countering this, the surgeon told the court that he is ‘‘engaged by a private hospital’’ and paid an honorarium of Rs 4,000 per month. He even produced his I-T returns showing he was not earning much.
Not satisfied with the doctor’s arguments, the court last month asked him to pay a monthly alimony of Rs 15,000 from January 3. Aggrieved by this order, Vidhani approached the high court claiming he was not in a position to pay ‘such a huge amount’. Justice Akil Kureshi, however, upheld the sessions court’s decision and asked him to pay Rs 15,000 monthly as alimony.
Cannot be higher merely if husband working abroad
Man working abroad not liable to pay wife more money: HC, Oct 15 2016 : The Times of India
Just because a man is employed abroad and earns in local currency , a wife is not entitled to seek enhanced main tenance, the Delhi high court has said.
The court said he has to spend also on the higher cost of living abroad and cannot be assumed to be capable of paying more maintenance in India.
A bench of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Pratibha Rani dismissed an appeal filed by a woman seeking enhancement of maintenance on the ground that her husband works in Dubai and has no other liability .
In 2014, a trial court had granted her maintenance of 5,000 per month along with Rs 2,000 per court visit for attending the hearing on a divorce plea filed by the husband and Rs 500 as dearness allowance.
However, the woman had approached the high court seeking enhancement of maintenance.
…and should not be a form of extortion for highly qualified wife
A family court rejected a Delhi resident’s claim of monthly maintenance from her estranged husband and said Sarita Vihar — where she lives — is by no means a “lower locality”. The woman, who had sought the court’s intervention for claiming the maintenance from her husband who lives in Singapore, said he lived in a “upscale colony” and was earning handsomely, whereas she was living in city’s Sarita Vihar.
Family court judge, Madhu Jain, however, found the woman to be “highly qualified” and said that the provision of law under which the wife was claiming maintenance was neither meant to “extort money”, nor to be used to “blackmail”.
“Counsel for the wife argued that the husband is living in a very upscale colony in Singapore, but this cannot be the sole criteria to award maintenance to the wife. If he is living in Singapore, he also has expenditure in Singapore dollars... whereas the locality of Sarita Vihar, New Delhi, cannot be termed as a lower locality or it is not a slum area where
the applicant/wife cannot be expected to live,” the court observed.
Advocate Prabhjit Jauhar, who appeared for the husband, had told the court that though his client was living in Singapore, he had to incur expenditure in Singapore dollars. “The husband had to pay a huge amount of rent and had to incur other necessary expenditure as cost of living in Singapore was very high,” argued Jauhar.
The wife’s lawyer, on the other hand, informed the court that she was living and working in Mumbai, but coming to Delhi to attend regular court proceedings was not feasible. She, as a result, took up a job in Gurgaon and currently stays in Sarita Vihar. She had sought Rs 2.5 lakh maintenance apart from Rs 1.5 lakh as litigation cost under Section 24 of the Hindu Marriage Act.
The provision entails that either the wife or the husband, as the case may be, has no independent income sufficient for her or his support.
“Though this application was filed by her when she was jobless for some time even after getting a job and living a decent life, she has not withdrawn this application. The present application is nothing but gross abuse of law... this provision of maintenance is being used as a legal extortion,” the court said.
Need to ascertain the true income to pass appropriate order on maintenance: HC
Abhinav Garg, August 9, 2020: The Times of India
Estranged spouses moving court will have to list every single detail of money spent by them and even their social media presence.
In a bid to evaluate the true income and gauge lifestyle status of warring couples, the Delhi high court has drawn up a comprehensive affidavit that needs to be filed by husband and wife, before the court takes a call on maintenance, alimony or right to joint properties.
From the brand of mobile phone, wrist watch, pen, wages and number of maids/domestic help, expenditure incurred on functions and festivals, to particulars of social media accounts including Facebook, Twitter, Instagram etc, the new format finalised by HC contains 99 entries to be disclosed in the affidavits to be placed before the courts.
Justice J R Midha said that such a detailed affidavit of the assets, income and expenditure of both the spouses is necessary to determine their true income to enable courts to grant proper relief. The court also noted that matrimonial jurisdiction deserves special attention and maintenance applications should be decided swiftly.
“It is the duty of the court to ascertain the true income of the parties and then pass the appropriate order relating to maintenance. Truth is the foundation of justice. Dispensation of justice, based on truth, is an essential feature in the justice delivery system. People would have faith in courts when truth alone triumphs,” the court noted. It added that such mandatory filing of the affidavit in a detailed prescribed form should be incorporated in the statutes, as in the developed countries and asked the Centre to consider the suggestion.
According to the latest affidavit, a salaried person has to share particulars of employment including salary, dearness allowance, commissions, bonus, perks, other benefits and income tax.
The verdict said that a self employed person has to disclose the nature of business/ profession, share, net worth, number of employees, annual turnover, gross profit, income tax and regular monthly withdrawal.
The parties are also required to disclose income from other sources, like agriculture, rent, interest on bank deposits, investments, profits on sale of assets, particulars of immovable properties, financial assets including bank accounts, DEMAT accounts, safety deposit lockers, loans, insurance policies and foreign investments.
In movable assets, they have to disclose motor vehicles, mobiles, computers, laptops, electronic gadgets, gold, silver and diamond jewellery, intangible assets and properties acquired by the family members or inheritance.
The affidavit further requires them to disclose their standard of living, credit/debit cards, membership of clubs, social media accounts, domestic helps and their wages, mode of travel in city and outside, category of hotels, hospitals for medical treatment, frequency of foreign travel, brand of mobile, wrist watch, pen, expenditure ordinarily incurred on functions, festivals and marriage of family members. They also have to disclose expenditure on housing, household and medical, maintenance of dependents, transport, entertainment and vacations.
“These modified directions/guidelines shall apply to all matrimonial cases including cases under Hindu Marriage Act, Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, Section 125 CrPC, Hindu Adoption and Maintenance Act, Special Marriage Act, Indian Divorce Act, Guardians and Wards Act and Hindu Minority and Guardianship Act,” the high court said.
HIGH COURT SAYS
It is the duty of the court to ascertain the true income of the parties to pass appropriate order on maintenance
Take conversion rate, cost of living into account
`Mechanical' award of maintenance set aside by court, Jan 30, 2017: The Times of India
Finding fault with the “mechanical“ manner in which a family court computed the monthly maintenance to be paid to a woman by her Dubai-based husband, the Delhi high court has set aside the decision, saying the man's cost of living there and the wife's expected expenses were overlooked.
A bench of justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Yogesh Khanna said the family court “casually“ calculated the annual income of the husband from 2012 to 2016 on the basis of the Dirham to Rupee conversion rate of 2016 and not the earlier years.
HC noted that though the woman had moved an application for maintenance in November 2012, she had stayed with at her matri monial home till July 2015 and in the intervening period the man had borne the family expenses, including school fees of their two children.
It directed the family court to re-decide the maintenance application by examining the couple on oath regarding their sources of income, investments and expenses as well as the “huge inflow and outflow“ of money from their accounts. The bench set aside the family court's decision to award the woman Rs 5,86,143 per month from the date of her application for maintenance. The high court directed the husband to pay Rs 2 lakh per month as interim maintenance with effect from August 1, 2015.
Alimony for wives
Court orders Muslim man to pay ex-wife maintenance
Vasantha Kumar, Oct 20, 2021: The Times of India
“A Muslim marriage is not a sacrament, (and) does not repel certain rights and obligations arising from its dissolution,” the Karnataka high court has said, rejecting a man’s plea and coming to the rescue of his ex-wife, who has been battling for enforcement of the trial court’s maintenance decree for the past decade.
Contracting another marriage after pronouncing talaq upon his first wife, a Muslim man cannot say he has to maintain the new wife and their child, and cite the same as a ground for not discharging maintenance, Justice Krishna S Dixit said.
The petitioner, Ezazur Rehman, had pleaded that he could not pay maintenance to his ex-wife, Saira Banu, as he had remarried and had to provide for his wife and their child. The judge, in his order, said Rehman ought to have known his responsibility towards his ex-wife, who does not have anything to fall back on. The responsibility of paying maintenance arises from his own act of talaq, and prior to marrying another woman, the court said.
Quoting the Quran and Hadith, the judge said the right of a divorced woman for maintenance is conditioned on three cumulative factors — insignificant mehr amount, inability of the woman to sustain herself, and if she does not remarry. A Muslim marriage “dissolved by divorce, per se does not annihilate all the duties and obligations of parties by lock, stock and barrel”, the judge noted in the order passed on October 7. The judge also said Rehman’s contention is repugnant to law, morality and ethics and that if such a contention is countenanced, it would only encourage talaq which the law shuns.
Man‘s obligation to provide maintenance
Amit Anand Choudhary, Oct 6, 2022: The Times of India
NEW DELHI: The Supreme Court has said a husband is required to earn money “even by physical labour” to meet his sacrosanct duty to provide financial support to the estranged wife, minor children and couldn’t avoid his obligation.
A bench of Justices Dinesh Maheshwari and Bela M Trivedi said provision for maintenance under CrPC Sec 125 is a measure of social justice that was specially enacted to protect women and children and refused to accept plea of a husband who submitted he had no source of income as his party business has now been closed.
“The respondent (husband) being an able bodied, he is obliged to earn by legitimate means and maintain his wife and the minor child. Having regard to the evidence of the appellant-wife before the family court, and having regard to the other evidence on record, the court has no hesitation in holding that though the respondent had sufficient source of income and was able-bodied, had failed and neglected to maintain the appellant,” it said.
The Supreme Court directed a man to pay maintenance of Rs 10,000 per month to his wife and Rs 6,000 to his minor son.
The bench said the Section 125 of CrPC was conceived to ameliorate the agony, anguish and financial suffering of a woman who is required to leave the matrimonial home, so that some suitable arrangements could be made to enable her to sustain herself and the children. It pulled up a family court to deny maintenance to the woman and her children after she left the matrimonial home and started living separately and said that the court was not alive to the objects and reasons, and the spirit of the provisions under Section 125 of the code.
“The family court had disregarded the basic canon of law that it is the sacrosanct duty of the husband to provide financial support to the wife and to the minor children. The husband is required to earn money even by physical labour, if he is an able-bodied, and could not avoid his obligation, except on the legally permissible grounds mentioned in the statute. In Chaturbhuj vs Sita case, it has been held that the object of maintenance proceedings is not to punish a person for his past neglect, but to prevent vagrancy and destitution of a deserted wife, by providing her food, clothing, and shelter by a speedy remedy,” the bench said.
The bench also disapproved the Punjab and Haryana high court passing order in a very casual manner by upholding “such an erroneous and perverse order of family court”. The court passed the order in favour of the wife who approached the apex court and was fighting a legal battle for maintenance for around a decade after she left her matrimonial home in 2010 .
Alimony for adulterous wife
‘Adulterous wife not entitled to alimony’
‘Adulterous wife not entitled to alimony’
Rebecca Samervel TNN
Mumbai: A city court rejected a 38-year-old South Mumbai woman’s plea for maintenance from her estranged husband after it found she was involved in an adulterous relationship.
“The wife who engaged herself in (an) adulterous relationship cannot claim maintenance and cannot be allowed to take advantage of her own wrongdoings,” the court said.
The court accepted the 40-year-old husband’s plea seeking divorce on grounds of cruelty and adultery.
The couple was married in 1999 and had a son in 2001. The man carried out business at Nana Chowk and used to return home after 10pm. In his petition, he alleged that when he returned home early one day, he saw that his child had been left alone. The husband alleged that he repeatedly made attempts to contact his wife on the phone, but it was switched off. He stated that when the woman finally returned home at 7.45 pm, she gave evasive answers.
The man claimed the woman confessed the next day that she had gone out with her paramour to a hotel. The man further alleged that he confronted his father-in-law about the problem and told him that he could no longer co-habit with the woman. He filed the divorce petition in December 2005.
Both the wife and the man against whom her husband had levelled allegations gave their version to the court and denied having an affair. The woman claimed she was forced to write the confession and it was false. She alleged that it was her father-in-law, stepmother-in-law and sisters-inlaw who had harassed her for dowry and forced her to leave the home.
Taking the letter into consideration, the court observed that the woman could have easily complained to police and her parents about being forced to write it once she was at her parents’ home. In the absence of such complaints, the court said her version was not believable.
The court observed that a man cannot be asked to continue his marital relations with a woman who has breached the marital trust.
Madras HC: no alimony for adultress
The Times of India, Aug 17 2015
HC: No alimony if woman divorced over adultery
A woman divorced on the ground of adultery cannot claim maintenance from her ex-husband, the Madras high court has ruled. The judge made the observation while allowing a criminal revision case filed by a government staffer challenging a lower court's order to pay a monthly maintenance of Rs 1,000 to his former wife, whom he divorced in 2011 on the ground of adultery .
“Just as a man has an obligation to maintain his divorced wife, the woman also has an obligation not to have illicit relationship with another man,“ Justice Nagamuthu said. “The divorcee would suffer disqualification from claiming maintenance if she had relationship with another man. She was entitled to get maintenance from the person with whom she had relationship and not from the ex-husband,“ he said.
Occasional adultery does not disentitle maintenance: Delhi HC
April 16, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi: Occasional or isolated acts of adultery by a wife do not disentitle her from receiving maintenance from her husband, the Delhi high court has ruled. The bar on paying maintenance will apply only if there is “definite evidence” of continuous and repeated acts of adultery by the wife, Justice Chandra Dhari Singh said, while hearing a man’s plea against a trial court order that had directed him to pay his wife Rs 15,000 a month. The man argued that the direction for payment of maintenance cannot be sustained on several grounds in this case, including cruelty, adultery and desertion by his wife. However, the HC pointed out that “cruelty and harassment do not stand ground” for non-payment of maintenance, and noted that even in cases where a divorce is granted on the ground of cruelty, courts have awarded permanent alimony.
The HC added that law emanating from various precedents of the Supreme Court and high courts establishes the position of payment of maintenance. On adultery, it opined that the husband in this case did not establish even a prima facie case against the wife and the law required her to be “living in adultery” to bar her from receiving maintenance under section 125 CrPC.
The ground of desertion was also rejected by the court, and the husband’s challenge to the trial court order was subsequently dismissed.
Alimony/ maintenance for husbands
2018: Woman to pay rent to estranged husband
Mumbai: Elderly woman ordered to pay rent to estranged husband, October 1, 2018: The Times of India
Bombay high court has upheld a Pune family court order directing an elderly woman to pay Rs 20,000 monthly rent to her estranged husband for staying in a flat jointly owned by him and the couple's son.
Justice Rajesh Ketkar said there was an agreement between the couple that she would live in Kalyaninagar flat by paying rent, while he would continue to stay in the Koregaon Park apartment, jointly owned by the couple.
The woman had challenged the family court order, contending since she was still the man's legally wedded wife, she was entitled to reside in the apartment. She cited her son's email allowing her to stay in the flat without paying rent and also sought recourse under the Domestic Violence Act.
The HC dismissed the claims. "Notwithstanding the Domestic Violence Act, there was an agreement between the parties to the effect that the woman would pay Rs20,000 per month to the (husband)," said the judge.
The court rejected the woman's claims about a subsequent settlement and that he had agreed to not charge her rent. "If at all there is a settlement before the court, obviously it has to be in writing and the court has to record satisfaction about the settlement being legal and valid. No such material is produced to that effect," the judge said. The woman's submission of her son's email, too, was not accepted. There is no agreement between the couple over rent waiver, the court ruled.
A proposal for reconciliation floated by the court was rejected by the couple. The judge suggested the man could shift to the Kalyaninagar apartment, while the woman could live in the Koregaon Park flat. The husband was not agreeable and suggested his wife could come and live with him in the Koregaon Park flat. The woman rejected the offer.
The couple, in their 60s, had got married in 1981. In 2013, she sought divorce under the Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act. The man filed an application seeking rent for the Kalyaninagar flat. The woman said she had agreed to pay rent as, otherwise, her husband would not allow her to live there.
Alimony/ maintenance for women who desert husbands
Woman deserting husband entitled to alimony
Preferring social welfare to legal technicality , the Supreme Court has held that even if a woman is disentitled to maintenance from her husband during the period of separation after deserting him, she will be entitled to it after divorce if she is unable to sustain herself.
The judiciary has resorted to Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code irrespective of the religion of married couples, including in the Shah Bano case by the SC in 1985, to grant alimony to women during pendency of divorce proceedings or those facing destitution after divorce.
However, sub-section (4) of Section 125 provides three cir cumstances when a woman is not entitled to maintenance: if she is living in adultery, refuses to live with the husband without sufficient reason or if the couple, by mutual consent, decide to live separately .
The SC faced a dilemma when Manoj Kumar, through advocate Nisha Priya Bhatia, challenged a judgment of the Himachal Pradesh HC which had ordered him to pay alimony of Rs 3,000 per month to Champa Devi despite the divorce being granted on grounds of desertion. Bhatia argued, and a SC bench of CJI J S Khehar and Justices D Y Chandrachud and Sanjay Kishan Kaul appeared to accept it for most part of the proceedings, that when a woman during subsistence of marriage was not entitled to alimony under Section 125(4) of CrPC if she had wilfully deserted her husband, how could she, after divorce being granted on ground of desertion, be entitled to alimony .“Grant of alimony in such a case would be in the teeth of Section 125(4),“ she said.
The bench appeared to have made up its mind when it told Champa Devi's counsel Anil Nag, “If Section 125(4) was not there, we could have said whatever is the fault of the woman, she is entitled to maintenance to prevent destitution, especially when the state is not obliged to maintain her. But the legislation categorically says if it is adultery or desertion by free will, then she is not entitled to maintenance.“
From a hopeless position, Nag rallied to save the day for Champa Devi by citing an earlier SC judgment which had stressed on social welfare intent of the legislation to prevent destitution of divorced women. Nag said a divorced woman had an indefeasible right to get maintenance irrespective of the ground for dissolution of marriage.
The SC in its March 2000 judgment had said, “As a wife, she is entitled to maintenance unless she suffers from any of the disabilities indicated in Section 125(4). In another capacity, namely , as a divorced woman, she is again entitled to claim maintenance from the person of whom she was once the wife. A woman after divorce becomes a destitute. If she cannot maintain herself or remains unmarried, the man who was once her husband continues to be under a statutory duty and obligation to provide maintenance to her.“
This retrieved Champa Devi from the jaws of being denied alimony . The bench upheld the Himachal HC order granting her alimony and said it would not interfere in the grant of alimony to divorced women under all circumstances, a logic that had consistently been the thread of SC rulings for last 25 years.
Alimony/ maintenance for working/ earning women
Wife should not sit idle and be parasite on husband
`Can't be parasite on hubby's earnings', Mar 27, 2017: The Times of India
A Delhi court has refused to enhance the monthly interim maintenance awarded to a woman in a domestic violence case, saying she was not supposed to sit idle at home and be a parasite on the husband's earnings.
Additional Sessions Judge R K Tripathi declined the appeal of the woman seeking enhancement of Rs 5,500 awarded to her as monthly interim maintenance to Rs 25,000 while noting that she was more qualified than her estranged husband.
“The appellant herself is a well-educated lady having post graduation degree i.e.MA, B.Ed and LLB and is reported to be more qualified than the respondent (husband). She can earn herself.She is not supposed to sit idle at home and be a parasite on the earnings of the respondent,“ the judge said. A magisterial court had in 2008 awarded Rs 5,000 per month to the woman. In 2015, the amount was enhanced by 10%. The woman had appealed against the orders seeking further enhancement to Rs 25,000.
The sessions court, while upholding the 2015 magisterial court's decision, said it took note of practical realities prevailing in the society.
Can’t deny maintenance because wife capable of earning: HC
September 22, 2018: The Times of India
Merely because a wife is capable of earning doesn’t mean she can be denied maintenance, a Delhi court has said, while awarding a whopping Rs 2.5 lakh as interim maintenance in a case.
Additional Sessions Judge Sandeep Yadav, in a recent order, enhanced the interim maintenance payable to an estranged wife by her husband after taking note of his earnings on the one hand and the family’s lifestyle before the split.
The court’s order came in a case lodged under Prevention of Domestic Violence Act. “Their child, stated to be seven years old, admittedly is living with wife and requires all care and attention of wife. The court cannot compel the wife to leave her child alone in the house or at the mercy of some servant so as to earn for her own maintenance.”
ASJ Yadav also upheld directions by a magistrate to the husband to also pay school expenses of the child, and expenses if the mother-son decided to shift to an independent residence from that of her parents.
The wife had appealed under the DV Act against maintenance of nearly Rs 1 lakh awarded by the magistrate. Through advocate Prabhjit Jauhar, she pointed out that the husband had a thriving business, which was not reflected from the Income Tax returns filed such as the fact that he travelled abroad atleast 3-4 times a year in business class and the fact that he though took a huge loan for which he paid Rs 6-7 lakh per month as instalment.
Jauhar also argued that even if it is held that wife is capable of earning, the same cannot be a sufficient reason to deny her maintenance. The husband argued their child is now aged seven and doesn’t need her constant care.
But the court cited a Delhi high court ruling to stress that “while granting maintenance, the spouse claiming maintenance should as far as possible be kept in the same status which he or she enjoyed while being in the matrimonial life with the other spouse and the family status should also be considered.”
‘Wife actually earning and capable of earning are two different things’: HC
Abhinav Garg June 8, 2019: The Times of India
HC: Woman’s capability to earn no ground to deny maintenance
New Delhi:
Broadening the welfare scope of the Domestic Violence Act, the Delhi high court has said the mere fact that a woman is capable of earning can’t be used as grounds to deny her maintenance.
The HC held in a case where a wife’s working status is disputed, the court cannot assume that because she is educated, or was employed prior to her marriage, she would again be gainfully employed.
Justice Sanjeev Sachdeva noted that granting maintenance under the protective umbrella of the DV Act is not dependent upon the expression “unable to maintain herself ”, as is found in CrPC Section 125 which also deals with maintenance.
The HC specified that whether the wife was actually earning or was qualified and capable of earning were two different things, and set aside the order of a lower court withdrawing maintenance being paid to a woman by her estranged husband.
The woman had challenged the court order denying her maintenance of Rs 16,500 per month on the grounds that she was duly qualified, educated and gainfully employed.
According to the petition, the couple got married on February 14, 2015. Later, the wife alleged that she was harassed and subjected to cruelty by her in-laws who were dissatisfied with the dowry.
The HC directed the husband to pay his wife Rs 16,500 per month as maintenance from the date of filing the maintenance application on May 3, 2017. The court also granted the husband four weeks to clear the entire maintenance arrears.
It noted that under Section 20 of the DV Act, the magistrate has the power to direct the husband to pay monetary relief to meet the expenses incurred and losses suffered by the aggrieved person, and any child of the aggrieved person, as a result of domestic violence. It also observed that under Section 20(2) of the act, monetary relief granted has to be adequate, fair and reasonable, and consistent with the standard of living to which the aggrieved person was accustomed.
Alimony for ‘more qualified’ wife
Wife ‘more qualified’, court rejects alimony plea
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
New Delhi: A trial court has refused interim maintenance to a woman saying she was professionally more qualified than her estranged husband, and had failed to show why she didn’t look for a job. The judge dismissed the woman’s plea after noting that she was a graduate from Delhi University, held a diploma in library science and was once employed as lab technician in the varsity itself while her husband had studied till higher secondary.
“She has not assigned any reason as to why she has not tried to do any other job with the said qualification. It is not her case that she searched for one and could not obtain. Admittedly, there is no issue of the wedlock, and as such, the applicant/wife is free to take up an employment. ...since the applicant herself has failed to disclose the reason for not doing any job in spite of being able bodied and educationally and professionally qualified; and much better qualified than the husband, she has failed to make out an entitlement for any interim maintenance for herself,” additional district judge Sujata Kohli said.
The judge relied upon a judgment of the MP high court while taking the decision. “A spouse who is well qualified to get service immediately with less efforts is not expected to remain idle to squeeze out, to milk out the other spouse by relieving him of his or her own purse by a cut in the nature of pendente lite alimony....” the court said. The couple had moved the court for separation and in the meantime, the woman filed a plea for interim maintenance of Rs 25,000.
Financially stable wife can’t claim maintenance: Bombay high court
Shibu Thomas,TNN | Feb 24, 2014
(Names of the couple changed to protect identities)
MUMBAI: Only a wife with no sufficient source of permanent income can claim maintenance from her husband, the Bombay high court has ruled. A division bench of Justice Vijaya Kapse-Tahilramani and Justice P N Deshmukh rejected an application by an Andheri resident, Sheela Sharma (61), who had sought Rs 15,000 as monthly maintenance from her husband, Nitin Sharma, who is based in Australia.
"It is a well-settled law that only a wife who has no sufficient permanent source of income can claim and get maintenance from her husband who has sufficient means," said the judges. The Sharmas have a son and daughter who are married and settled abroad. The couple has been living separately since 2007.
The court pointed out that it had come in evidence that Sheela had invested Rs 50 lakh in fixed deposits and also made investments in mutual funds. She has also invested another Rs 2 lakh that she got from Nitin in a fixed deposit. She resides in a flat that she had bought with Nitin, who said she had exclusive possession of the house. This meant there was no rent to be paid. "It is seen that the wife is getting more than Rs 37,500 per month as interest. She has more than Rs 50 lakh in the bank. In addition, (her) son is providing money for her maintenance and other expenses. No one is dependent," said the judges.
Nitin had moved the court for divorce on the grounds of cruelty, which was dismissed by a family court. Meanwhile, Sheela too moved the court. The family court allowed her plea and granted the couple judicial separation and asked Nitin to shell out Rs 25,000 as monthly maintenance. Nitin challenged the maintenance order and a single bench of the HC set aside the maintenance order. Following this, Sheela challenged the orders and sought Rs 15,000 as maintenance.
Maintenance for working woman refused
The Times of India, Sep 08 2016
Abhinav Garg
HC refuses maintenance to working woman
A professionally qualified woman should be able to take care of herself, the Delhi high court has said, denying maintenance demanded by a chartered accountant from her estranged husband.
“The appellantwife, who is a qualified chartered acco untant and has been in the profession since 2003, need not be granted interim maintenance under Section 24 of the Hindu Marriage Act,“ a bench of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Pratibha Rani observed while rejecting her plea.
The wife had appealed against a trial court order that awarded her Rs 22,900 a month towards maintenance of her two children but declined to award an interim maintenance to her, pointing out that she was a chartered accountant with sufficient means to maintain herself.
According to the woman's petition, the duo had got married in 2005 in Delhi. The estranged husband, an electri cal engineer, runs his own business. He filed for divorce owing to “differences“.
The wife had sought an interim maintenance of Rs 3 lakh per month for herself and their two children, and around 1 Rs lakh towards litigation expenses. When the trial court refused she ap pealed against it arguing that her income is Rs 7,000 per month but HC refused to buy the claim and noted that “a well-qualified wife who is working as a CA since 2003, cannot be expected to earn only Rs 7,000 per month, which is below the minimum wages payable to an unskilled worker.“
The wife also mentioned her reasonable wants from her husband which includes house rent, household expenses, miscellaneous expenses as well tuition fees and transport charges.But the trial court dubbed her claim of having no sufficient means to support herself and children as “jugglery of accounts.“
Appearing for the husband advocate Anirudh Mudgal assured HC that he will ensure good education for his children and bear the additional burden in case the school fee or transport allowance is increased The court then dismissed the plea of the wife saying the terms set by the trial court are reasonable.
Wife with income not entitled to maintenance: HC
‘Wife with income not entitled to maintenance’, Nov 11, 2017: The Times of India
When a woman earns as much as her estranged husband and has an independent source of income, she is not entitled to maintenance, ruled the Bombay high court.
Justice Shalini Phansalkar Joshi dismissed the application filed by a Pune resident, who is a director in a company, seeking Rs 25,000 monthly maintenance from her husband. The man, an engineering graduate from VJTI and a Thane resident, is also the director of a company founded by him.
"Assuming there is some difference in the earning and income of the wife and husband, provisions of interim maintenance are not made for equalising their income, but to ensure either spouse does not suffer because of paucity of income in the course of proceedings," said the judge.
The judge pointed out that in a divorce case, the Special Marriage Act provides that only when it appears "a wife has no independent income sufficient for her support and necessary expenses of the proceedings, the court can order the husband to pay her expenses of the proceedings and also interim maintenance." In the present case, the court said that records showed the woman has an independent source of income. "Since both the woman and her husband are on an equal footing, the family court has rightly rejected the wife's claim for interim maintenance."
At the same time, the high court also rejected an application filed by the man challenging the family court's order asking him to pay Rs 25,000 monthly maintenance to his minor daughter who lives with the mother.
The couple had got married in 2011, but have been living separately since 2013. Subsequently, the woman filed a petition seeking divorce and permanent alimony. When the family court rejected her plea seeking Rs 25,000 monthly maintenance from her husband, she challenged the order in the high court.
She claimed she was living with her parents and did not even have her own house. The man produced records which showed that she was the director of a family-owned company and held its shares. She claimed she had the responsibility of looking after her child and, therefore, was not actually earning an income. The court said the woman practically owned 50% shares of the company and, even if she was not looking after its day-to-day affairs, she had a share in the earnings and profits of the company. "Her case that she has no source of income at present and her father is maintaining her cannot be accepted," the high court held.
Alimony for wives subjected to violence
Wives subjected to violence need not depose for maintenance
Swati Deshpande, Battered wives needn’t depose for maintenance, April 1, 2018: The Times of India
In a landmark ruling that comes as a boon to wives battling for maintenance from estranged husbands under the domestic violence act, the Bombay high court has held that an affidavit filed by the women would suffice as evidence.
A woman need not depose in court to make her case. The court, though, can permit the husband to cross-examine her based on the affidavit. The question before the high court was whether a woman who has filed an application under the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005 can be allowed to submit evidence in the form of an affidavit alone.
A magistrate in Pune had permitted such a submission, prompting the husband to move the HC last year.
‘Court can allow evidence on affidavit’
He and his lawyer Abhijit Sarawate wanted the woman to first step into the witness box and depose. They claimed that an affidavit cannot substitute oral evidence recorded in court in the presence of both sides in a DV case. The wife’s lawyer, Abhijeet Desai, though, argued that the magistrate was right in allowing her affidavit in evidence.
After interpreting salutary provisions of the DV Act, the high court answered in favour of the wife.
Justice Anuja Prabhudessai, who passed the judgment, held that the DV Act allows the court to devise its own procedures to ensure speedy disposal. “The court, in its discretion, can allow evidence on affidavit and permit cross-examination to test the veracity of the evidence,” she held, adding that “a narrow interpretation would defeat the purpose of the act”.
The DV Act provides effective and speedy protection to women who are victims of domestic violence, setting out a disposal deadline of 60 days.
The HC observed, “Though... there is no specific provision in the DV Act to give evidence on affidavit, Section 28(2)... gives flexibility to the court to depart from the procedure prescribed under Section 28(1) and to devise its own procedure in deciding application under Section 12...” This is an “enabling provision” which intends to achieve the object of the act.
Child’s maintenance
Child’s maintenance if former wife earns
Even if former wife earns, man must provide for child : Bombay HC The Times of India Shibu Thomas,TNN | Oct 27, 2014
Justice M S Sonak upheld a family court’s interim order, directing Pune resident Prakash Mehta to pay Rs 8,000 a month for the rent of a flat where his estranged wife Seema and their child live.
MUMBAI : A man cannot be relieved of his responsibility of contributing to the financial needs of his child merely because his estranged wife is economically sound, the Bombay high court has ruled.
Justice M S Sonak upheld a family court's interim order, directing Pune resident Prakash Mehta to pay Rs 8,000 a month for the rent of a flat where his estranged wife Seema and their child live. Mehta had claimed Seema, an IT engineer, earned over Rs 60,000 a month, while his monthly salary was Rs 35,000.
"The conclusion in all cases cannot be that if a wife can provide for their child, her spouse is altogether relieved of his obligation to contribute to the financial needs of the child," said the judge. The HC also rejected Mehta's contention that the family court could not have passed the order for providing a residence as the main application for maintenance under the Hindu Marriage Act was still not decided. The court said an application, seeking relief of residence under Domestic Violence Act, was maintainable.
"There is no question of awaiting the disposal of the main proceedings and only then, giving an order for providing a residence. If such a strained interpretation is permitted, the very object is likely to be frustrated," the judge said. The court pointed out that Seema bore all the expenses of maintenance, education and medical needs of their minor child, while Mehta did not shell out anything.
"There can be no doubt that the responsibility to provide maintenance and shelter to a minor child is equal for both the parents," the judge added.
Seema had approached the court, seeking maintenance for herself and her child from Mehta. She sought interim relief, claiming Mehta had allowed the leave and licence agreement of their matrimonial flat in Pune to lapse in order to harass her. She was then forced to find a new house and paid a rent of Rs 9,000 per month. Mehta claimed Seema and the child lived in her brother's flat and did not pay rent. The HC, however, disagreed and said Seema's brother was not under any legal obligation to provide her residence gratis.
Both parents not equally responsible for child support’
May 2, 2019: The Times of India
‘Both parents not equally responsible for child support’
New Delhi:
Delhi high court has said that “it would be incorrect to hold both the parents equally responsible for the expenses of the child”. Justice Sanjeev Sachdeva’s observation came on Tuesday as the court agreed with a trial court decision directing a husband to pay for the maintenance of his minor daughter till she attained the age of majority.
The high court also enhanced the maintenance amount to Rs 20,000 per month from Rs 10,000 a month fixed by the trial court. It also held that the wife was in a position to maintain herself and as such she was not entitled to any maintenance. However, the high court maintained that “the view taken by the trial court that both parents are responsible for meeting the day-to-day requirement, nourishment, medical and other expenses of the child, is erroneous.”
“A child for her upbringing does not only require money. A lot of time and effort goes in the upbringing of a child. It would be incorrect to hold that both the parents are equally responsible for the expenses of the child. A mother who has custody of a child not only spends money on the upbringing of the child, but also spends substantial time and effort in bringing up the child. The trial court has erred in equalising the effort of both parents in upbringing of the child,” the court said.
“One cannot put value to the time and effort put in by the mother in upbringing of the child. No doubt, the mother, if she is earning, should also contribute towards the expenses of the child, but the expenses cannot be divided equally between the two,” it added. The court was hearing a maintenance application of a couple who got married on June 23, 2002. A girl was born to them on March 7, 2004. The woman alleged that she was forced to leave her matrimonial house in April 2005 after being mentally and physically tortured by her husband’s family.
The marriage was dissolved in March 2007. IANS
Maintenance of 18+ son living with divorced wife
June 23, 2021: The Times of India
NEW DELHI: A father’s obligation doesn’t end on son turning 18 years as the entire burden of his education and other expenses cannot fall only on the mother, Delhi high court has said.
It granted Rs 15,000 interim maintenance to a divorced woman for her adult son till he completes graduation or starts earning, saying the court cannot shut its eyes to the rising cost of living. The court said it was unreasonable to expect that the mother alone would bear the entire burden for the son with the small amount of maintenance given by her estranged husband for the maintenance of their daughter.
The court was hearing a woman’s plea challenging a 2018 trial court order declining maintenance to her and granting it only to their two children, who are living with her.
“The woman has to take care of the entire expenditure of the son who has now attained majority but is not earning because he is still studying. The family court, therefore, failed to appreciate the fact that, since no contribution is being made by the respondent (man) towards the son, the salary earned by the woman would not be sufficient to maintain herself,” Justice Subramonium Prasad said.
The couple got married in November 1997 and had two children. They got divorced in November 2011 and the son and daughter are 20 and 18, respectively. The Family Court said the son was entitled to maintenance till he turned an adult, while the daughter would be entitled to maintenance till she gets employment or gets married, whichever is earlier.
The court noted that, “The two children are living with the mother. Since the purpose of granting interim maintenance is to ensure the wife and the children are not put to starvation, the courts while fixing interim maintenance are not expected to dwell into minute and excruciating details and facts which have to be proved by the parties.”
It said this court could not shut its eyes to the fact that the man, who got remarried and has a child from the second marriage, has to maintain that child also and the reduction of the amount for maintenance by the family court could not be found fault with.
Financial rights of women
As in 2020
RIJU MEHTA, Financial rights of women in case of divorce, February 10, 2020: The Times of India

From: RIJU MEHTA, Financial rights of women in case of divorce, February 10, 2020: The Times of India
If there’s trouble brewing in your marriage or you are headed for a divorce, here are the steps you should take to secure your finances
Divya Kapoor got married at 21, separated at 40, and divorced at 50. She walked out of the marriage with only ₹1,700 in hand, as all the assets and investments were in her husband’s name. Still, she did not ask for maintenance during divorce. “At that point, closure and peace of mind were paramount, not money,” she says. She lost nearly ₹40 lakh in unclaimed assets and savings.
The 2011 Census pegs the number of divorced people in India at 1.36 million, even as the number of divorcees has doubled in the past two decades, as per a recent report from United Nations. The number of women who are divorced and separated are far more than men because the latter have married again. “For non-working women, the situation after divorce is difficult. With no future income and a life span that is longer than men, the one-time settlement is often not enough,” says Priya Sunder, Director, PeakAlpha Investments. This is only one aspect they are ignorant about. What are the financial steps they need to take as soon as they realise there is trouble in the marriage? Which assets belong to them and which don’t? How should they divide the assets and property? Find out:
WHEN MARITAL TROUBLE BEGINS…
If you are headed for a separation, don’t rush to announce it to the husband. This one mistake can cost you financially since it may become difficult to access the documents that can ensure a fair split. It is advisable, of course, not to leave everything till the last moment. “It’s impossible to plug into the family’s finances all at once. The woman should be clued into the income, cash flow, assets and investments through the entire course of her marriage, so that it is easier to deal with finances if she were to separate,” says Sunder.
Hire a financial planner and lawyer: If you have no idea how to go about the process of divorce, hire a good financial planner and a lawyer because the financial benefits that will accrue to you will be worth every rupee spent on their fees. While the lawyer will apprise you of the documents you need to strengthen your case, the planner will help you with the calculations to arrive at the optimum figure, which will help you seek sufficient alimony and child support.
Collect information & documents: With the help of the lawyer and planner, make a list of all the documents you will need to submit in the court, such as address proof, marriage certificate, salary statements, marriage photos, bank statements and tax returns, among others. Access these and make photocopies.
List of assets & liabilities: “Next, make a list of all your assets and liabilities and collect the receipts or ownership documents for all these. Then write down the market value of all assets for the purpose of division,” says Rohan Mahajan, Founder & CEO, Lawrato. “Once the market value of assets has been assessed, evaluate the individual shares of husband and wife,” he adds. The distribution will take place as per the individual equity or as decided between the parties, if it is a mutual consent divorce.
Get hold of streedhan: This is another important step since you will probably have a lot of assets gifted to you before marriage, during marriage ceremonies, and on the birth of kids. “A woman retains the ownership to streedhan even after separation, including all movable and immovable property, gifts, and money, among others,” says Raj Lakhotia, Founder, Dilsewill. The best option for you is to stash away your things either with your parents or in a safe place away from your current residence.
Change nominee details: If you have made investments or taken insurance in which you have listed the husband as the nominee, change the details. These could include the Provident Fund, PPF, bank account, demat account, mutual funds and life insurance.
Close joint accounts: If you have a joint savings account, the spouse can withdraw money since the balance is shared equally, irrespective of who deposits it. Similarly, foreclose fixed deposits and other joint investments, which are shared equally between the partners.
Seek interim maintenance: If you don’t have a source of income and your relationship with the husband has soured to the extent that he refuses to give you any money, you can approach the court to seek maintenance for the duration before the final divorce settlement.
WHILE SEPARATING…
The last leg of separation is excruciating, especially if the divorce is contested. The mutual consent divorce is favoured because it is less expensive, less time-consuming, and not as exhausting emotionally. It is also the stage where most financial mistakes take place.
Division of assets: Streedhan belongs to the woman, “but if the husband has contributed to its purchase, he can file a suit and claim ownership to the extent of his contribution,” says Rajesh Mahindru, Advocate, Delhi High Court. Unless the divorce is contested, the spouses should decide the distribution of assets themselves. If the assets have been bought from contributions made by both, share it on the basis of individual equity.
Nominee in investments, insurance: In case of investments and insurance where the woman is a nominee, says Mahindru: “A nominee under law has no right over the investment or insurance. The role of nominee comes only after the death of the person. So during the husband’s lifetime, the wife has no right over it. After his death, she is eligible to make a claim over the investment as she is a Class I legal heir.”
Splitting homes & loans: Most conflicts expectedly and invariably take place over immovable property. “The wife has full right over her property and is the sole owner whether it is gifted, inherited or earned by her,” says Lakhotia. However, she has no right over the husband’s ancestral or self-acquired property unless she inherits it from the deceased husband. “The wife can only make a claim in case a property is jointly owned by the husband and wife at the time of divorce. If the property is bought by the husband while the two were together and he holds the title, the wife can make a claim if she can prove her equity in the property,” says Mahajan.
If a property is purchased and paid for by one person and the title is held by the other, the person in whose name the property is will be considered its legal owner. If the house has been financed jointly through a loan, it can be sold and the money split as per the share of each spouse. If one spouse wants to retain the house, he or she can buy the share of the other and repay the loan. If, however, the husband refuses to pay the EMI, the entire responsibility of repaying the loan can shift to the wife.
Alimony or maintenance: “You have only one go at alimony, so make the most of it by arriving at the figure carefully,” says Sunder. This should ideally be done in consultation with a planner taking into account inflation and all future expenses. “The woman should get a sum in which she is able to maintain her existing lifestyle, take into account her longer life span and earning capacity,” says Sunder. It is also better to opt for a lumpsum settlement instead of a monthly payout as it is tax-free and not subject to erosion of value due to inflation. The woman should also opt for as many liquid assets as possible, which will help her start her life afresh after divorce.
The court decides on the maintenance by considering the husband’s income, the needs of wife, the liabilities, and wife’s earning capacity, among others. As per a Supreme Court ruling, 25% of the husband’s income is considered a just amount to be given as maintenance. However, if she is earning while the husband is not, she may be denied maintenance. If she is earning but unable to maintain a comfortable lifestyle, the husband will have to shell out money.
A Muslim wife is entitled to the dower or mehr agreed to at the time of marriage, and after divorce, she is eligible to maintenance till the iddat period. After this period, she can seek maintenance from her parents or District Waqf Board under Section 4 of the Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act. The Indian Divorce Act, 1869 governs the maintenance rights of Christian women, where the husband is liable to pay maintenance till a woman’s lifetime. Under the Parsi Marriage and Divorce Act, 1936, the court can award a maximum of one-fifth of the husband’s net income to a Parsi woman for her lifetime.
Other alimony issues
Daughter, single and adult: maintenance for
‘Single daughter can claim maintenance’, April 8, 2018: The Times of India
An unmarried daughter is entitled to claim maintenance from her father even after attaining the age of 18 if her parents are divorced or estranged, the Bombay HC has ruled.
Also, a woman can file an application on behalf of her major daughter to seek maintenance, Justice Bharti Dangre ruled on Friday.
The court was hearing a petition filed by a city-based woman challenging the family court’s order dismissing her application seeking maintenance from her estranged husband for the couple’s 19-yearold daughter. The couple, which got married in 1988, got separated in 1997. Their three children — two boys and one girl — lived with the mother.
Till the time the kids were minors, their father paid a monthly maintenance for each child to their mother. However, after the daughter crossed 18 years of age, the father refused to pay maintenance for her.
Her mother, in her petition, claimed that though her daughter had attained majority, she was still financially dependent on her.
Daughter’s wedding
Abhinav Garg
The Times of India, Nov 30, 2014
HC ORDER - Man to pay Rs 37L for daughter's wedding
Holding the father liable for bearing “reasonable” wedding expenses of his daughter, the Delhi high court has ordered a man to pay Rs 37 lakh to his estranged wife for their daughter's marriage next month.
“If the man can own a bungalow in Sainik Farms, have a major stake in a firm which owns a resort in Manali and own various properties, he can spend a good amount on his daughter's wedding,“ Justice G P Mittal observed in an interim order granting relief to the two women.
The man's wife and her 25-yearold daughter had moved HC filing a suit for maintenance. Through advocate Prabhjit Jauhar, the wife told HC that soon after their wedding in 1982, she was mistreated and had to leave the matrimonial home. Later, the couple's daughter and son also followed suit because they were subjected to cruelty by their father. Jauhar submitted that if the father can give interest-free unsecured loans to the tune of Rs 2.5 crore, the claim of marriage expenses of Rs 66 lakh should not be seen as excessive.
However, Justice Mittal was guided by the term “reasonable expenses“ mentioned in the Dowry Prohibition Act 1961 to limit the expenses to Rs 37 lakh.
The girl's father, through senior lawyer Y P Narula, had offered to contribute Rs 5 lakh, apart from agreeing to take care of the catering.
The court also brushed aside the father's claim that jewellery or gifts given at the time of marriage may amount to dowry, saying that as per the Act itself, presents given by the bride's parents at the time of her marriage without any demand from the other side is permissible provided they are entered in a list maintained in accordance with the Act and not excessive having regard to the financial status of the parties.
Difficulties in getting alimony
SC may have benchmarked alimony at 25% but women still struggle to get their due from grudging ex-husbands and a slow legal system
Schoolteacher Sangeeta Kumar (name changed) decided to divorce her husband of 12 years, after she found that he was cheating on her. Hurt, upset and unable to think straight, she left Delhi with their fiveyear-old son, to live with her parents in Bihar. Sangeeta had no inkling of the protracted and demeaning legal battle that she was in for.
“I realised later that I had given up ownership to our flat in that one impulsive decision. Now I was in a new city , forced to start life from scratch, earn a living, find a school for my child and manage my expenses. My husband agreed to the maintenance but the cheques would sometimes land up months late, or not at all. But expenses don't stop. I would end up having un pleasant conversations to make him realise that his re sponsibility to the child was not just for vacations but forever, Sangeeta says tearfully . It has been six years since the divorce but the monthly wait for what she calls “doles continues.
A Supreme Court order this week set a benchmark, saying 25% of a husband's net salary might constitute a “just and proper“ amount. While the decision has been welcomed, many women and lawyers argue that the struggle to get estranged husbands to cough up alimony is an uphill task.
“The battle for women does not end with securing an order of maintenance.The reality is that it begins only then, noted Pune family court judge Swati Chauhan last month. The second innings in court is time consuming, complicated and cumbersome. “When husbands default on the payment, wilfully or otherwise, the wives, left with a `paper order', have to once again go back to court for its execution. A woman ought not to have to spend her prime crowding court corridors waiting to receive the money , said Chauhan.
A 2013 study , based on 405 divorced and separated women across the country , says that getting justice from courts has always been a gamble for women. The survey is part of a book `Separated and Divorced Women in India: Economic Rights and Entitlements in India' by lawyer Kirti Singh. In nearly half the cases, women did not seek maintenance either because they lacked resources (41.5% women had no income after separation, while 27% earned less than Rs 2,000 per month) or were unaware. The majority (almost 60%) of women were living in marital homes acquired by inlaws, and a large number (71%) were forced to live with their families after the separation. Although 58.5% surveyed were able to work outside their home, their earnings were too low for them to survive independently .
In 89 cases where maintenance was allowed, only 12 women re ported receiving a satisfactory amount. Of the 60 women who answered the question on main tenance, those with no income at all received merely 13% of the salary on an average for financial support.
Not only were wom en given shor t shrift, they were also forced to wait for a long time be fore they received the paltry amount.
No one knows this better than a 50-year-old Pune housewife who recently won her battle for maintenance after 27 years. The amount: a paltry Rs 500. Her husband, a government servant, had filed for divorce. It was dismissed but he deserted her and got “married to another woman. She has a maintenance order but her husband is irregular with payments with arrears mounting up to Rs 7 or 8 lakh. He has health issues and is unable to pay her, he claims.
Cases can drag on for 10 years at a time, says Delhi-based lawyer Vikas Tiwari. “More than a share of the salary, a reform sorely required in the law for maintenance is revision of the amount keeping in mind inflation and the salary growth of the husband. The aggrieved party should not be aggrieved further by the system, he says.Mridula Kadam, divorce lawyer in Mumbai says, “In large metros where the cost of living is immense, there cannot be a blanket cap and the alimony has to be reviewed case to case. Lawyers say that while the SC order is with reference to permanent alimony , it is likely to be used as a yardstick to grant interim maintenance in pending divorce litigations. “A salary alone cannot form the basis of a permanent alimony. A husband may also have other movable and immovable assets which need to taken into account, said Kadam. Supreme Court lawyer Geeta Luthra agrees, and adds that so far, the courts have been granting 15th to 12 of the husband's salary, and in some cases even 50%-60%.
The test is when a husband doesn't earn or has a business income, complicated to assess. Lawyers say that very often, husbands and wives do not disclose their true income or job status. Businessmen show only a fraction of what they earn, disguise the rest as company expenses to avoid paying higher maintenance charges, while women do not disclose that they have a job to ensure they get a larger amount.
The HC order is expected to come as a respite for several similarly situated unmarried girls
In-laws not liable to pay maintenance
PTI, In-laws not liable to pay maintenance, says court, Oct 11 2016
A wife is entitled to seek maintenance only from her husband and is not liable to be maintained by her inlaws, a special court has said.
Special judge Anil Kumar made the observation in a domestic violence case while barring a married woman from entering her matrimonial house, noting that the property belonged to her mother-in-law who had disowned her son.
The court allowed the appeal filed by the woman's mother-in-law against a magisterial court's order which had allowed the woman to enter her matrimonial house.
“In my opinion a wife cannot be allowed to claim maintenance, including accommodation, from her in-laws exonerating her husband. A wife is entitled to seek maintenance from her husband and she is not liable to be maintained by in-laws.
“In view of the above ob servations it is held that respondent complainant (wife) has prima facie no right to reenter the house of her motherin-law,“ the court said. The woman had filed a complaint before the trial court that after her marriage in January 2011, she started residing with her husband and other in-laws in her matrimonial house in Najafgarh area of Southwest Delhi.
However, in March 2015, she and her husband were barred by her in-laws from entering the matrimonial house after a quarrel.
Maintenance a right even if wife waives it: HC
Rebecca Samervel, December 28, 2018: The Times of India
In a significant order, the Bombay high court held that a woman’s right to maintenance cannot be done away with even if she had specifically waived it in an earlier agreement. In a recent judgment, Justice MS Sonak said, “There are several rulings taking the view that an agreement, in which the wife gives up or relinquishes her right to claim maintenance at any time in the future, is opposed to public policy and, therefore, such an agreement, even if voluntarily entered, is not enforceable.” The HC in its judgment cited observations of another such ruling, which said the statutory right of a wife for maintenance cannot be bartered, done away with or negated by the husband by setting up an agreement to the contrary.
In the judgment, the HC dimissed the writ petition submitted by man who said his former wife’s application seeking maintenance be dismissed since she had waived her right to it in the consent terms for divorce. The woman had moved the maintenance plea before a magistrate court in 2010. The man sought a dimissal of the plea and cited the consent terms. On October 13, 2011, the court rejected the man’s application. He then challenged it before sessions court which too rejected his plea. In 2016, the man submitted writ petition before the HC.
Maintenance can be sought under different laws
Vasantha Kumar, Dec 12, 2022: The Times of India
BENGALURU: There is no bar on an aggrieved woman seeking maintenance under the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act as well as under Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code or under the Hindu Marriage Act or even under the Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956, the Karnataka HC has observed in a recent judgement.
The only rider would be that the amount to be paid to the wife will be inclusive of the maintenance awarded under each of the four jurisdictions and not exclusive, justice M Nagaprasanna noted in his order, while upholding the Rs 30,000 per month interim maintenance granted to a woman from Mangaluru.
In the Rajneesh vs Neha (2021) case, the Supreme Court has observed that in the light of overlapping of jurisdictions, the grant of maintenance under section 20(1)(d) of DV Act would be in addition to the maintenance granted under section 125 of CrPC, and also held that there is no bar on seeking maintenance under the DV Act and section 125 of CrPC or the Hindu Marriage Act, or Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956," the judge noted.
Dismissing the petition filed by the man, the court said the SC has held that if the husband is an able-bodied man, it is his duty to maintain his wife. The petitioner from Belthangady taluk in DK district got married on December 31, 2018 and the couple has no children.
On December 11, 2020, the wife alleged harassment by the husband and his family and registered a case against them. on February 22, 2021, she filed a petition under the DV Act before a court in Moodabidri, seeking interim maintenance. She was awarded Rs 20,000 per month as maintenance. The husband challenged the proceedings under the DV Act and the high court granted a stay on the same.
Maintenance is not a blanket liability
June 30, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi: Maintenance payable to wife is not a blanket liability for all times to come and can be increased or decreased on account of change in circumstances of the husband or the wife, Delhi High Court has clarified.
Justice Chandra Dhari Singh stated that the intent behind granting interim or permanent alimony is not to punish the other spouse but to ensure that the dependent spouse is not reduced to destitution or vagrancy on account of the failure of the marriage.
The court’s observations came on a plea by a woman seeking enhancement of the maintenance to be paid to her by her husband.
The court pointed out that under Section 127 (1) of Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC), a provision is made to increase or reduce the allowance if there is a “change in the circumstances of the parties at the time of the application for alteration of the original order of maintenance” and it “must be shown that there has been a change in the circumstances of husband or of the wife” while seeking enhanced maintenance.
“The change of circumstances referred to in sub-section (1) of Section 127 CrPC is a comprehensive phrase which also includes the change of circumstances of the husband. The amount of maintenance once fixed under Section 125(1) CrPC is not something which can be taken to be a blanket liability for all times to come. It is subject to variation on both sides. It can be increased or decreased as per the altered circumstances,” the court added.
In her plea, the wife sought a monthly maintenance of Rs 35,000 and said that the amount of Rs 3,000, which was awarded by the trial court, was inadequate for her sustenance considering that the husband was drawing a salary of Rs 82,000 per month. She alleged that he hid his ac- tual earnings from the court but the husband maintained that he earns a meager amount of Rs 15,000 per month by working as a cab driver and living in a rented property and also had to take care of his old and ailing parents.
The court dismissed the wife’s plea and noted that to fix appropriate quantum of maintenance, the financial capacity of the husband, his actual income with reasonable expenses for his maintenance as well as dependant family members and liabilities would be required to be taken into consideration. It said that neither did the petitioner place on record any documents to assess the respondent’s exact income and establish that he was earning such a handsome amount of money nor was there any change in circumstances.
Marriage should not be terminated merely because handsome alimony is promised
Apex court hits gender parity note in divorce case
Dhananjay Mahapatra TNN
The Times of India 2013/07/02
New Delhi: Irretrievable breakdown of marriage, coupled with promise of large amount of money as permanent alimony, has been cited by rich and powerful men to seek divorce from their wives when all was not well in the marital relationship.
Striking a gender equality note, the Supreme Court on Monday turned the tables and asked whether it would have granted divorce to a woman from her husband, who on developing some mental disorder had become completely dependent on her, if she promised a huge sum as permanent alimony.
The case related to Darshan Gupta and Radhika Gupta, who married in 1997 when they were barely out of their teens. Radhika’s first pregnancy was terminated due to medical reasons. The second pregnancy was again a very complicated one and the child had to be delivered through Caesarian section. She remained unconscious for a long time and developed serious mental disorder. The child died eight days after birth.
Though she was treated in reputed hospitals, she allegedly remained mentally ill. The husband claimed separation from her since 2002, breakdown of marriage and offered a large sum of money as permanent alimony to seek termination of marriage.
A bench of Justices P Sathasivam and J S Khehar rejected the husband’s plea and wondered whether a similar request by a woman would have been entertained by the apex court for grant of divorce from a husband who developed some mental disorder. Justice Khehar, authoring the judgment, concluded, “We have no doubt... that on a reversal of roles, the husband... would have never accepted as just the dissolution of his matrimonial ties...”
Settlement not easy to challenge: HC
The Times of India Jan 02 2016
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
The Delhi high court forced a woman to withdraw her plea challenging a divorce decree as she had already received Rs 5 crore as settlement.
Justice Manmohan, in a re cent order, took a grim view of the fact that despite getting the settlement amount, the woman again turned up in court claiming that the decree had been passed in a fraudulent manner.She challenged the divorce decree granted by a matrimonial court on the ground that the husband initially promised to pay her more than double the amount. The woman also sought to restrain him from marrying a second time in her plea. HC agreed to hear the mat ter but asked the woman to first cough up the Rs 5 crore she had been paid and deposit it with court registry . The court opined that if the woman claims the decree was obtained by fraud, both parties must start on a fresh note. At the next hearing, however, the wife promptly withdrew her case, admitting it was not “maintenable.“
The high court's order came on a contempt petition filed by the estranged husband who complained that even after a court endorsed settlement and payment of a huge alimony , his exwife wants to revive the dispute a year later on the eve of his second marriage.
Appearing for the husband, advocate Prabhjit Jauhar informed the court his client and former wife entered into a settlement approved by a matrimonial court where the wife surrendered all claims for a lump sum of Rs 5 crores. Accusing her of contempt, the husband urged HC to begin proceedings since the woman had breached the terms of the settlement terms and her own undertaking before court.
Justice Manmohan upheld the principle that no person after entering into a settlement before a court can back-track and challenge it on the ground of fraud.
Tax on alimony
No tax on lump-sum alimony: Tribunal
Experts Caution Ruling Comes With Riders, Say Single Payment No Way Out
Lubna Kably TNN 2013/06/30
Mumbai: Marriages are made in heaven, but divorces happen on earth. Thus, tax implications are inevitable.
However, in a recent decision, the Delhi Income-tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) has held that a lump sum payment received from a former husband, against relinquishment of monthly maintenance, is a capital receipt which is not taxable.
A Delhi-based resident received a lump sum amount of $99,000 from her ex-husband, who was based in the United States, which she did not offer for tax. Based on today’s exchange rate this sum is approximately Rs 60 lakh.
Under Indian tax laws, any sum of money received by an individual without any consideration (without anything in return), in excess of Rs 50,000 in a year, is taxable. However, if the same is received from a relative, such as a spouse, or on certain occasions such as marriage, it is exempt.
The tax officer, in this case, had held that as the divorce had taken place several years ago, the Delhi-based resident was not a ‘relative’ and hence such payment was not exempt but taxable as “income from other sources” in her hands. This approach adopted by the tax officer was rejected at the first level of appeal — Commissioner of Income-tax (Appeals).
The Commissioner (Appeals) held that the amount was paid by way of alimony only because they were husband and wife. Thus the payment received was from a relative (which includes spouse).
Further it cannot be said that the lump sum amount was received without any consideration — it was received against relinquishment by the wife of her right to receive monthly alimony payments (both past arrears and future payments). Such monthly payments were provided for in the divorce agreement.
Hearing an appeal filed by the tax officer, the Delhi ITAT upheld the order of the CIT (Appeals). It observed: “In this case, the taxpayer was to receive monthly alimony which was to be taxable in each year. As such monthly payments were not received they were not offered for tax as income. The lump sum received by the assessee was a consideration for relinquishing all past and future claims.” It was a non-taxable capital receipt not liable to tax, concluded the ITAT.
“Tax on alimony payment cannot be avoided by merely taking a lump sum consideration. Various facts such as the period of time the monthly alimony was not received, action taken for receipt of such alimony, and the fact pattern of the final settlement by way of lump sum payment will determine whether it will be treated as non-taxable,” cautions a civil advocate, attached to the Mumbai high court.
PART II
Cooling-off period
SC 2017, Delhi HC, 2019: Can be waived in mutual consent cases
May 13, 2019: The Times of India
HC waives cooling-off period, allows woman to remarry
New Delhi:
Delhi high court has allowed a woman to end her marriage with her estranged husband and plan a remarriage soon by waiving off the cooling-off period for divorce.
Justice Prateek Jalan took into account that there was no likelihood of reconciliation between the estranged couple and relied on a verdict of the Supreme Court that divorce can be granted without the mandatory 18-month period of separation between the parties in exceptional cases.
The apex court had, in 2017, said that the six-month “coolingoff ” period can be waived off by courts in cases of divorce through mutual consent.
The court, in the process, allowed a petition by the woman for waiving the statutory period of six months under Section 13B (2) of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 and set aside an order of a family court that had rejected the woman’s application. Granting relief to the couple, the court said a holistic reading of the apex court’s judgment leads to the conclusion that a purposeless marriage, which has no chance of reunion, ought not to be prolonged.
As per the plea in court, the couple got married in July 2017 and started living separately from October 25, 2017. During the proceedings under Domestic Violence Act, 2005, the parties settled their disputes through mediation. A settlement took place that the marriage be dissolved by mutual consent and it was agreed that the man will pay Rs 3.5 lakh to the woman. They approached the family court to dissolve the marriage and after completion of first motion, the parties filed an application for waiver of the statutory period of six months since the woman intended to remarry another person on May 2 but a day before, the family court had rejected the plea for wavier of the statutory period.
Cruelty: applicability
Relatives, distant, can also be booked: HC
Vaibhav Ganjapure, Jan 20, 2023: The Times of India
NAGPUR: Bringing relatives not staying under one roof under the purview of Section 498-A regarding cruelty to married women, the Nagpur bench of Bombay high court has held that even such kin could be booked and their physical presence is not necessary in the household.
“Such being the nature of mental cruelty, it is not necessary that it must take place in the physical presence of persons. It (mental cruelty) can be handed out even from a distant place,” a division bench comprising justices Sunil Shukre and Manohar Chandwani ruled.
Rejecting plea by relatives of a complainant-woman’s husband hailing from Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi, the bench also imposed Rs10,000 fine on them for abusing the process of law. They were told to deposit the amount within three weeks with the High Court Bar Association (HCBA) here for developing its library. In case of failure, the HC registry was asked to recover the amount from them.
“For meting out mental cruelty to the complainant-woman, in a prima facie way, petitioners seem to have employed modern means of communication, i.e. telephone. On many occasions, they have also remained present in her company. Therefore, this is not a case where the petitioners, by virtue of their separate residence, could be presumed to not have treated her in a cruel manner,” the bench said.
The petitioners had moved HC for quashing FIR against them filed by the woman under sections 498-A, 323, 524 read with 34 of IPC and sections 3 and 4 of Dowry Prohibition Act. The police have filed a charge sheet before the judicial magistrate first class (JMFC) court in the city based on the FIR.
Contending that there were no specific allegations against them, the petitioners pointed out that there was no proof that they had resided together with the woman and her husband.
The justices said though the petitioners appear to be residing away from the woman’s matrimonial home, the allegations in FIR and witnesses’ statements do indicate that there used to be several occasions when all or some of them, on one or other occasion, had resided with her. “They also had opportunities to talk personally or on telephone with the complainant. During their such encounters, they subjected her to humiliation, harassment and cruelty,” the bench noted.
Pointing out that cruelty as envisaged under Section 498-A is not only physical, the judges said it also takes within its fold several other forms, including mental.
“Mental cruelty is an abstract concept, and it is a matter of experience for a person who is subjected to it. Many times, certain taunts are made but it all depends upon the way the person takes those remarks or responds to them. Sometimes, the taunts might be seen to be innocuous by one person, while they may not be necessarily so perceived by another. There are also certain derogatory remarks, which have been held by the Supreme Court to be presumptively constituting cruelty, as for example consistently suspecting the wife’s fidelity,” they said.
SC: Woman can file plaint for cruelty after divorce
A woman can lodge a complaint under the domestic violence law against the excesses committed by her ex-husband even after the dissolution of marriage, the Supreme Court has said. The top court refused to interfere with the order of the Rajasthan high court which held that the absence of subsisting domestic relationship in no manner prevents a court from granting relief to the aggrieved woman.
Cruelty: definition
Abortion, forcible
Ajay Sura, Sep 29, 2022: The Times of India
CHANDIGARH: The Punjab and Haryana high court held that motherhood is innate, natural, and fulfilling to every woman and a husband denying his wife this through forcible abortion would amount to mental cruelty providing her with a ground to annul the marriage. The high court passed these orders while allowing an appeal filed by a woman seeking divorce from her husband because he forced her to terminate her pregnancy on the ground that he had no means to bring up the child.
"The list of acrimonious allegations by the appellant against the respondent and his family are endless. Be that as it may, motherhood is innate, natural, and fulfilling to every woman; and the fact that the appellant was denied the same and was forced to terminate her pregnancy against her will, at the insistence of the respondent (husband), and thereafter could not conceive again due to gynaecological complications in our view, constitutes cruelty," observed the division bench comprising Justice Ritu Bahri and Justice Nidhi Gupta while allowing a plea for divorce filed by the woman. She was challenging the order dated September 28, 2018 of the Hisar family court dismissing her plea seeking divorce.
Abusive in-laws
Apr 26 2015
Abusing in-laws a ground for divorce, says SC
Amit Anand Choudhary
Abusing in-laws and not allowing them to reside in the matrimonial home by a woman amounts to cruelty to her spouse, ground enough for grant of divorce, the Supreme Court has ruled while allowing an NRI's plea for legal separation from his wife. A bench of Justices Vikaramajit Sen and A M Sapre said such incidents could not be termed as “wear and tear“ of family life as held by Madras High Court which had said that a couple must be prepared to face such situations in matrimonial relationship.
The NRI had filed a divorce petition alleging that his wife was abusive to his family members and did not allow his parents and siblings to stay in his house when they visited the US.
Referring to an incident, the husband told the court that his wife had once locked him and his sister out of the house and abused them saying they belonged to a `prostitute family'. She refused to allow her sister-in-law to enter the house and even lodged a police complaint against her husband.
Taking into accounts all the evidence produced by the husband including abusive voicemails and emails he received from wife, while she was in India, the bench said it was a clear case of mental cruelty and husband was entitled for divorce.
“If a spouse abuses the other as being born from a prostitute, this cannot be termed as `wear and tear' of family life. Summoning police on false or flimsy grounds cannot also be similarly viewed. Making it impossible for any close relatives to visit or reside in the matrimonial home would also indubitably result in cruelty to the spouse,“ the bench said.
Adultery charge by spouse Amounts To Cruelty
Grants Man Divorce As It Amounts To Cruelty Adultery charge by spouse painful: HC Nov 25 2016 : PTI
Allegation of adultery levelled by a spouse is most “painful“ for a person, the Delhi high court observed while granting divorce to a man who was accused by his wife of having illicit relationship with another woman.
A bench of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Yogesh Khanna said that allegation of adultery was a “serious charge“ and would constitute cruelty, if not proved.
The court held it was established that the woman had levelled false allegation of adultery and harassment for dowry against her husband.
“Nothing can be more painful to a spouse other than the allegations of adultery made by the opposite spouse. It is settled law that a charge of adultery is a serious charge and if not proved would constitute cruelty ,“ the bench said.
The court's judgment came on a petition filed by the man who had moved the high court against the trial court's verdict dismissing his plea seeking divorce.
In its verdict, the high court also noted that no one has appeared before it on behalf of he woman.
It granted divorce to the man on the grounds of cruelty and desertion, observing that the couple have not lived together since 1995 and their marriage has “irrevocably broken“.
The marriage between them was solemnised in February 1995. In 1996, the man had filed a petition before a trial court seeking divorce on the ground of cruelty , but he withdrew it in 2001after his wife gave the assurance that she would live amicably with him.
He told HC that his wife had returned to her parental house in 1995 and despite giving assurance, she never returned to live with him after which he filed a fresh divorce petition before the trial court in 2009.
The woman had contested the plea before the trial court and in her written statement, she had alleged that her husband was having an illicit relationship with another woman.
She had also claimed that her husband was harassing her for dowry after which she had lodged an FIR against him.However, the man was acquitted by a court in the dowry harassment case.
The trial court had dismissed the divorce plea filed by the man on the ground that he had failed to prove allegations levelled by him against her wife.
The high court noted that “withdrawal from the consortium without a cause would also be an act of cruelty“.
Allegation of infidelity is cruelty: HC
The Delhi high court has granted divorce to a man holding that his estranged wife's false allegation of illicit relation between him and his widowed sister-in-law amounted to cruelty.
Holding that the allegations of illicit relations were not true, Justice J R Midha granted divorce to the man while setting aside a trial court's order of judicial separation of the couple who were married in 1978 and were residing in London.
A decree of judicial separation does not dissolve a marriage and gives the couple time to introspect about their relationship and decide if they want to get back together, unlike a divorce which marks an end to marriage.
Both the man and woman had challenged the trial court decision by separate appeals.
The man wanted divorce contending that his wife was extremely suspicious, often accused him of flirting around, abused him, threw tantrums and was callous and irresponsible towards his mother.
He had also said that since filing of the divorce plea in 2002, they have been living separately and there is no possibility of retrieval of their marriage.
The woman had challenged the trial court decision claiming she was not cruel to her husband and instead he was cheating on her with his sister-in-law whenever he came to India.
Rejecting the woman's claims, the high court said it "agrees with the trial court that the respondent (wife) has treated the petitioner (husband) with cruelty and he has neither condoned the acts of cruelty nor cohabited with her."
"The petitioner has not taken advantage of any wrong as alleged by the respondent. This court is of the view that the petitioner is entitled to a decree of divorce on the ground of cruelty," it said, adding, "the marriage between the parties is dissolved by a decree of divorce on the ground of cruelty".
Backing off divorce consent is cruelty
Withdrawal of consent by a spouse after mutually agreeing to divorce constitutes mental cruelty , the Delhi high court held in an important ruling.
Such withdrawal of consent without any sufficient or just cause adds to misery of the other partner, a bench of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Yogesh Khanna observed last week, granting divorce to a woman on grounds of mental cruelty.
The bench recognised “unilateral withdrawal of consent by the husband, despite the fact that the wife was always willing to abide by the terms and conditions of the settlement deed entered in the joint statement“ as one of the grounds adding to misery of the wife and a form of cruelty meted out to her.
The court also took into account an almost confessionary letter written by the husband to Delhi Police's Crime Againt Women cell (CAW) apologising for beating his wife.
The husband had appealed against the lower court order challenging the divorce.
“Considering the conduct of the parties, there seems to be no possibility of their joining together so to insist to retain this matrimonial bond in the circumstances stated above would rather be putting the wife under intense mental cruelty ,“ HC noted.
Bad honeymoon, cruelty to in-laws
PTI, `Bad honeymoon, cruelty to in-laws ground for divorce' Oct 10 2016
A spoilt honeymoon and subjecting the husband and his family to “worst kind of mental cruelty“ by levelling false accusations, have been held as grounds for divorce in a case heard by the Delhi high court.
The HC has dubbed the case as an “exception“ in which “the marriage could not take off right from inception“ between the couple who were in the age group of 30 plus at the time of marriage and were “quite mature“.
While allowing dissolution of their 12-year-old wedlock, it noted that the husband and wife returned with “bitter memories and a spoiled honeymoon“. “The respondent husband was able to establish that during their honeymoon not only consummation of marriage was resisted by her, even thereafter causing embarrassment and humiliation accusations have been made against him and his entire family ,“ the bench noted in its judgement..
The remarks were made in the judgement by a bench of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Pratibha Rani, which dismis sed the plea of a woman who had challenged the verdict of a trial court allowing the man's petition seeking dissolution of their marriage on grounds of cruelty .
The bench said the conduct of the woman was such that it was not possible for the man to bear such kind of cruelty .
Career of husband targeted
Ajay Sura, April 10, 2022: The Times of India
Chandigarh: The Punjab and Haryana high court has ruled that if a wife is bent upon destroying the career and reputation of her estranged husband by making complaints against him to his seniors, it would amount to mental cruelty and he would be entitled to a divorce. A division bench, comprising Justice Ritu Bahri and Justice Ashok Kumar Verma of the HC, has passed these orders while a llowing the plea filed by an Indian Air Force (IAF) personnel to divorce his wife, who was living separately since 2002. Referring to various SC judgments on such issues, the HC also observed that in o rder to make out a case of mental cruelty, “no uniform standard can be laid down and each case will have to be decided, on its own facts and circumstances”. “The conduct of the wife in filing a complaint making unfounded, indecent and defamatory allegations against her husband and parents-inlaw indicates that she made all attempts to ensure that appellant and his paren ts are put in jail and the appellant is removed from his job. We have no manner of doubt that this conduct of wife has caused mental cruelty to husband,” observed HC while accepting husband’s plea for divorce. In this case, the couple was married in 1998. The husband was an IAF officer and it was a love-cum-arranged marriage. One son was born in 1999 out of wedlock and the couple lived together till 2002. According to the husband, she deserted the appellant in April 2002 and since then she had not returned to the matrimonial home.
Comparing wife with other women is cruelty: HC
August 17, 2022: The Times of India
Kochi: A man comparing his wife to other women and repeatedly taunting her that she doesn’t meet his expectations amounts to cruelty and is a ground for divorce, Kerala HC has said.
Adivision bench of Justices Anil K Narendran and C S Sudha said this on August 4 while considering an appeal filed by a husband challenging a family court’s ruling granting divorce on his wife’s plea on the ground of cruelty. “Constant and repeated taunts of the respondent/ husband that the petitioner is not a wife of his expectations; comparisons with other women, etc. would certainly be mental cruelty,” it said. TNN
Can’t expect wife to put up with comparisons: HC
The Kerala HC said, “Comparisons (of one’s wife) with other women, etc. would certainly be mental cruelty, which a wife can’t be expected to put up with.” The wife had alleged that her husband used to constantly remind her that she did not meet his expectations in terms of looks, that she was not cute enough for him, and that she was a letdown when compar ed to other women, including some prospective brides of his brother.
While public interest demands that the “married” status should be maintained a s far as possible, when a marriage has bee n wrecked beyond the hope of salvage, p ublic interest lies in recognition of the fact, the HC said while declining to interfere with the divorce granted by the family court.
Complexion of wife: cruelty about
Saibal Sen, July 1, 2020: The Times of India
Cruelty to wife for her dark complexion is a penal offence, punishable under Section 498A of the IPC, the Calcutta high court has ruled. The judgment was in a case of alleged marital torture and death of a woman in West Bengal’s Cooch Behar district in 1998.
“Causing cruelty to the deceased victim for her black complexion (sic) even after her marriage by the in-laws would definitely attract Section 498A/34 IPC against the in-laws, including the accused husband,” a division bench of Justices Sahidullah Munshi and Subhasis Dasgupta remarked in a 31-page order on June 25. Recounting the woman’s ordeal, additional public prosecutor Arun Kumar Maity said: “Three days into her marriage in October 1997, the woman was made to stay in a cowshed. The high court has made it clear that mental harassment by the husband and in-laws because of her dark complexion is an offence under Section 498A IPC.”
The woman was ill-treated and even assaulted with a cycle chain by her in-laws. She was constantly threatened by her husband that he will annul their marriage and remarry. Four days before she was found hanging, her father had asked her to come back.
A trial court had indicated Maziul, the victim’s husband, and his parents for murder and mental torture and sentenced them to life behind bars. His father died in custody in 2013.
Complexion of wife derided
Calling wife ‘kali kaluti’ ground for divorce: HC, May 30, 2018: The Times of India
The Punjab and Haryana high court allowed a woman to divorce her husband who called her “kali kaluti” (dark skinned), citing it as a case of maltreatment. The woman said her husband taunted her about her skin colour in front of other people. A bench of Justice M M S Bedi and Justice Gurvinder Singh Gill set aside the verdict of a family court which had dismissed her plea.
Demand for privacy is not cruelty: HC
PTI, `Wife's demand for privacy not cruelty towards husband', Oct 17 2016 : The Times of India
Demand for privacy by a married woman after she enters her matrimonial home cannot be dubbed as cruelty towards the husband to grant him divorce, the high court has held.
“Privacy is a fundamental human right. When a woman enters into matrimony , it is the duty of family members of her matrimonial home to provide her with some privacy ,“ a bench of Justices S Ravindra Bhat and Deepa Sharma said.
The observation came as the bench dismissed a plea by the husband who had challenged a 2010 trial court order dismissing his petition seeking dissolution of his marriage.
Besides cruelty , the husband had also raised the ground of “irretrievable breakdown“ of marriage by narrating that their wedlock has virtually lost its meaning as they were living separately for the past 12 years and had reached a point of no return.
However, the bench said though the Supreme Court had recommended to the Centre in 2006 the amending of the Hindu Marriage Act to “incorporate irretrievable breakdown of marriage as a ground for divorce. Yet till date this ground of divorce has not been added to the Act“.
While holding that the demand for privacy by the wife can't be termed as cruelty , HCt noted that the trial court had rightly observed that her demand to set up a separate home was “not unreasonable“. [However, see ‘Trying to separate spouse from in-laws: SC’ on this page]
Demand for too much sex
Demand for too much sex is cruel, grounds for divorce: SC
Dhananjay Mahapatra, TNN
From the archives of The Times of India 2007, 2009, Oct 21, 2010, 10.02pm IST
NEW DELHI: Persistent demand for excessive sex causing injury can be ground for seeking divorce, the Supreme Court has ruled.
Dealing with the undefined term "cruelty" under Section 13 of the Hindu Marriage Act, which provides grounds for divorce, a Bench comprising Justices P Sathasivam and B S Chauhan said the onus was on the one seeking divorce to prove with evidence that a particular conduct of the other partner had caused him/her cruelty.
The ruling came on a plea by an aggrieved husband.
While dealing with the whole gamut of what can be called "cruelty", entitling a spouse to move court for divorce, the Bench said even a single act of violence which was of grievous and inexcusable nature could fit the definition.
"Persistence in inordinate sexual demands or malpractices by either spouse can be cruelty if it injures the other spouse," said Justice Sathasivam, who wrote the judgment for the Bench.
However, a few isolated instances of cruelty over a certain period of time would not amount to cruelty as married life should be assessed as a whole, the Bench said while rejecting one Gurbux Singh's appeal seeking divorce on the ground of cruelty.
"Making certain statements on the spur of the moment and expressing displeasure about the behaviour of elders may not be characterised as cruelty. Mere trivial irritation, quarrels, normal wear and tear of married life which happens in day to day life in all families would not be adequate for grant of divorce on the ground of cruelty," the Bench clarified.
Having failed to prove cruel behaviour of his wife, Singh tried to impress the apex court to grant him divorce saying the marriage had broken down irretrievably as he and his wife were living separately since 2002 and there was no chance of their reunion.
The Bench said divorce has to be granted strictly under the grounds provided in Section 13 of Hindu Marriage Act though the apex court might have dissolved marriage on account of irretrievable breakdown in one case.
dhananjay.mahapatra@timesgroup.com
Denial of sex by pregnant wife not cruelty
PTI, Denial of sex by pregnant wife not cruelty: HC, Nov 07 2016
Denial of sex by a woman during her pregnancy is not cruelty towards her husband and does not entitle him to get divorce on that ground, the Delhi high court has said.
The HC also said that if the wife woke up late or wanted tea to be served in bed would at best show that she was lazy, and “laziness is not cruelty“. The observations by the HC came while dismissing a man's appeal against a family court's decision rejecting his plea for divorce on grounds of cruelty .
“Carrying a foetus in the womb she would obviously be inconvenienced by sex and assuming she totally shunned sex with the petitioner (husband) as her pregnancy grew would not constitute cruelty ,“ Justice Pradeep Nandrajog and Justice Pratibha Rani said.
Derogatory words, the use of
Feb 17, 2023: The Times of India
New Delhi : Delhi High Court has observed that repeated use of derogatory and humiliating words by a woman against her husband and his family amounts to cruelty.
The division bench of Justices Sanjeev Sachdeva and Vikas Mahajan said every person is entitled to live with dignity and honour and no one can be expected to live with constant abuse being hurled at him. “In the present case, the conduct of the appellant-wife, which has been proved on record, is of such quality, magnitude and impact as would have caused mental agony, pain, anger and suffering to the respondent-husband on a regular and continuous basis and, thus, clearly amounting to cruelty,” said the bench.
The high court dismissed the wife’s appeal challenging the divorce order passed by the family court, which allowed the husband’s petition under Section 13(1)(i-a) of Hindu Marriage Act, 1956 seeking dissolution of marriage on the ground of cruelty.
Referrring to the comments attributed to the wife, the high court said “repeated use of the words of the nature as extracted herein are clearly humiliating and would certainly amount to cruelty”. The bench upheld the findings of the family court, which had observed that the husband was treated with cruelty by the wife and that she used to abuse him and his parents in filthy language.
The high court was satisfied that cruelty, which was proved on record, was sufficient and constituted cruelty as required under Section 13(1)(i-a) of Hindu Marriage Act. “Consequently, we find no infirmity in the judgment allowing the petition and granting divorce on the ground of cruelty. We, accordingly, find no merit in the appeal. The appeal is consequently dismissed,” the bench noted.
Extra-marital affair, false allegation of / HC
March 24, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi:Unfounded allegations of extramarital affair levelled against a spouse constitute mental cruelty, the Delhi high court has said.
“It has repeatedly been held that accusations of unchastity or extramarital relationship is a grave assault on character, status, reputation as well as health of the spouse against whom such allegations were made. It causes mental pain, agony, suffering and tantamounts to cruelty. The allegations of extramarital affairs in a relationship are serious allegations, which have to be made with all seriousness. The tendency of making false allegations has to be deprecated by the courts,” a bench of Acting Chief Justice Vipin Sanghi and Justice Dinesh Kumar Sharma noted in a recent order.
The HC upheld a family court’s decision granting a divorce decree in favour of a husband on the grounds of cruelty to him by his wife. It agreed with the trial court’s decision and said it correctly found that the wife, by making unfounded allegations amounting to character assassination against the husband and father-in-law, inflicted mental cruelty upon the man.
The couple had got married in June 2014 and soon after that, the relations between the couple turned sour and they started residing separately.
Failed marriage: forcing spouse to stay on is cruelty: HC
February 17, 2022: The Times of India
Kochi: A man or woman cannot force their spouse to carry on a failed marriage and denying divorce “on mutual consent” in such a relationship amounts to cruelty, the Kerala HC has said in its judgment after considering separate appeals from an estranged couple.
“If one of the spouses is refusing to accord divorce on mutual consent after having convinced of the fact that the marriage failed, it is nothing but cruelty to spite the other spouse. No one can force another to continue in a legal tie and relationship, if the relationship deteriorated beyond repair,” ruled a division bench led by Justice A Muhamed Mustaque. In this case, the wife had challenged a court’s decision to grant divorce to her husband citing cruelty. TNN
False criminal case filed by spouse
The Times of India, August 1, 2016
HC: False criminal case filed by wife grounds for seeking divorce
The Punjab and Haryana high court has held that a husband is entitled to seek divorce on the grounds of “mental cruelty“ when the wife has filed a false criminal case against him and his family members in which they end up being acquitted. HC passed this order while allowing a petition filed by Hisar-based Army officer seeking divorce from his wife.
False criminal complaint against husband is cruelty
March 13, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi: Delhi High Court has dissolved a marriage between a Hindu couple, saying that the wife filed a false criminal complaint against her husband, which caused him “immense mental cruelty and agony”.
A bench comprising justices Vipin Sanghi and Jasmeet Singh said that false allegations levelled by the estranged wife amount to "a clear and categorical character assassination" of the husband, as well as his family members.
It said that the wife did "everything to get the appellant and his family entrapped in the criminal case" and set aside a family court order that refused to grant divorce to the couple, stating that the family court ignored that visiting a police station must have caused mental harassment and trauma to the husband, who did not know when a case would be registered against him and he would be arrested.
"The appellant (husband) had to make 30-40 visits to the police station in connection with the said complaint. A police station is not the best place for anyone to visit. . . it must have caused mental harassment and trauma each time he was required to visit the police station, with the Damocles Sword hanging over his head, and he not knowing when a case would be registered against him and he would be arrested,” the HC observed.
It said the wife filed an unsubstantiated criminal complaint against the husband and his family members “which caused them immense mental cruelty and agony” and allowed the plea of the husband to grant the divorce. Interestingly, the husband had first filed a petition seeking restitution of conjugal rights after the wife suddenly left him. The marriage between the parties was solemnised in May 2008.
The court noted that after nearly two years of leaving the matrimonial home, and three years of the marriage, the wife had filed a complaint before the crime against women (CAW) cell, alleging dowry demands, abuse, physical and mental torture, and harassment, amongst other cruelties, and all these allegations remained unsubstantiated.
Noting that the wife also failed to justify not returning to the matrimonial home and cohabiting with the husband, the court opined that the appellant was “able to make out a case of being subjected to cruelty and desertion”. The court opined that the relations between the parties were “sufficiently beyond repair” since they have not lived together for the last 12 years.
False charges of infidelity equal cruelty
I
`False charges of infidelity equal cruelty'
Rebecca Samervel The Times of India Oct 25 2014 Mumbai:
Observing that making false accusations of infidelity and humiliating a person on the basis of this amounts to cruelty, a family court has granted divorce to a deputy municipal commissioner, whose wife falsely accused him of having an affair with a colleague’s wife.
The alleged paramour’s husband testified in the petitioner’s favour and said that the woman had damaged his wife’s reputation too.
The court said that the estranged wife’s behavior— quarreling, humiliating the man with his alleged affair — had caused him pain and anguish. “These and various other allegations, coupled with the fact that there is no challenge to the petitioner’s evidence that they have had no sexual intercourse from 2001 until 2009... are sufficiently grave and weighty instances of cruelty committed by the wife towards the petitioner husband,” the judge said.
II
Spouse's adultery allegation painful: HC, Nov 25 2016 : The Times of India
Allegation of adultery levelled by a spouse is most “painful“ for a person, the Delhi high court has observed while granting divorce to a man who was accused by his wife of having an illicit relationship with a woman. It said allegation of adultery was a “serious charge“ and would constitute cruelty, if not proved.
Hiding abortion, mental illness is cruelty
The Times of India, Nov 30, 2016
Aamir Khan
Hiding abortion, illness cruelty: HC
Delhi high court has termed concealing mental illness and termination of pregnancy a ground for divorce as it amounts to cruelty. The court was hea ring a petition of a man who was denied divorce in a family court.
During cross-examination in front of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Yogesh Khanna, the wife admitted to have undergone treatment for depression.
The court said that termination of the second pregnancy had added to the “mental torture inflicted upon the man“ and granted divorce to the man on grounds of “cruelty and desertion.“
The man's counsel Sahil Munjal argued that the wife left her husband's house on June 10, 2000, and did not return. She gave birth on March 29, 2001, but neither the husband nor his family were kept in the loop. The concealment, therefore, caused “immense mental torture“ when they learnt about it, he argued. In 2001, she hid the fact about her second pregnancy that she had terminated, the counsel added.
The woman, in her written statement, denied the man's claims and said her entire salary was pocketed by her in-laws who would “torture“ her for dowry .
Household/ domestic work by daughter-in- law
May 31, 2020: The Times of India
It is quite common for elders in a family to reprimand younger members and making a daughter-inlaw do household or domestic work is not unusual, the Kerala high court observed in a recent judgment.
The observation was made by a division bench comprising Justices AM Shaffique and Mary Joseph while considering whether a wife trying to force her husband to throw out her mother-in-law from their home amounted to “cruelty” and therefore sufficient grounds for grant of a divorce.
In the judgment authored by Justice Mary Joseph, the court said: “No family is totally devoid of clashes. It’s common for elders to scold and sometimes abuse youngsters. Making a daughter-in-law do the household/domestic work is also not something unusual. From the evidence tendered by the respondent (daughterin-law), it is all the more clear that the afore-stated factors formed the basis for her illwill to the petitioner’s mother. We do not find any other justifiable reason for her to get the petitioner’s mother excluded from the family.”
The bench, considering an appeal by the husband against a Thalassery family court ruling that had turned down his plea for divorce on grounds of “cruelty”, referred to the SC’s 2003 judgment (Vijayakumar Ramachandra Bhate Vs Neela Vijayakumar Bhate) to point out that in Hindu society it is a pious obligation of the son to maintain the parents and that the wife must have justifiable reason to attempt to deviate from the normal practice and custom. The HC reversed the family court order and passed a decree on grounds of cruelty for dissolution of marriage in favour of the husband.
Household chores, going to work are not cruelty
Rebecca Samervel, Sep 11, 2022: The Times of India
MUMBAI: Finding that waking up at 4am for household chores, then going to work and returning home and doing more chores, does not amount to cruelty but was part of her responsibilities, a sessions court said, acquitted a 30-year-old man and his mother on charges of abetting his wife's 2015 suicide.
The court said Priyanka Shelar, a housekeeper who took her life in her employer's Vidyavihar home, belonged to the lower strata of society where women were expected to perform household chores and eke out a living to make ends meet. "It was the responsibility of Priyanka to do household work and earn for a living. Therefore, asking Priyanka to do household work apart from her work would not amount to cruelty to Priyanka, as alleged by the prosecution," the court said.
Among those to depose against Kurla's Prashant Shelar (30) and Vanita (52) were Priyanka's mother and sister. The couple married in 2014 after being in a relationship for a few years. The accused allegedly taunted her over her complexion, suspected her character, would not allow her to talk to her family and forced her to walk over six km to her work place daily.
The court said whatever was stated by prosecution witnesses in their evidence usually occurs in daily life of a woman of lower starta of society to which Priyanka belonged. "There was no danger to life of Priyanka when she was residing with accused in one room. Insults, taunting and restrictions such acts do not generally drive a person to commit suicide unless there is a persistent scuffle and mental torture with criminal mind of accused to see that by such acts would drive victim to commit suicide," the court said. The court said the victim was made to walk to work as her husband could not afford to get her transport.
The court found that the allegations against the accused amounted to daily wear and tear of family affairs where a mother-in-law sometimes complains that her daughter-in-law does not work properly. "The factual circumstance cannot be termed as causing mental cruelty as it a natural phenomena and could be seen generally in this stature of the family to which both parties belonged," the court said.
The court said there was no clear picture as to what prompted Priyanka to die by suicide.
Household work by married woman is not cruelty
PTI, Oct 28, 2022: The Times of India
MUMBAI: If a married woman is asked to do household work for the family, the same cannot be equated to the work of a maid servant and would not amount to cruelty, the Aurangabad bench of the Bombay High Court said while quashing a case lodged by a woman against her estranged husband and his parents for domestic violence and cruelty.
A division bench of Justices Vibha Kankanwadi and Rajesh Patil, on October 21, quashed the FIR lodged against the man and his parents. The woman, in her complaint, had alleged she was was treated properly for a month after marriage, but thereafter, they began treating her like a maid servant.
She also claimed her husband and his parents, a month after the marriage, started demanding Rs 4 lakh to buy a four-wheeler. In her complaint, the woman said she was then subjected to mental and physical harassment by her husband over this demand.
The HC, in its order, noted the woman had merely stated she was harassed but had not specified any such act in her complaint.
“If a married lady is asked to do household work definitely for the purpose of the family, it cannot be said it is like a maid servant. If she had no wish to do her household activities, then she ought to have told it either prior to the marriage so that the bridegroom can rethink about the marriage itself or if it is after marriage, then such problem ought to have been sorted out earlier,” the court said.
It further said mere use of the words harassment ‘mentally and physically’ is not sufficient to attract Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code unless such acts are described.
“Unless those acts are described, it cannot be concluded whether those acts amounted to harassment or subjecting a person to cruelty,” the HC order stated.
The omnibus allegations the wife made against the husband would not attract the offence under the provision, the court said, and allowed the petition filed by the husband and his parents seeking to quash the case.
Impotency slur is mental cruelty
November 22, 2020: The Times of India
Impotency slur equals to mental cruelty: HC
New Delhi:
A false allegation of impotency against a spouse amounts to mental cruelty, Delhi High Court held, while dissolving a marriage at the request of the estranged husband.
A bench of justices Manmohan and Justice Sanjeev Narula took strong exception to the unsubstantiated allegation of impotency levelled by the wife against the husband. “It was not a one-off casual retaliatory remark. The stand in the written statement was sustained all throughout the trial, till the stage of final decision. The imputation and allegation made by the (wife) appellant have been repeatedly reinforced during the trial” the bench pointed out, adding that “significant effort was made to establish that the respondent was indeed impotent and incapable of sexual intercourse.”
The court saw merit in the stand of advocate Prabhjit Jauhar, counsel for the husband, that the allegations levelled by the wife were “grave and serious” and likely to impact the man’s self-image and adversely affect his mental well-being — amounting to cruelty — and upheld the divorce granted by the trial court.
“Having regard to the law on the subject, we find no infirmity in the findings and observations of the trial court that the allegation of the wife, with respect to impotency, clearly falls within the concept of cruelty as defined under law,” the bench noted.
It underlined that claims made by a party in its written submissions “have to be given due sanctity and treated with seriousness” as these allegations were brought in public domain and the court was expected to give its verdict on their basis.
In the plea, the man had sought to declare the marriage null and void on the ground that it could not be consummated due to the woman’s alleged impotency, and that his consent was obtained by concealing several material facts related to her psychological disposition. Had he known them, he would not have consented for the marriage, he maintained. But the woman, through advocate Manish Sharma countered by alleging that the man was suffering from impotence (erectile dysfunction), which was the true cause of nonconsummation of marriage.
The court said the woman’s allegation was rejected by the trial court on the basis of the testimony of an expert witness, who, after physically examining the man, had found that he was normal.
False allegation of impotence a ground for divorce, says SC
AmitAnand Choudhary, August 5, 2021: The Times of India
Making baseless and false allegations against one’s spouse regarding impotency of life partner amounts to cruelty and divorce can be granted on that ground, the Supreme Court has said and upheld a Delhi high court order allowing divorce on that ground.
A bench of Justices L Nageswara Rao and Aniruddha Bose declined to interfere with the HC verdict and dismissed the plea of a woman who had made the allegation against her husband in the court and challenged the divorce granted on his plea. The couple got married in 2012. But soon after the marriage, the man moved the court seeking to declare the marriage null and void on the ground that it could not be consummated due to the woman’s alleged impotency.
No infirmity in findings of trial court on wife’s allegation: SC
Countering his allegation, the wife submitted in family court that the man was suffering from impotency (erectile dysfunction) which was the true cause of non-consummation of marriage and also that her in-laws demanded dowry and she was cruelly treated. The man thereafter sought divorce on the ground of cruelty for making false allegation against him.
As the wife’s allegation was found baseless after examining medical report and taking into account the statement of a medical expert, the family court allowed the divorce plea of the man. The woman then moved the high court, which turned down her plea and said her allegations were “grave and serious”, and was likely to adversely affect the man’s mental well-being.
“Thus, having regard to the law on the subject, we find no infirmity in the findings and observations of the trial court that the allegation of the appellant (wife) in the written statement with respect to the impotency clearly falls within the concept of cruelty as defined under law,” the high court had said.
The wife approached Supreme Court and pleaded that divorce on the ground of cruelty be quashed and she be allowed to get divoce through mutual consent. But her plea was opposed by her husband’s advocate, Prabhjit Jauhar.
Kicking the daughter in law
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
Kicking bahu not cruelty? SC to review
Dhananjay Mahapatra | TNN
New Delhi: After stirring up a controversy last year by ruling that a mother-in-law who kicks her daughter-in-law or repeatedly threatens her with divorce attracts no punishment for cruelty under Section 498A of the Indian Penal Code, the Supreme Court has agreed to take a second look.
After the verdict on July 27, 2009, women’s organizations had protested vociferously. CPM leader Brinda Karat met law minister Veerappa Moily and urged him to take steps to correct the flaw in the “retrograde” judgment.
The National Commission of Women said the ruling would defeat the purpose of the provision to protect women from cruelty and harassment in matrimonial homes.
Second Opinion
Court had in 2009 said kicking daughter-in-law and threatening her with divorce does not amount to cruelty CPM leader Brinda Karat wrote to law minister against ‘retrograde’ ruling SC takes up curative petition, to be heard in open court
Lack of toilet is cruelty
A 24-year-old woman has divorced her husband for not constructing a toilet at home, in what is perhaps the first such case in the country . A family court in Bhilwara said the absence of a toilet amounted to “cruelty“ against the wife before it allowed the marriage to be dissolved on Friday .
Married in 2011, the woman moved the court in 2015, saying that despite repeated requests, her husband didn't construct a toilet or bathroom at home, forcing her to defecate and bathe in the open.She also had to wait until dusk to go out to the fields to relieve herself, which she felt undermined her dignity .
But her husband said he found his wife's demand for a toilet unusual because most of the women in his village defecated in the open. The woman's family hadn't raised the issue of toilet construction at the time of marriage, he alleged. Treating the absence of a toilet at home as “cruelty“ akin to “outraging the modesty of a woman“ the court allowed the marriage to be dissolved, two years after she had filed the divorce petition.
“We spend money on buying tobacco, liquor... but are unwilling to construct toilets to protect the dignity of our family . In villages, women have to wait until sunset to answer nature's call. This is not only physical cruelty but also outraging the modesty of a woman,“ the court said.This is perhaps the country's first such case where absence of a toilet was considered as a grounds for divorce.
Lone case of cruelty no ground for divorce
AmitAnand Choudhary, `Lone case of cruelty no ground for divorce', Mar 9 , 2017: The Times of India
Separation Only If Spouse Abuse Is Regular: SC
The Supreme Court held that isolated incidents of cruelty against spouse cannot be a ground to seek divorce, and marriage could be dissolved only if such incidents were of a recurring nature.
A bench of Justices R K Agrawal and A M Sapre also ruled that a husband or wife could not seek divorce on the basis of incidents which took years before the petition was filed. It set aside the order of a family court and the Delhi high court which had granted divorce to a man on the basis of alleged incidents of cruelty against him, which took place a decade before he approached the court for dissolution of marriage. Six years after the marriage was dissolved by the family court, the apex court allowed the plea of his wife for restitution of her conjugal rights. “A petition seeking divorce on some isolated incidents alleged to have occurred 8-10 years prior to filing of the petition cannot furnish a subsisting cause of action to seek divorce after 10 years or so of occurrence of such incidents.The incidents alleged should be of recurring nature or continuing one and they should be in near proximity with the filing of the petition,“ the bench said. The court noted that the couple had started living together after the alleged incidents, which means that her conduct was condoned by the husband and he could not raise that ground. The court refused to take into account a recent incident when the wife had chided him in his office in the presence of his colleagues.
“In the first place, no de cree for divorce on one isolated incident can be passed. Secondly , there could be myriad reasons for causing such isolated incident. Merely because both exchanged some verbal conversation in the presence of others would not be enough to constitute an act of cruelty unless it is further supported by some incidents of a like nature,“ the court said.
“In our considered opinion, both the courts below failed to take note of this material aspect of the case and thus committed jurisdictional error in passing a decree for dissolution of marriage,“ the apex court said and set aside the divorce order. It said the couple should live together to take care of their two daughters and bring peace, harmony and happiness in their life.
“We hope and trust that the parties would now realise their duties and obligations against each other as also would realise their joint obligations as mother and father towards their grown up daughters. Both should, therefore, give quiet burial to their past deedsacts and bitter experiences and start living together and see that their daughters are well settled in their respective lives,“ the bench said.
Multiple litigations against spouse is cruelty/ SC
AmitAnand Choudhary, Sep 14, 2021: The Times of India
It took two decades for a marriage, which could not take off and was never consummated with the spouses’ starting litigations just a fortnight after marrying, to be legally dissolved with the Supreme Court allowing the divorce plea of a husband holding that multiple litigations initiated by the wife against him amounts to cruelty.
A bench of Justices Sanjay Kishan Kaul and Hrishikesh Roy invoked special power under Article 142 of the Constitution to grant divorce on the ground of irretrievable breakdown of marriage and also on account of cruelty in light of conduct of the wife for filing multiple cases in courts against him including a plea in the HC for disciplinary action against her husband who was working as an assistant professor in a government college.
The court noted that law has not been amended despite recommendations of the Law Commission to recognise irretrievable breakdown of marriage as a ground of divorce and the matter is also pending in the apex court. It, however, said that it would not serve any purpose to keep the matter pending and dissolved the marriage by invoking its special power to do justice.
The bench said that the trial court and the high court did not find adequate material to come to the conclusion that the husband was entitled to divorce on grounds of cruelty and the wife’s conduct during the pendency of the case had to be examined. The court noted that the wife had taken recourse to not just litigations but also publicly threatened him in his office. It said that the HC wrongly brushed aside these incidents as “wear and tear of marriage”.
“These continuing acts of the respondent would amount to cruelty even if the same had not arisen as a cause prior to the institution of the petition, as was found by the trial court. This conduct shows disintegration of marital unity and thus disintegration of the marriage. In fact, there was no initial integration itself which would allow disintegration afterwards. ,” the bench said.
Not offering water to husband is not cruelty: HC
Shibu Thomas, March 3, 2018: The Times of India
Not taking care of a husband’s needs or failing to even offer him water when he returns home late from work does not amount to cruelty,” said the Bombay high court.
The court dismissed a plea by a 52-year-old Santacruz resident seeking to divorce from his wife (40) on the grounds that she treated him cruelly. One of the allegations levelled by the man, a bank employee, was that his wife would not look after his needs or offer him water when he returned home late from work. A division bench of Justice Kamalkishor Tated and Justice Sarang Kotwal said it would not amount to cruelty and pointed out that the woman herself was employed as a teacher. “In addition to attending to her job, she was admittedly cooking in the morning as well as in the evening. The evidence shows that on her way she used to purchase vegetables. It is obvious that she herself used to get tired and still she was cooking for the family and doing other household work,” said the bench.
The couple had married in 2005 and lived in their matrimonial home with the man’s parents. According to his divorce plea, the man claimed his wife used to come home late from work and pick up quarrels with his aged parents. He alleged that the food cooked by her was not tasty and she would constantly insist that his parents be driven away from the matrimonial home. In 2006, he claimed that she left home while the wife alleged that she was locked out and driven away. In the family court he called in his father as a witness to substantiate his claims while the woman called in their neighbour and a cousin of the man. The neighbour testified that the woman would be constanly working at home and faced taunts from her in-laws. The family court had dismissed the divorce application in 2012, which the man challenged in high court.
The high court perused the evidence and pointed out that both the man and his wife were out at work during the day therefore there was little time for friction between the woman and her in-laws or for him to have witnessed any fights. The man had also cited a non-cognisable complaint that he had lodged against the woman a few months before his divorce plea accusing her of scratching and twisting his fingers. “It is quite unbelievable that just for scratching and for twisting of fingers the man had to take treatment in an hospital. In our opinion, this was done by him to prepare the ground for filing petition for divorce,” said the high court.
Not talking while living together
Ajay Sura, May 13, 2022: The Times of India
Chandigarh: Dismissing a plea filed by a woman from Haryana’s Kurukshetra district against grant of divorce on the grounds of causing mental cruelty to her husband, the Punjab and Haryana high court said that “even if a husband and wife are staying together and husband does not speak to the wife, it would qualify as mental cruelty”.
A division bench of the HC comprising Justice Ritu Bahri and Justice Ashok Kumar Verma observed, “A spouse staying away by sending vulgar and defamatory letters or notices or filing complaints containing indecent allegations or by initiating a number of judicial proceedings can make the life of the other spouse miserable. ”
Afamily court in Kurukshetra had granted divorce through its order of October 21, 2016, on the grounds that the wife had filed several complaints against her husband, which were later found to be untrue, and he was acquitted. The couple was married in 1992 and have four children. According to the husband, the attitude of the wife was very cruel, barbaric, rude, and crude towards him from the very beginning.
Partying by wife not mental cruelty: HC
The Times of India, Aug 02 2015
Shibu Thomas
Wife partying not mental cruelty, says Bombay HC
The Bombay high court has ruled that a family court was wrong in granting divorce to a man who had claimed that his wife partied a lot and misbehaved, constituting cruelty. Justice M L Tahaliyani said social mores and traditional roles were changing and upheld an appellate court's order overturning the divorce verdict.
Poking fun without motive to cause hurt is not cruelty
Vasantha Kumar, August 5, 2021: The Times of India
Poking fun without any motive to cause hurt or a stray remark can by no stretch of imagination be construed a cruel act, the Karnataka high court observed while quashing the proceedings against a Los Angelesbased dentist and his Gurugram-based parents.
The proceedings were initiated based on a complaint filed by the dentist’s wife with the police in Bengaluru in 2017 alleging ill-treatment and infidelity against the husband and her in-laws. An FIR was registered for offences under sections 406 and 325 of Indian Penal Code and also sections 3 and 4 of Dowry Prohibition Act.
Perusing the records, Justice G Narendar noted that apart from self-serving statements, there was absolutely no material placed by the complainant to demonstrate any illicit relationship. “The very fact that the complainant (wife) was sponsored on dependent visa would only go to demonstrate that the third petitioner (husband) had voluntarily offered to support her during her stay in the US... That very fact that she was permitted into the US on a dependent visa is sufficient to discard her allegations,” the court observed.
Refusal to speak to bride is not cruelty: SC
The Supreme Court said it was not cruelty punishable under the dreaded Section 498A of IPC if no one at the matrimonial home, including the husband, spoke to a bride for days.
In her complaint under Section 498A to the police, a woman alleged that after her marriage, she stayed with her husband for 20 days, during which she was left completely alone and no one talked to her.
She alleged that her husband was “not even willing to talk freely to her despite her sincere efforts“. She accused the husband of evading her and refusing to consummate the marriage. The SC had ear lier ruled that refusal to cohabit could be a ground for seeking divorce.
After the husband left for Australia where he worked, no one in his family talked to the woman, forcing her to leave the matrimonial house for her parent's place. She claimed that her parents had spent Rs 15 lakh on the marriage and Rs 20 lakh on gold ornaments. The Cyberabad police filed a chargesheet and the case is pending before the metropolitan magistrate. The high court at Hyderabad rejected a petition by the husband and his parents seeking quashing of the case. They appealed in the apex court. A bench of Justices Arun Mishra and Mohan M Shantanagoudar perused the wife's complaint and said her story did not reveal any offence under Section 498A (cruelty at matrimonial home to drive the woman to commit suicide, cause injury to her or harassment for dowry) or Section 406 (breach of trust) of IPC as there was no demand for dowry .
The bench quashed the case terming the complaint to be devoid of any charge under Section 498A or Section 406.
Spouse’s silence may amount to cruelty
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
Spouse’s silence may amount to cruelty, says SC
Dhananjay Mahapatra | TNN
New Delhi: Silence is golden. But married couples shouldn’t take it literally. The Supreme Court has said silence of a partner could amount to cruelty, which under the Hindu Marriage Act is a ground for divorce.
Section 13 of the Act says a person can move a divorce petition if he or she has been treated with cruelty by the spouse or has been deserted for a continuous period of not less than two years.
Delivering its judgment in a matrimonial case, a bench comprising Justices P Sathasivam and Ashok Kumar Ganguly said: ‘‘At times, it may be just an attitude or an approach. Silence in some situations may amount to cruelty. Therefore, cruelty in matrimonial behaviour defies any definition and its categories can never be closed.’’
That is why,the court said, the Act deliberately did not define ‘cruelty’. ‘‘In a marriage, cruelty would obviously mean absence of mutual respect and understanding between spouses which embitters the relationship and often leads to various outbursts of behaviour which can be termed cruel,’’ it said.
This judgment came in a case where the husband after forcing the wife to live separately because of his illtreatment moved the court for divorce saying she had treated him with cruelty by deserting him. The Mandi district magistrate granted divorce terming the desertion as cruelty on her part.
But Himachal Pradesh HC saw through the design by noticing that the daughter was unambiguous in her statement that her father used to beat her mother and that’s why she left her home. It said whether a husband or wife was cruel to the partner had always to be judged taking into account the facts and circumstances.
Sterilisation and Cruelty To Spouse
Got sterilised secretly? It’s mental cruelty SC Defines Criteria For Cruelty To Spouse As Ground For Divorce Dhananjay Mahapatra | TNN
New Delhi: In a path-breaking decision, Supreme Court has defined what connotes ‘mental cruelty’ — the ground that has been frequently cited as the reason for those seeking divorce but which had so far lacked a precise definition.
The court laid down elaborate criteria of what would constitute “mental cruelty”. However, it said that the behaviour patterns so mentioned must persist over a period of time to warrant the conclusion that the marriage between the parties had irretrievably broken down and qualified to be the ground for divorce.
In fact, the verdict seems to strike the right balance between the competing considerations of rescuing people trapped in unhappy alliances and the anxiety to save marriages from divorce petitions based on false allegations and on impulse. The definition, part of a verdict annulling the marriage of senior IAS couple Samar and Jaya, came close on the heels of the court’s bid to define the legal concept of “outraging of modesty”.
While the court said that, given the complexities of human mind, “no court should even attempt to give a comprehensive definition of mental cruelty”, it tried to get a handle on the issue with help from previous judgments.
It listed specific actions as amounting to mental cruelty. The court, however, balanced that by inserting the caveat that it is pattern persisting over a period rather than isolated instances which should constitute the basis for divorce in what can be seen as reflecting its anxiety to ward off divorces being sought on false pretenses, or even in fits of anger and on impulse.
“Conduct must be persistent for a fairly long period and is so offensive that the other party finds it difficult to live together,” said the court.
Clarity From The Court
What is
Undergoing sterilisation without knowledge or consent of spouse Wife having abortion without medical reason or without consent of spouse Not having intercourse without physical incapacity or valid reason Unilateral decision not to have child Sustained reprehensive conduct, studied neglect Actions aimed to derive sadistic pleasure Abuse and humiliation Sustained unjustified conduct affecting physical & mental health of spouse Frequent rudeness, indifference and neglect
What isn’t
Wear & tear of marriage Jealousy, selfishness & possessiveness causing unhappiness or stress Mere coldness or lack of affection
A final caveat
View married life as a whole; isolated instances not cruelty ‘Review married life as a whole’
New Delhi: The Supreme Court also stressed that while deciding any divorce petiition based on the ground of mental curelty, “married life should be reviewed as a whole” and “that a few isolated incidents over a period of years will not amount to cruelty”.
The focus of the Bench was on “sustained”. It said that “mere coldness or lack of affection cannot amount to cruelty” but made allowance for the fact that “frequent rudeness of language, petulence of manner, indifference and neglect may reach such a degree that it makes the married life for the other spouse absolutely intolerable”.
In the case at stake, Jaya, an IAS officer, after divorcing her first husband who also was an IAS officer and from whom she had a daughter, married a second time in December 1984. She, however, refused to cohabit with her second husband, Samar, on the ground that she did not want any more children and told him not to interact with her daughter from the previous marriage.
Finding this humiliating, Samar filed a divorce petition in Alipur, Kolkata. He also mentioned that he had been forced to live separately since August 1990. Jaya, however, denied the allegations and said that the divorce petition was filed by her husband at the instigation of his relatives, whose interference in her married life she had resented.
While trial court granted divorce on the ground of mental cruelty and the additional district judge agreed with it, the Calcutta High Court reversed the judgment. The husband moved the apex court in appeal.
An apex court Bench comprising Justices B N Agrawal, P P Naolekar and Dalveer Bhandari upheld the trial court verdict and said the HC was unnecessarily obsessed by the fact that the woman was also an IAS officer even though it is proved that she inflicted mental cruelty on her husband that led to both living separately for long without there being any reconciliation.
‘‘Even if the appellant had married an IAS officer, that does not mean that the normal human emotions and feelings would be entirely different,’’ said Justice Bhandari writing the judgment for the Bench.
Telephone calls, frequent, to another man
February 22, 2022: The Times of India
A wife making discreet and frequent phone calls to another man “disregarding the warning of the husband” is matrimonial cruelty, the Kerala high court has observed. Producing call records, a man contended that his wife was in an affair before and after their marriage and made frequent calls to her paramour. The court said while this may not prove adultery, the question is if it amounts to matrimonial cruelty.
Tormenting and traumatising each other
Abhinav Garg, Best to dissolve marriage in face of bickering: HC, The Times of India, Oct 23 2016
In face of “mutual bickering“ between couples where both cause each other mental torture, it is best to dissolve the marriage the Delhi high court has said. It granted divorce in one such case to the husband who was falsely accused by the wife of hitting her and causing abortion of her foetus.
Allowing the plea of the husband to end the marriage, a bench of Justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Pratibha Rani pointed out that where “there is evidence that the husband and wife indulged in mutual bickering leading to remonstration... to the stage where they target each other mentally, insistence by one to retain the matrimonial bond would be a relevant factor to decide on the issue of cruelty, for the reason the obvious intention of said spouse would be to continue with the marriage not to enjoy the bliss thereof but to torment and traumatise each other.“ The HC found enough evidence to conclude there was an “irretrievable breakdown of marriage“ and also found merit in the husband's claim that falsely accusing him of causing death of the foetus amounts to mental cruelty .
“Evidence establishes that both Sandhya and Manish gave a very serious twist to the unfortunate abortion which Sandhya had. It establishes that both have the propensity to twist facts so as to suit their convenience,“ the bench noted, refusing to prolong the marriage.
Wild allegations
Wild allegations against spouse is cruelty: HC Shibu Thomas | TNN
Mumbai: Making wild and baseless allegations in court against your spouse and in-laws amount to cruelty, Bombay high court has ruled while upholding a trial court’s order dissolving the marriage of a Mumbai couple in their 30s.
Following an application for divorce filed by Mazgaon resident Jitesh Agarwal, his wife Geeta had alleged that there was a bizarre custom in her in-laws’ family where they shared each other’s wives. Geeta claimed that she was persistently told to have illicit relations with her husband’s brother and brother-in-law and there was even an attempt to outrage her modesty.
‘‘The allegations levelled by Geeta against the husband and other members of the family at various places and at every stage are absolutely baseless, irresponsible, wanton and scandalous and they were made for the reasons best known to her,’’ said a division bench of Justice D B Bhosale and Justice R Y Ganoo. ‘‘The expression — treating the other party with cruelty (in the Hindu Marriage Act) — is wide enough to cover cruel treatment (even after the filing of the petition) by making wild and serious allegations which, according to the accused spouse, are false and scandalous. A (divorce) decree could be passed based on such allegations.’’
Geeta’s lawyers claimed that as Jitesh had not amended his petition to include her allegations as cruel, a divorce could not be granted on that ground. The HC judges, however, did not agree. ‘‘If these allegations were true, neither the appellant nor her father would have kept quiet for such a long time,’’ said the division bench even as it said the family court was right in granting divorce on the ground of cruelty.
The court added that Geeta’s behaviour even before she lodged criminal complaints against her husband would amount to cruelty. ‘‘(Geeta’s conduct) shows that she had made Jitesh and his family’s lives miserable. The manner in which she used to lodge criminal complaints one after another against Jitesh undoubtedly would constitute mental cruelty,’’ said the HC.
Womaniser, calling husband one
Rosy Sequeira, Oct 26, 2022: The Times of India
MUMBAI: Observing that a wife's labelling of her husband as a womaniser and alcoholic had shredded his reputation in society, the Bombay High Court upheld a family court's order that dissolved their marriage.
Justices Nitin Jamdar and Sharmila Deshmukh on October 12 dismissed the 2006 appeal of the wife against the Pune FC's November 2005 order. While her appeal was pending, the husband died and his legal heir was brought on record in his place.
The judges noted that the FC's order was based on the wife's "unsubstantiated" allegations - that he was constantly under influence of liquor, out late at night and on some pretext visited her sister. Her sister only deposed that he drank liquor. "The evidence on record produced by the petitioner fails to prove the allegations made by her in pleadings," they said.
In his evidence before FC, the husband stated she separated him from his children and grandchildren, defamed him and due to her conduct "his marital and social life has been completely destroyed."
The judges noted that in February 2002, when the husband's divorce plea was dismissed, the same allegations were not held to constitute cruelty as he did not say he suffered mental torture due to them. In the appeal, he made a specific case that she had defamed him by her false and baseless allegation causing him mental agony.
"It is a settled position in law that 'cruelty' can broadly be defined as a conduct which inflicts upon the other party such mental pain and suffering as would make it not possible for that other party to live with the other," the judges said. They noted that the husband was "a retired army major" and the wife's petition said he "belongs to the upper strata of society and has a standing" in society.
"...the petitioner has repeatedly made allegations assassinating his character in both rounds of litigation and failed to prove them. The conduct of the petitioner in continuing to make unwarranted, false and baseless allegations pertaining to the respondent's character labelling him as an alcoholic and womaniser has resulted in shredding his reputation," the judges said. They added that the husband's stand that he could not continue with the matrimonial relationship "cannot be said to be unjustified." They concluded that the wife's "conduct constitutes cruelty" under the Hindu Marriage Act.
Custody of children
Virtual access no solution
The Times of India, Aug 01 2016
Swati Deshpande
Court slams non-custodial parent's virtual access to kid in custody row
Giving a noncustodial parent only virtual access to a child during divorce battles is not a longterm solution and would become an empty ritual, a Pune family court said when a woman, who went to Switzerland on a work assignment in 2015, wanted to extend her stay there with her preschooler.
Last week, the judge allowed the techie to extend her stay abroad till the end of the year, provided she sends her daughter to Pune for a week or makes arrangements for her husband to visit Switzerland for a week and have access to their child. “For any parent, having only virtual access to their children cannot be a long-term solution...Without proper justification (it) will make such vir tual access an empty ritual.It will not benefit either the non-custodian parent or the child,“ judge Swati Chauhan said, adding that when done without proper justification, such virtual access will become an empty ritual. The order is significant at a time of more divorces occuring where one parent works in another state or abroad.
Such divorce cases deprive the other parent of time with the child and increasing chances of “parent alienation syndrome. The couple has been fighting a divorce battle since 2014. In June 2015, the wife sought permission to go to Switzerland for nine months for an assignment in the “interest of her career“. The child was then less than four. Her husband first apprehended that she would alienate the child from him. The father-child bond may be jeopardised, he said. After counselling, they agreed she could stay abroad till July 2016 during which he would get access to the child via video-con ferencing thrice a week and on Sundays.
On June 24, 2016, when she sought an extension till December 31, the court said, “Her request is not bona fide and fair... (she had) not bothered to explain whether her request is to complete the original assignment or begin a new one whose end date is January 10, 2017, as documents submitted later reveal“.
The husband pointed out that she had lived abroad for a year on work, leaving the child, then one year old, with her parents.The court agreed that the “father-daughter bond should not be allowed to get diluted by separation“.
Balancing the wife's plea to enrich her career and earn money and the husband's right to spend time with his child is an “unpleasant situation said the court.
Custody of minor children to be with mother
Custody of minor shall be with mother, rules SC
Amit Choudhary The Times of India Mar 04 2015
In a custody battle between estranged parents, a minor child, under five years , shall be allowed to remain with the mother, the Supreme Court has ruled saying that in such cases the child should not be treated as a “chattel“. The court said that under Hindu Minority and Guardianship (HMG) Act, Section 6(a), a father can be guardian of the property of the minor child but not of his person if the child is less than five years old.
“There can be no cavil that when a court is confronted by conflicting claims of custody there are no rights of the parents which have to be enforced; the child is not a chattel or a ball that is bounced to and fro the parents. It is only the child's welfare which is the focal point for consideration. Parliament rightly thinks that the custody of a child less than five years of age should ordinarily be with the mother and this expectation can be deviated from only for strong reasons,“ a bench of Justices Vikramajit Sen and C Nagappan said.
The apex court quashed the Bombay high court's or der which granted custody of a two-year-old child to father on the ground that the mother had not established her suitability to be granted interim custody of the infant.
“The HMG Act postulates that the custody of an infant or a tender aged child should be given to hisher mother unless the father discloses cogent reasons that are indicative of and presage the livelihood of the welfare and interest of the child being undermined or jeopardized if the custody is retained by the mother,“ it said.
“The Act carves out the exception of interim custody , in contradistinction of guardianship, and then specifies that custody should be given to the mother so long as the child is below five years in age,“ it said.
The bench added, “The Act immediately provides that the custody of a minor who has not completed the age of 5 years shall ordinarily be with the mother.“ It further said, “The use of the word `ordinarily' cannot be over-emphasized. It ordains a presumption, albeit a rebuttable one, in favour of the mother.“
Children's report cards can determine custody: SC
Mother Given Custody As Kids Do Better While Staying With Her
A child's performance in exams while staying with a parent would have a major bearing on the outcome of the legal battle between couples for their custody , the Supreme Court has said.
Remarkable improvement in two children's grades while in their mother's interim custody , compared with failure in exams during their stay with their father, convinced a bench of Justice A K Sikri and Justice Ashok Bhushan to award their custody to the mother, setting aside a Bombay high court order in the father's favour.
After being married for over 15 years, the woman had walked out of her matrimo nial home, alleging mental and physical cruelty. The couple's children -a boy aged 14 at the time and a girl of 10 -remained with the father. The woman got interim maintenance from her husband, but a trial court allowed the father custody as the children were in boarding school. There is some dispute as to how the children came in the custody of the mother. The husband claimed she did not return the children after taking them out during a court-permitted visitation period.The woman said her husband, without any court order, had handed over custo dy to her as the son had “miserably failed in his Class 9 exams and he wanted her to teach him so that he did not waste a year“.
When the couple first moved court, the magistrate interacted with the children and granted custody to the mother. The sessions court rejected the husband's appeal. But the HC, on February 17 last year, directed the woman to hand over custody to their father. She appealed against the order in the SC.
Justice Sikri, writing the judgment, said though the HC correctly discussed the `welfare principle', it gave no reasons as to how the princi ple weighed in favour of the father in the given facts and circumstances of this case.
“After the children came to stay with the mother... the son's academic performance improved significantly . He is getting very high grades... In fact, academic performance of the daughter has also gone up. This factor, though noticed by the HC, has been brushed aside with the observation that if the children were not doing well earlier, blame cannot be put on the father as it could be the result of the disputes between the parents,“ said the bench.
“In the process, what is ignored is that, in spite of the dispute still existing, the academic performance of the children, while in their mother's custody, has gone up tremendously ,“ it added.
Indian courts can decide custody cases despite foreign court’s verdict
Dec 23, 2022: The Times of India
Kolkata : Indian courts had the power to decide on child custody cases irrespective of what aforeign court had ordered, the Calcutta HC said, granting interim custody of a six-year-old child — a US citizen by birth — to his Rourkela-based mother, while allowing his US-based father visitation rights, reportsSaibal Sen.
A California court had directed that the child be repatriated to his father’s sole custody. The fatherthen filed a habeas corpus petition for his child, so that they could return to California. The HC held that the “principle of comity of courts” required “consideration of an order passed by a foreign court”, and not “its enforcement”.
The father had argued that his financial position allowed him to provide his child the best educationin the US. The child had s pent more time with his mother in India than in the US and repatriating him would mean he would have to spend a lot of time a lone, g iven his father’s busy schedule, the HC said.
Parent denied custody must be allowed to talk to child daily: SC
Amit Anand Choudhary, January 21, 2020: The Times of India
NEW DELHI: Holding it to be a part of human rights of a child to get love and affection of both parents who are estranged and locked in matrimonial dispute, the Supreme Court said the parent denied custody of the child should have the right to talk to him or her for 5-10 minutes every day.
A bench of Justices Deepak Gupta and Aniruddha Bose said most courts while granting custody to one spouse do not pass any orders granting visitation rights to the other spouse.
“A child, especially a child of tender years requires love, affection, protection of both parents... Just because the parents are at war with each other, does not mean that the child should be denied the care, affection, love or protection of any one of the two parents...,” the bench said.
The SC, while adjudicating the custody battle of a US-based NRI couple, said even if custody is given to one parent, the other parent must have sufficient visitation and contact rights. The court said it is only in extreme circumstances that one parent should be denied contact with the child and courts must assign the reason.
“ Unless there are special circumstances to take a different view, the parent denied custody of the child should have the right to talk to his/her child for 5-10 minutes everyday,” the bench said.
The court passed the order on a plea filed by a wife challenging order of the Rajasthan HC which directed her to go back to US to subject herself to court proceedings there on custody of two-and-half year-old daughter. She had left the US with her child despite a US court directing her not to leave the country.
The bench agreed with the contention of husband’s lawyer Prabhjit Jauhar who said it was his wife who initiated proceedings in the US court and the case must be adjudicated by that court. In case she refuses to go, the court directed that she then has to hand over the child to her husband or in-laws before the Register General of HC on February 3.
“In case the child goes to USA with the husband or either of his parents, the husband shall ensure that the child talks to her mother through video calling facilities everyday,” the court said.
SC: Child deserves love of both parents
Oct 20, 2019: The Times of India
The Supreme Court has said a child should not be deprived of the affection of either of the parents who are fighting a legal battle for custody and family courts should grant visitation rights in such a manner that the child gets love of both.
A bench of Justices Deepak Gupta and Suyra Kant, while deciding the plea of a man seeking visitation rights to his child whose custody was given to his wife, said courts should keep the interest of the child “at the foremost” while deciding such issues and passed the order in favour of the petitioner.
“However, we give liberty to the petitioner to approach the family court for enhancement of his visitation rights and we direct the family court to ensure that visitation rights are fixed in such a manner that the child gets to know and love his father. A child has a right to the affection of both his parents... The family court may also make suitable arrangements for visitation/ interim custody during vacation periods,” the bench said.
The court passed the observation days after another bench agreed to hear a plea for adopting joint parenting system under which a child will be looked after by both the parents after divorce instead of giving custody to one of them.
The apex court had issued notice to the Centre on a petition filed by an NGO ‘Save Child India Foundation’ which contended that a child suffers the most in a matrimonial dispute and mechanism should be put in place on how to deal with such cases to protect his or her interests.
Divorces granted by religious bodies
Ecclesiastical tribunals' decisions (Church courts)
The Supreme Court refused to give legal sanctity to divorce decrees granted by ecclesiastical tribunals, popularly known as church courts. This means that anyone remarrying after such a divorce decree would be committing the offence of bigamy.
A bench of Chief Justice J S Khehar and Justice D Y Chandrachud dismissed a four-year-old petition by Bengaluru-based octogenarian Catholic advocate Clarence Pais, who had sought legal sanctity for such decrees. He had pleaded that marriage and divorce among Catholics were governed by the church and in the absence of its recognition by law, unsuspecting men were facing prosecution for bigamy .
Additional solicitor general Neeraj Kishan Kaul said the Supreme court ruling in the Molly Joseph vs George Sebastian case in 1996 had settled the issue on the authority of the church courts.
Kaul said the SC had ruled that “unless Divorce Act recognises the jurisdiction, authority or power of ecclesiastical tribunal (sometimes known as church court), any order or decree passed by such tribunal cannot be binding on the courts which have been recognised under the provisions of the Divorce Act to exercise power in respect of granting divorce and adjudicating in respect of matrimonial matters“.
The dismissal of the petition means any Catholic man who remarries after a divorce decree granted by a church court would be committing the offence of bigamy unless his divorce was sanctified by a court decree under the Christian Divorce Act, 1869.
“If criminal courts, while considering prosecution under IPC Section 494 (bigamy), reject the application of canon law as the personal law of Catholics, a very serious result will follow and hundreds of spouses under second marriage will have to face prosecution, jail and fine,“ Pais said.
Cannot override law
Divorce granted by church court can't override law: Supreme Court, Jan 19, 2017: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
SC has said that divorces granted under Christian personal law are not valid
Divorce granted by ecclesiastical tribunal under Christian personal law are invalid as it cannot override law, it said
Divorce granted by ecclesiastical tribunal under Christian personal law are not valid as it cannot override the law, the Supreme Court said on Thursday as it rejected a PIL that sought according legal sanction to such separations granted by the Church Court. A bench comprising Chief Justice J S Khehar and Justice D Y Chandrachud dismissed the plea filed by Clarence Pais, a former president of a Karnataka Catholic association, saying the issue has been settled by it in its 1996 verdict delivered in the case of Molly Joseph versus George Sebastian. "Canon Law (personal law of Christians) can have theological or ecclesiastical implications to the parties. But after the Divorce Act came into force, a dissolution or annulment granted under such personal law cannot have any legal impact as statute has provided a different procedure and a different code for divorce or annulment," the apex court had then ruled.
Pais, in his PIL filed in 2013, had said the divorce granted by a Church, set up under its personal law, should be considered valid under the Indian common law as was done in the case of Muslims with regard to 'triple talaq'. Former Attorney General Soli Sorabjee, appearing for Pais, had contended that when oral 'triple talaq' could get legal sanctity for granting divorce to Muslim couples, why could Canon law decrees not be made binding on courts of law. He had alleged that many Catholic Christians, who married after getting divorce from Christian courts, faced criminal charges of bigamy as such divorces are not recognised by the criminal and civil courts.
Pais, in his plea, had said, "It is reasonable that when the courts in India recognise dissolution of marriage (by pronouncing the word talaq three times) under Mohammedan Law which is Personal law of the Muslims, the courts should also recognise for the purpose of dissolution of marriage Canon Law as the personal law of the Indian Catholics."
The plea contended that Canon Law is the personal law of Catholics and has to be applied and enforced by a criminal court while deciding a case under section 494 (bigamy) of IPC.
"This is also applicable for sanction of prosecution considered for alleged bigamy of a Catholic spouse who has married after obtaining a decree for nullity of the first marriage from the Ecclesiastical Tribunal (Christian court)," it had said.
The Centre, however, had opposed the plea saying Canon law cannot be allowed to override Indian Christian Marriage Act, 1872 and Divorce Act, 1869.
Foreign courts' decisions
Ex parte divorce decree invalid: HC
‘Irretrievable Marriage Breakdown Not Recognized Under Act’
Smriti Singh TNN 25/04/2013
New Delhi: In what can have serious implications for divorces involving NRIs, Delhi high court has held that a divorce obtained by an NRI from a foreign court without the spouse’s submission to the jurisdiction of that court is invalid.
The court has also held that a divorce granted by a foreign court on the ground of “irretrievable” breakdown of marriage is not recognised under the Hindu Marriage Act and the dissolution of marriage cannot be valid. The court’s ruling came while rejecting the claim of an Indian-origin UK resident that the Ilford County Court, UK, had in 2011 already granted a divorce.
The man had challenged the trial court’s order which had declared that divorce invalid. He sought dropping of the divorce proceedings against him on his wife’s plea for dissolution of marriage under the Hindu Marriage Act. The woman, through her counsel, Prashant Mendiratta, claimed that the foreign divorce decree was an ex parte decree which she had been unable to contest. “The said decree is not recognised in India, and as such, the petitioner is not entitled to any relief,” the counsel said.
The court cited a Supreme Court judgment which had held that a decree of divorce granted by a foreign court is not valid in India if the ground is not recognised by Indian law.
“Both parties are Indians and the marriage between them was solemnized at New Delhi according to Hindu rites and both are governed by the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA). Their marriage has been dissolved by a court in the UK on the ground of having broken down irretrievably which is not a ground for divorce under HMA ...” Justice Veena Birbal said.
The court also rejected the man’s argument that the UK court had made the decree “absolute” on the ground of “irretrievable breakdown” of marriage and his wife was also informed about the proceedings there.
Accepting the wife’s argument that the divorce granted by the court in the UK was an ex parte divorce decree, Justice Birbal said, “Respondent (wife) never submitted herself to the jurisdiction of the said (UK) court. On June 15, 2011, she had lodged a representation before the Ilford County Court informing that she was in India and had filed a divorce petition here.
“She also informed (the court) that she was in acute financial difficulty (and won’t be able) to come to London to contest the divorce case. She wrote in detail about her financial condition and also informed that she had already filed a divorce petition in India. She requested the UK court not to make the divorce decree ‘absolute” ... In these circumstances, it cannot be said that she had submitted to the jurisdiction of the foreign court,” the court said.
REINING IN RUNAWAY GROOMS: HC RULES
An ex parte divorce by a foreign court is invalid
To get a divorce from a foreign court, both parties have to submit to its jurisdiction
Ground of “irretrievable breakdown of marriage” not a ground under Hindu Marriage Act
STANDING INSTRUCTIONS
When faced with ex parte divorce cases, courts in India rely on a celebrated 1991 Supreme Court judgment
SC has empowered matrimonial courts to issue non-bailable warrants to enforce attendance of parties
In one case, HC prohibited NRI from obtaining one-sided divorce decree from a foreign court
If any NRI ignores court stay on ex parte divorce, it’s considered contempt of court
Grounds for divorce
Character assassination
`Character assassination ground for divorce' Oct 08 2016 : PTI
A false character assassination charge by a spouse would be “matrimonial cruelty“ entitling the other to seek divorce, the Delhi high court said on Friday .
“It is now beyond cavil that if a false character assassination allegation is made by either spouse, it would invariably constitute matrimonial cruelty to entitle the other spouse to seek divorce,“ a bench of justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Pratibha Rani said.
The court observed this while dismissing a woman's plea challenging a trial court order allowing her husband's petition for divorce on the ground of cruelty .
Concurring with the trial court findings, the high court said the reasons recorded by the Family Court while granting divorce was fully borne out from the material available on record and “cannot be faulted with“.
“Therefore, the decree of divorce granted by the Family Court has to be upheld,“ the bench added.
The man, who is a teacher in a school here, had sought divorce claiming he was a nonsmoker and a teetotaler, but was defamed by his wife as an alcoholic and a womaniser.
“This adversely affected his reputation in the family so much so that he even thought of committing suicide,“ the high court noted in its verdict.
The woman, however, had refuted his claim and said she was harassed by demand for dowry . Brushing aside the woman's contention, the court observed that “the disgusting accusations made by the wife against the husband of being in illicit relationship, referring him as a drunkard, are serious in nature assassinating his character and harming his reputation as a teacher.
“She has failed to prove any of the above but yet resisting the divorce which, if accepted, would make life of the two even more complex and unbearab le.“ it added.
Broken marriage
Ajay Sura, January 10, 2022: The Times of India
CHANDIGARH: It would be disastrous if divorce is not granted to a couple whose marriage has broken once and for all, the Punjab and Haryana HC has said while overturning a Gurgaon family court’s order in 2015 that rejected a husband’s plea for divorce from his long estranged wife.
“…Marriage, which is dead for all purposes, cannot be revived by the court’s verdict if parties are not willing since marriage involves human sentiments and emotions and if they have dried up, there is hardly any chance of their springing back to life on account of artificial reunion created by court decree,” the HC division bench of Justice Ritu Bahri and Justice Archana Puri said.
The couple was living separately for around 18 years and the woman was allegedly not ready to settle the dispute amicably. While the husband wanted a divorce and was ready to pay one-time alimony, the wife was not accepting that.
The man approached the Gurgaon family court and sought dissolution of his marriage on the grounds of mental cruelty. The court dismissed his plea in May 2015. He filed an appeal in the HC later. The HC observed that the man and his wife have been living separately since November 2003. The husband offered Rs 7.5 lakh to his wife to agree to divorce through mutual consent. But on October 12, 2021, the court was informed that the woman was not ready for mutual divorce. The man was directed to make a fixed deposit of Rs 10 lakh for his wife.
Denial of sex
Denying sex ground for divorce: HC, Oct 13 2016 : The Times of India
Husband Says Suffered For Over 4 Years
The Delhi high court has dissolved a marriage on the ground that the woman denied sex to husband for a long period amounting to mental cruelty .
A bench of justices Pradeep Nandrajog and Pratibha Rani said denial of sex without justification counts as a ground for divorce and allowed the plea of the husband seeking divorce. He had complained that his wife subjected him to mental cruelty by denying physical relations for four-anda-half years, though she was not suffering from any physical disability that could be used as a justification.
In its judgment, the bench referred to the settled legal position that “denial of sex to a spouse itself amounts to causing mental cruelty“. “The appeal being well-founded deserves to be allowed,“ it said, adding “we grant a decree of divorce in favour of the husband“.
In its verdict, HC also took into account the fact that the wife had not contested the allegation before the trial court.
The husband had approached the high court challenging a trial court order which dismissed his divorce petition, saying that the instances of cruelty pleaded and proved by him did not prove adequate to count as a ground for divorce. However, the high court pointed out that the wife had even stopped appearing in court after a few initial hearings and it was forced to proceed ex parte. The husband informed the high court that their marriage was solemnised in 2001 and they have two children.
The husband said that even his family members were subjected to mental cruelty by his wife as she did not do any household work. When her conduct became unbearable, his parents asked the couple to live in a separate portion of the same house. In her written statement filed before the trial court, the wife had initially contested the divorce plea filed by the husband and denied the allegations
Filing of multiple complaints by spouse
AmitAnand Choudhary, February 27, 2021: The Times of India
The Supreme Court said that filing of multiple complaints by an educated person against their life-partner amounts to mental cruelty as it affects the reputation and career of a person and divorce can be granted on that ground.
A bench of Justices Sanjay Kishan Kaul, Dinesh Maheshwari and Hrishikesh Roy said such behaviour on the part of spouse cannot be termed as “normal wear and tear” of married life, particularly when the person is educated and well aware of the adverse consequences of filing complaint. It allowed divorce plea of an army officer whose wife had filed multiple complaints against him before various authorities, including the Army chief.
The officer contended that his wife had made several defamatory complaints to his superiors in the Army for which a court of inquiry was held against him. He said that similar complaints were also filed before other authorities, including the State Commission for Women. His wife, however, contended that she filed complaints out of her desperation to save the matrimonial relationship.
The Bench, after hearing both sides, said her action undermined the dignity and reputation of the officer and the wronged party cannot be expected to continue with the matrimonial relationship and there is justification for him to seek separation.
“Here the allegations are levelled by a highly-educated spouse and they do have the propensity to irreparably damage the character and reputation of the appellant. When the reputation of the spouse is sullied amongst his colleagues, his superiors and the society at large, it would be difficult to expect condonation of such conduct by the affected party,” the bench said.
The apex court quashed the Uttarakhand HC order which had set aside the divorce granted by a family court. The HC had termed the conduct of the parties as “squabbles of ordinary middle class married life” and had passed the order in favour of the wife.
Forcible sex
Forcible sex is ground for divorce: Punjab and Haryana high court June 9, 2018: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
The HC recently allowed a woman's plea for dissolution of marriage, almost 4yrs after the lower court turned it down.
The lower court had said it was for her to establish that her husband had committed unnatural sex against her
The lower court also held that no specific instance had been mentioned by her.
The Punjab and Haryana high court has held that "forcible sexual intercourse" and "adoption of unnatural means" which are forced upon the other spouse are grounds for divorce.
The high court recently allowed a Bathinda woman's plea for dissolution of her marriage, almost four years after the lower court had turned it down. The lower court had said it was for her to establish that her husband had committed oral and unnatural sex against her, and held that no medical evidence or a specific instance had been mentioned by her.
"Be that as it may, we find that the claim of the appellant has been wrongly rejected," the division bench of Justices M M S Bedi and Hari Pal Verma said in the June 1 judgment.
"The act of sodomy, forcible sexual intercourse and adoption of unnatural means which are forced upon the other spouse and result in unbearable pain to the extent that one is forced to stay away would certainly be a ground to seek separation or decree of divorce," it said.
The woman, a postgraduate diploma holder in Computer Application, had married the Bihar resident in January 2007 and had a child with him. According to the woman's plea, her family had even given dowry. The woman's family had been told that the man was an engineer with a private company, a claim which the petitioner alleged turned out to be false. The woman alleged that for fulfilling his lust, her husband often beat her up and adopted "unnatural means". In its judgment, the court observed that the nature of the allegations levelled by the woman was very serious.
Irretrievable breakdown
AmitAnand Choudhary, Oct 10, 2019: The Times of India
Though ‘irretrievable breakdown of marriage’ is not a ground for divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act and Special Marriages Act, the Supreme Court has said divorce can be granted if a marriage is totally unworkable, emotionally dead and beyond salvage.
Coming to the rescue of a man fighting a legal battle for divorce for the last two decades as his plea was rejected by a lower court and Andhra Pradesh HC after his wife refused to consent for separation, a bench of Justices S K Kaul and M R Shah invoked the SC’s inherent powers under Article 142 to do “complete justice” and allowed the petition saying the marriage had broken irretrievably. The couple had been living separately for 22 years after their relationship ran into rough weather a few years after marriage in 1993.
It’s fit case to invoke Art 142 to dissolve marriage: SC
The apex court in a series of verdicts has asked the Centre to amend the law to introduce irretrievable breakdown as a ground of divorce but the law remains unamended and divorce is denied even if a couple are not living together for years and their relationship bruised beyond repair. This effectively denies them an opportunity to explore life afresh as their marriage survives in law even if not in substance.
Even the Law Commission, in its reports in 1978 and 2009, recommended the Centre to take “immediate action” to amend the laws with regard to “irretrievable breakdown” where a “wedlock became a deadlock”. As the Centre failed to act on the suggestions, the apex court has from time to time invoked Article 142 to grant divorce even though existing laws do not recognise the ground for divorce.
The SC said, “In the present case, admittedly, the husband and wife have been living separately for more than 22 years and it will not be possible for the parties to live together. Therefore, we are of the opinion that while protecting the interest of the respondent wife to compensate her by way of lump sum permanent alimony, this is a fit case to exercise the powers under Article 142 to dissolve the marriage between the parties.” The bench rejected the wife’s plea that the marriage cannot be dissolved without her consent and granted relief to husband after noting that all efforts to continue the marriage had failed and there was no possibility of a reunion between the parties.
Marital rape
See also Marital rape: India
August 7, 2021: The Times of India
KOCHI: Marital rape can be accepted as a ground to grant divorce by recognising it as a form of cruelty, the Kerala high court has held. The Supreme Court had, in 2019, turned down a plea to accept marital rape as a ground for divorce. The high court gave its ruling while hearing an appeal filed by a husband against a divorce granted by a family court in 2014.
“Treating wife’s body as something owing to husband and committing sexual act against her will is nothing but marital rape. Right to respect for his or her physical and mental integrity encompass bodily integrity; any disrespect or violation of bodily integrity is a violation of individual autonomy...,” the high court said.
Though such conduct cannot be penalised, it falls in the frame of physical and mental cruelty,” said a division bench of Justices A Muhamed Mustaque and Kauser Edappagath, while referring to the allegation of unnatural sex against the husband.
The case involves a doctor who married the daughter of a realtor in February 1995. A car, a flat and 501 sovereigns of gold were gifted but the husband suffered heavy losses in real-estate business. The father-in-law had also given Rs 77 lakh to the man to pay off debts and it was also alleged that he misappropriated the gold. The woman sought a divorce in 2009. The HC also said a uniform, secular law on marriage and divorce that makes it easier for a spouse to exercise his/her free will to separate is the need of the hour.
The HC said the present legislation on divorce curtails an individual’s free will to separate by limiting it through defined grounds, such as cruelty, adultery, desertion, etc. “A spouse in a marriage has a choice, a choice not to suffer, which is fundamental to the autonomy guaranteed under natural law and the Constitution. Law cannot compel a spouse to suffer against his/her wish by denial of divorce,” it said.
Trying to separate spouse from in-laws: SC
PTI, `Divorce valid if wife tries to separate spouse from in-laws' Oct 09 2016 : The Times of India
In a Hindu society , it is a “pious obligation“ of the son to maintain parents and the persistent effort of the wife to constrain the husband to be separated from his family constitutes an act of `cruelty' enabling him to get divorce, the Supreme Court has said.
A bench of Justices Anil R Dave and L Nageshwara Rao made the observations while confirming the decree of divorce sought by a Kar nataka-based man.
The order was passed while setting aside the Karnataka high court judgment which had dismissed the decree of divorce granted by a Bangalore family court in 2001.
“In a Hindu society, it is a pious obligation of the son to maintain the parents. If a wife makes an at tempt to deviate from the normal custom of the society , she must have some justifiable reason for that and, in this case, we do not find any justifiable reason, except monetary consideration of the wife.
“In our opinion, normally , no husband would tolerate this and no son would like to be separated from his old parents and other family members, who are also dependent upon his income. The persistent effort of the wife to constrain the husband to be separated from the family would be torturous for husband and in our opinion, the trial court was right when it came to the conclusion that this constitutes an act of `cruelty', the HC said.
It further said, “It is not a common practice or desirable culture for a Hindu son in India to get separated from his parents on getting married at the instance of the wife, especially when the son is the only earning member in the family .A son, brought up and given education by his parents, has a moral and legal obligation to take care and maintain the parents.
Wife forcing husband to live away from parents
Aheli Banerjee, April 10, 2023: The Times of India
KOLKATA: The Calcutta High Court has recently ruled that a husband has the right to file for divorce on grounds of mental cruelty if his wife tried to compel him to separate from his parents without justifiable reason.
The court added it was the "pious obligation of the son to live and maintain the parents", adding a son living with his parents was "absolutely normal in Indian culture and ethos". Saying this, the division bench of justices Soumen Sen and Uday Kumar on March 31 turned down a woman's plea challenging a fam-ily court's decision to grant her husband divorce.
The case dates back to 2009, when a family court in West Midnapore granted Prashant Kumar Mandal div-orce from his wife, Jharna, on grounds of cruelty.
The high court bench was hearing the wife's plea, challenging this order.
The family court had bas-ed its order on the premise that since their 2001 marriage, Jharna had publicly insulted Prashant, calling him "unemployed" and a "cow-ard". He was then teaching part-time in schools and giv-ing private tuitions, and his income was insufficient to support the family. To make ends meet, he would occasionally ask Jharna - who was earning Rs 1,400 a month - to help out with the finances. Even as Prashant was in the process of joining a government job, Jharna filed a criminal case against him and his parents on allegations of "torture", stopping him from getting the job.
NOT grounds for divorce
Infertility is no ground for divorce; Deserting wife is cruelty: HC
Saibal Sen, January 19, 2023: The Times of India
KOLKATA: Infertility cannot be a ground for divorce and deserting one's wife who is battling mental and physical health issues due to infertility is "mental cruelty", the Calcutta High Court has ruled.
The HC was hearing an appeal by a man for quashing of criminal charges slapped on him after he filed for divorce citing "persistent mental torment and agony" caused by his wife, who was battling mental health issues due to to primary infertility and premature menopause.
The couple were married for nine years and the wife, a schoolteacher, had also undergone treatment at Bengaluru's National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences.
A month after the husband filed for divorce in June 2017, the wife filed criminal charges against him. The Beliaghata police filed a charge sheet against the husband on December 6, 2017, implicating him for criminal breach of trust (406 IPC), physical and mental cruelty (498A) and voluntarily causing hurt (323 IPC).
The HC refused to interfere in the trial court proceedings.
"The reason of infertility is not a ground for divorce. There are several options to become parents. A spouse has to be understanding in these circumstances as it is the other who can help one to regain her/his mental, physical and emotional strength. To be able to face the world, the society in general, bravely together," Justice Shampa Dutt (Paul) said.
This is cruelty under 498A: HC
Hearing a case in which a husband sought divorce from his wife who developed premature infertility, Justice Shampa Dutt (Paul) took exception to the timing of the divorce plea. "The wife appears to have developed primary infertility with premature menopause, which is a great mental shock for a woman who is yet to become a mother.... further stress was added with the wife losing her mother.... it is the spouse's duty to be the strength which the other has lost," the judge said in order on Tuesday. The HC asked, "If the petitioner/husband had the problem, would he not expect support from his wife...?"
The judge said it was "insensitive of the petitioner to ask the opposite party in such traumatic situation for a divorce by mutual consent, which amounts to mental cruelty..." She said this was 'cruelty' under 498A IPC as it affected one's life & health.The HC said the case diary and the charge sheet "makes out a clear prima facie case of a cognizable offence against the accused/petitioner”.
No divorce for man with terminally ill wife: SC
The Times of India, Dec 04 2015
Amitanand Choudhary
SC rejects divorce plea of man whose wife is terminally ill
A husband is duty-bound to stand by his wife in difficult times, take care of her and refrain from seeking divorce when she is terminally ill and fighting for her life, the Supreme Court has said. A bench of Justices M Y Eqbal and C Nagappan said this while turning down the divorce plea of a man even though his wife had consented for separation after the court came to know that she is suffering from cancer and needs immediate treatment.
The court suspected the woman was being pressured into accepting a settlement because of her need for money for treatment and asked the husband to immediately make funds available. The court said that for a Hindu wife, her husband is god. The ruling by an SC bench of Justices M Y Eqbal and C Nagappan said a Hindu wife devotes her life in her husband's selfless service and this is why marriage law enjoins a corresponding duty on the husband to look after her comforts.
“Hindu marriage is a sa cred and a holy union of husband and wife by virtue of which the wife is transplanted in the household of her husband and takes a new birth. It is a combination of bone-to-bone and flesh-toflesh. A wife not only shares the life and love, but the joys and sorrows, the troubles and tribulation of her husband and becomes an integral part of her husband's life,“ it said.
The bench asked the husband to pay Rs 5 lakh for her treatment and said the divorce plea would be considered only after she gets well.Applying the principle of Contract Law, the bench said the wife might have given consent for divorce under undue influence as she needed money for treatment and the husband had agreed to pay Rs 12.5 lakh for settlement.
“It is evident that the wife needs money for the treatment of breast cancer. Hence, it cannot be ruled out that in order to save her life by getting money , she agreed for a settlement of dissolution of marriage,“ the bench said.
No divorce for falsehood, suppression of crucial information
Shibu Thomas, Woman who left hubby for lover denied divorce by HC, Oct 13 2016 : The Times of India
The Bombay high court refused to grant divorce to a Borivli woman who hid the fact that she was living with another man and also had a child from that relationship. A division bench of Justices Abhay Oka and Amjad Sayed also upheld a family court order imposing a Rs 50,000 fine on the woman, who had waged an over-decade-old litigation seeking divorce from her husband on the grounds of cruelty and desertion.
The court said the woman had suppressed crucial information--the fact that she was living in with another man and had actually gone to stay at her husband's house for a few days when she had fought with her partner, after she filed the divorce case.
“Her conduct of maintaining a relationship before filing the divorce petition and during pendency of the petition will dis-entitle her from seeking divorce on the grounds of cruelty and desertion,“ said the judges, adding, “The manner in which the material facts are suppressed by her are sufficient to draw a conclusion that her case is based on falsehood.“ Her last-ditch plea, that there was an irretrievable breakdown of the marriage, failed to move the court.
Not wearing mangalsutra, vermillion no ground
Not wearing mangalsutra, vermillion no ground for divorce, says HC
The Nagpur bench of the Bombay high court has ruled that men can't seek divorce on grounds of their wives not covering their head or wearing matrimonial symbols like mangalsutra and vermillion all the time. The move may help numerous married women who refuse to conform to age-old traditions but are forced to abide by the same only for their husbands.
The court dismissed a man's plea who demanded divorce contending that his wife often used to remove vermillion and take off her mangalsutra to irk him. She also refused to cover her head with her saree's pallu, as per the tradition in his family, he alleged. The court observed that, “Merely because a woman sometimes removes her mangalsutra and vermilion, a man can't seek the severance of matrimonial ties.A woman can't be expected to cover her head with a pallu in the 21st century. In any case, these can't be the sole grounds for divorce.“
Hindu Marriage Act
Procedure under HMA; divorce under Article 142
Khadija Khan, May 2, 2023: The Indian Express
A five-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court on Monday ruled that it can exercise its plenary power to do “complete justice” under Article 142(1) of the Constitution to dissolve a marriage on the ground that it had broken down irretrievably, without referring the parties to a family court where they must wait 6-18 months for a decree of divorce by mutual consent.
The Bench led by Justice S K Kaul held that the court could, in the exercise of this power, waive the mandatory six-month waiting period for divorce under The Hindu Marriage Act (HMA), 1955, and allow the dissolution of the marriage on grounds of irretrievable breakdown even if one of the parties was not willing. (Shilpa Sailesh vs Varun Sreenivasan case)
What is the current procedure for divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act?
Section 13B of the HMA provides for “divorce by mutual consent”. Both parties to the marriage must together file a petition to the district court “on the ground that they have been living separately for a period of one year or more, that they have not been able to live together and that they have mutually agreed that the marriage should be dissolved”.
Under Section 13B(2) of the Act, the parties must move a second motion before the court “not earlier than six months after the date of the presentation of the [first] petition…and not later than eighteen months after the said date, if the petition is not withdrawn in the meantime”.
The mandatory six-month wait is intended to give the parties time to withdraw their plea.
Thereafter, “the court shall, on being satisfied, after hearing the parties and after making such inquiry as it thinks fit…that the averments in the petition are true, pass a decree of divorce declaring the marriage to be dissolved with effect from the date of the decree”.
A petition for divorce by mutual consent can be moved only after a year of the marriage. However, Section 14 of the HMA allows a divorce petition sooner in case of “exceptional hardship to the petitioner or of exceptional depravity on the part of the respondent”.
A waiver of the six-month waiting period under Section 13B(2) can be sought in an exemption application filed before the family court.
In its 2021 ruling in Amit Kumar vs Suman Beniwal, the SC said, “Where there is a chance of reconciliation, however slight, the cooling period of six months from the date of filing of the divorce petition should be enforced. However, if there is no possibility of reconciliation, it would be meaningless to prolong the agony of the parties to the marriage.”
The process of obtaining a decree of divorce is often time-consuming and lengthy owing to a large number of similar cases pending before family courts.
And what is Article 142 of the Constitution?
Under Subsection 1 of Article 142, the Supreme Court “may pass such decree or make such order as is necessary for doing complete justice in any cause or matter…, and any decree so passed or order so made shall be enforceable throughout the territory of India”.
While the power available under Article 142 is sweeping, the SC has defined its scope and extent through its judgments. The majority opinion in Prem Chand Garg (1962) laid down that “an order to do complete justice…must not only be consistent with the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution, but it cannot even be inconsistent with the substantive provisions of the relevant statutory laws”. The seven-judge Bench in A R Antulay (1988) upheld Prem Chand Garg.
In the Bhopal gas tragedy case (Union Carbide Corporation vs Union of India, 1991) the SC underlined the wide scope of Article 142(1), which confers power “at an entirely different level and of a different quality”.
The present case was originally filed in 2014, where the parties sought a divorce under Article 142. While granting divorce to the parties, the SC said it can depart from procedure as well as existing substantive laws only if the decision to exercise the power under Article 142(1) is “based on considerations of fundamental general and specific public policy”.
The fundamental general conditions of public policy refer to the fundamental rights, secularism, federalism, and other basic features of the Constitution; specific public policy was defined by the court to mean “some express pre-eminent prohibition in any substantive law, and not stipulations and requirements to a particular statutory scheme”.
“Irretrievable breakdown”
What factors can courts consider while deciding if a marriage has irretrievably broken down? During the pendency of the case last year, the court said that it would determine what rules should be followed while dissolving marriages directly under Article 142 of the Constitution.
The first and most “obvious” condition is that the court should be fully convinced and satisfied that the marriage is “totally unworkable, emotionally dead and beyond salvation and, therefore, dissolution of marriage is the right solution and the only way forward”.
The court laid down the following factors:
- the period of time that the parties had cohabited after marriage;
- when the parties had last cohabited;
- nature of allegations made by the parties against each other and their family members;
- orders passed in the legal proceedings from time to time;
- cumulative impact on the personal relationship;
- whether, and how many attempts were made to settle the disputes by a court or through mediation, and when the last attempt was made.
The court also noted that the period of separation should be sufficiently long, and “anything above six years or more will be a relevant factor”.
It emphasised the need to evaluate the factors according to the economic and social status of the parties, including their educational qualifications; whether they have any children; their age; and whether the spouse and children are dependents.
Divorce for Hindu married to non-Hindu
Hindu married to non-Hindu can't get divorce under Hindu Marriage Act: Bombay high court
PTI | Dec 28, 2013
MUMBAI: The Bombay high court has held that a Hindu married to a non-Hindu in accordance with Hindu rituals cannot seek divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act.
Accordingly, a bench headed by Justice VK Tahilramani upheld a family court order which rejected a petition filed by Niranjani Roshan Rao, a Hindu, seeking divorce from husband Roshan Pinto on the ground that he was a Christian at the time of marriage and was professing the same religion till today.
As the family court rejected her petition, she moved the high court, which, on December 24, rejected her appeal and upheld the lower court order.
"We are of the view that an order passed by the learned judge of the family court is perfectly legal and calls for no interference in exercise of appellate jurisdiction," said the bench while dismissing the appeal.
The appellant had filed the petition in family court seeking a decree of nullity of marriage and alternatively claimed divorce on the grounds of cruelty. She said, on January 13, 1999, she was married to respondent as per Hindu rituals. At the time of marriage, she was a Hindu while the respondent was a Christian.
After their marriage, they continued to profess their respective religions. Even at the time of filing of the petition, they continue to practice and follow their respective religions.
The appellant-wife argued that their marriage was null and void as it was in contravention of essential condition of valid marriage provided under section 5 of the Hindu Marriage Act, i.e. both the partners should be Hindus at the time of marriage.
The family court rejected the petition in exercise of powers under Order 7 Rule 11 of CPC, as the petition did not disclose any triable cause of action.
In other words, the family court said the petitioner had no right to file such a petition under the Hindu Marriage Act and as such cannot seek any relief. Both were not Hindus at the time of marriage and hence do not fulfill the conditions laid down under the act.
The high court observed that the appellant herself has stated that the respondent was not a Hindu at the time of marriage or thereafter.
"If this condition is not fulfilled and there was no contravention of provisions under Section 5 of the Hindu Marriage Act, the family court was right in saying that she had no right to file such a petition", the bench said.
Moreover, provisions of Hindu Marriage Act can be applied in cases when both the spouses were Hindus and their marriage is performed as per Hindu rites and rituals, the judges said.
It is also an essential condition under the act that at the time of filing a petition for divorce, both the spouses were Hindus by religion, ruled the bench.
Incidence of divorce, separation
According to religion, 2001, 2011
See graphic: The incidence of divorce and marital separation among Buddhists, Christians, Hindus, Jains, Muslims and Sikhs in India, 2001, 2011

According to religion, 2011
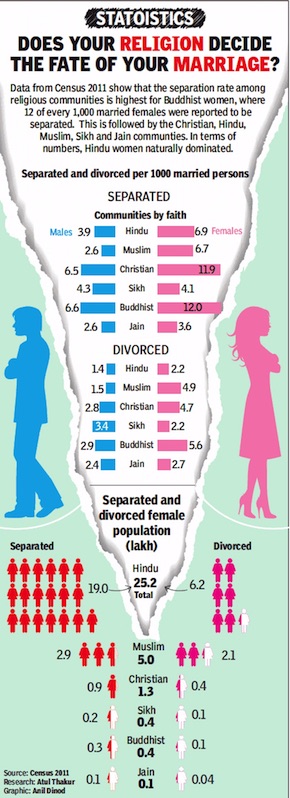
From: January 3, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Separated and divorced per 1000 married persons, 2011, religion-wise
Men’s rights
As in 2020
Men’s rights in case of separation, March 16, 2020: The Times of India
With men complaining of a legal skew in divorce and maintenance, here’s what they need to know about their rights, says Riju Mehta
Given that women are at the receiving end of most marital and financial problems, it’s no surprise that men in similar situations are often ignored. They not only complain of a legal skew in favour of women when it comes to divorce, maintenance and child custody, but also in dowry-related cases. Their claims could be well-founded considering the low conviction rate of 1.5% and high acquittal rate of 43.1% in crimes under the Dowry Prohibition Act, as per the 2018 National Crime Records Bureau data. Here are the legal rights married men should be aware of.
1 Divorce
The husband has a right to file a petition for divorce with or without mutual consent. For the latter, the grounds remain the same as that for a wife. These include cruelty, desertion, conversion, adultery, disease, mental disorder, renunciation and presumption of death. To ensure a favourable response by the court, keep a few things in mind before filing for divorce. Ensure a cordial relationship with wife, excluding physical, verbal or sexual abuse. Even if you find it difficult to stay under the same roof, do so to avoid the additional expense of a second house and to collect all documents related to divorce. It is also best not to enter into an extra-marital relationship before the divorce is finalised as it will weaken your case. Have a clean social media record, without any nasty messages, texts, threats or abuse sent to wife in the heat of the moment.
Conduct all financial transactions, sale or purchase before filing for divorce as it will impact the split of physical and financial assets in case the divorce is without mutual consent. If you think the wife may misuse your credit card or empty out a joint bank account, cancel the card and withdraw money before filing the petition.
2 Maintenance
Men’s rights to maintenance can vary under different Acts. Under the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955, both husband and wife can claim maintenance, while only the woman can do so under the Special Marriage Act, 1954. Men can avoid paying maintenance under certain circumstances. If the husband can prove the wife is earning enough to maintain herself, or that he is not earning enough to maintain himself, or that the spouse has remarried, deserted him or committed adultery, the husband does not have to pay maintenance. He may not have to pay interim maintenance either if he can prove that he is unable to earn and maintain himself, or that the wife is earning and can sustain on her own income.
3 Child custody
In a mutual consent divorce, the couple can decide about the child’s custody, which can either be full or joint, and the courts typically agree. In a contested divorce, men have an equal right to the child’s custody, even though earlier the mother was favoured by courts and granted full custody. Of late, the courts have started granting custody to the partner who is better able to look after the child’s needs.
Mutual consent
SC on Mutual consent divorces
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
HC verdict may speed up divorce by mutual consent
Swati Deshpade | TNN
Mumbai: A recent decision of the Bombay high court will now help speed up divorce for couples wishing to end their bitter legal battle through mutual settlement.
The HC has held that the six-month cooling off period for a couple, who file a joint petition for divorce on grounds of irretrievable breakdown of marriage, cannot be insisted upon by the family court if the couple are separate for a year and their divorce plea has already been pending in court for over six months. ‘‘Parties who settle their dispute are not required to be penalised for doing so,’’ said Justice Roshan Dalvi.
A couple married under the Hindu Marriage Act in May 2005 had lived for a year before separating. The husband then filed for divorce a year later on ground of cruelty by his wife. During the trial, both traded charges of cruelty and harassment against each other. But soon the couple agreed to bury the hatchet and withdrew their allegations to settle the dispute. In December 2009, they filed consent terms for a mutual divorce plea and sought a waiver of the six-month period, stipulated under law to enable the couple to reconsider their decision. But the family court judge, who presides over the seventh court, rejected their request for a waiver.
If couple wants divorce, courts cannot ask for reasons: Madras HC
The Times of India, Aug 11 2016
If a married couple wants divorce by mutual consent, it is not a court's business to deny them judicial separation by insisting on knowing the reason for their decision, the Madras high court has said.
Noting that a court could not act like a fact-finding authority , a division of Justice K K Sasidharan and Justice N Gokuldas said: “In case the marriage is a failure and the parties wanted to put an end to the marital bond, the court should respect the sentiments and grant divorce. It is not the intention of the legislature to deny divorce in spite of the parties taking a conscious decision to part ways.“
Rapping a family court in Tirunelveli for having dismissed a joint divorce plea filed by a couple that had been living separately for more than a year, the judges said: “Once it is convinced that it would not be possible for the parties to live together and that they have opted to dissolve the marriage peacefully the endeavour of the court must be to grant a decree of divorce rather than compelling them to live separately even thereafter.“
In the current case, the couple was married in May 2013, but started living separately from July 2014 onwards. In 2015, they filed a jo int petition for dissolution of the marriage, but it was rejected by the court on the ground that they had not mentioned the reasons for their separation.
The bench, disapproving of the order and setting it aside, said that under Section 13-B(2) of the Hindu Marriage Act, a court has to satisfy as to whether the marriage has been solemnised and that the averments in the petition are true. “In case the parties have been living separately for one year before the initiation of the joint petition for divorce and there is no scope for reunion, normally , the court has no other option than to grant the degree of divorce,“ the judges said.
The only reason assigned by the family court to dismiss the petition is that the parties have not assigned any reason for not being able to live together, the bench said, adding: “Whatever may be the reason, psychological or otherwise, it stands established that the parties have not been able to live together, and have been living separately from July 18, 2014 onwards. The parties have mutually agreed that their marriage should be dissolved. This is all Section 13-B of the Act requires, and when that ingredient stands satisfied, it is not possible to throw out the joint petition against the wishes of the parties.“
SC: 6-month wait for mutual consent divorce not mandatory
Two months after the Supreme Court held that a six-month wait for a mutual consent divorce is not mandatory, the Mumbai family court waived the “cooling off” period for a couple estranged for almost a decade.
It helped reduce the agony of a Mumbai woman battling cancer, and her husband of three decades who lives abroad. The waiver is the first in Mumbai since the SC ruling, in a freshly instituted mutual consent divorce plea, said advocate Anagha Nimbkar. She had sought the waiver on the couple’s behalf last month when she filed their joint divorce plea citing irretrievable breakdown of their long marriage.
The couple, married in 1987, have been living apart since 2008. Diagnosed with cancer and under treatment in the city since last month, the woman cited her health issues to say she did not wish to continue her trauma by prolonging the wait for a decree in a “dead marriage’’.
Relying on the SC verdict, Nimbkar sought waiver of the 6-month waiting stipulation for divorce by mutual consent.
Veteran divorce lawyer Mridula Kadam said she has not heard of such a waiver being granted by Mumbai family court judges since the SC in September laid down the criteria for a court to use its discretion to speed up divorce.
The order was lauded by many who felt it will pave the way for other such deserving cases. “Making couples stick to a statutory six-month period before a final decree would be meaningless when they can demonstrate that marriage is truly over,’’ said lawyer Mrinalini Deshmukh.
The court observed the couple has stayed apart for more than the statutory period of a year.
The court said, “Keeping the case pending would prolong her (the woman’s) agony and thus can be inferred to be a fit case to waive the statutory six month period.’’
10 years after husband’s death HC sets aside divorce
Husband dead but HC allows divorce plea, November 10, 2018: The Times of India
Ten years after her estranged husband died, the Delhi high court allowed a woman’s plea to set aside their divorce by mutual consent, saying she had not agreed to it in the trial court. Justice Anu Malhotra said that under the Hindu Marriage Act, divorce by mutual consent can be granted only if there was continued consent of both parties up to the date of decision.
The high court noted that in the instant case the woman was absent when the lower court had passed the order. It further said that trial court was under the law obligated to hear the parties to ascertain their consent, but this was “clearly not done in the instant case” as the woman was not present when the decree of divorce was granted on October 6, 2007.
Divorce granted without couple’s presence in court
Swati Deshpande, March 8, 2021: The Times of India
A couple, both jetsetting professionals in their 40s, recently got a divorce via mutual consent without placing a foot in the family court in Bandra. They were not in India when they filed for divorce, and when it was granted, the husband was stranded in Bali on a tourist visa and the wife in Dubai, where she works.
Next March they would have been a married couple for 20 years, but three years ago they began living separately, citing irreconcilable differences. During the Covid-19 pandemic and resultant lockdown, they decided to get moving on the dissolution of their marital ties.
The husband had been abroad on a two-month tourist visa. The visa was extended for over 10 months due to the pandemic flight restrictions and unprecedented contingency.
The Indian Consulate first rejected the husband’s application to attest his documents, but later, after several escalations, it played a role in even aiding the virtual dissolution.
The authorities in Bali made an exception and allowed him to attest his divorce petition and power of attorney documents to enable his lawyer in the city to file their petition in December last year.
Last month, they underwent virtual counselling and appeared before the court via video-conferencing to confirm their consent. Their lawyer Pipli Datta even sought and got them a waiver of the sixmonth cooling off period after their joint petition was filed last December. She said they complied with the criteria laid down by the Supreme Court.
Since the couple have been separated for over two years and seven months, the waiting period of six months in cases of mutual consent divorce petitions would “only prolong their agony’”. Datta said the consulate may not be able to attest the husband’s documents once again for the final hearing six months later and, citing the new strain of the virus now spreading, she had said that unless the cooling off period was waived the case would be left in the lurch.
The family court waived the statutory six months and on its second hearing date declared them divorced, said the decree released a few days ago.
No divorce under Art 142 if one side unwilling: SC
Oct 14, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi:The SC said it would not exercise its omnibus powers under Article 142 to annul an “irretrievably broken down” marriage on the husband’s plea when the wife wants to make the marriage work, reports Dhananjay Mahapatra. The bench said, “Marriage is not a casual event in India.
We haven’t reached western standards of ‘marriage today and divorce tomorrow’. You both are highly educated… (and) may adopt the western philosophy but powers under Article 142 cannot be exercised to annul the marriage when one party is unwilling. ”
No divorce under Art 142 if one side unwilling: SC
Oct 14, 2022: The Times of India
New Delhi:The SC said it would not exercise its omnibus powers under Article 142 to annul an “irretrievably broken down” marriage on the husband’s plea when the wife wants to make the marriage work, reports Dhananjay Mahapatra.
The bench said, “Marriage is not a casual event in India.
We haven’t reached western standards of ‘marriage today and divorce tomorrow’. You both are highly educated… (and) may adopt the western philosophy but powers under Article 142 cannot be exercised to annul the marriage when one party is unwilling. ”
Procedures
Restarting a divorce case after very long separation
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
After 17 years of separation, SC tells man to restart divorce case
Dhananjay Mahapatra | TNN
New Delhi: Army officer Deepak Kumar and lawyer Manisha Tyagi never lived happily as husband and wife. Their roller coaster personal life, which went through judicial separation and then divorce, was put in a rather piquant situation by the Supreme Court on Wednesday.
After staying separately for over 17 years and a divorce decree by the Punjab and Haryana HC in August 2006, an SC bench comprising Justices V S Sirpurkar and S S Nijjar set aside the HC order putting the estranged couple back to judicial separation stage. As soon as the judgment was pronounced, Kumar’s counsel Rajender Kumar pleaded that there was nothing left in the marriage and it was a mercy plea from husband for grant of divorce. The bench said, “You can take appropriate steps under law.”
Unable to endure alleged mental cruelty inflicted by his wife, Kumar, a now time-scale lieutenant colonel in the Army, had moved trial court for divorce. Though the trial court rejected his plea, a single judge bench of Punjab and Haryana HC found charges against the wife true and allowed judicial separation.
Tyagi appealed against the judicial separation order before a division bench of the HC, which went a step further and granted divorce. Tyagi’s counsel Kamini Jaiswal pointed out to the SC that on filing an appeal, the wife could not have been worse off, especially when the husband had not filed an appeal against the judicial separation order. Jaiswal stuck to the legal point even as the bench had wanted to know whether there was any room of reconciliation or arriving at a settlement. Kumar had agreed to pay Rs 10 lakh for a mutually agreed divorce.
Psychological, medical examination can be demanded
Swati Deshpande The Times of India, Sep 10, 2016
Man can seek wife’s test to show they never had sex: Bombay HC
Can a family court direct a wife to be medically examined to enable the husband to prove his claim of non-consummation of marriage? Certainly, said the Bombay high court as it upheld an order passed this July by the Mumbai family court in a divorce petition filed in 2011 on grounds of non-consummation.
Justice K K Tated of the Bombay HC recently rejected a challenge by a woman against an order passed by the family court which had directed her to "undergo a physical and psychological examination medical examination to be conducted by the medical board of Sir J J Hospital, Mumbai". The family court judge had called for such an examination on a plea made by the husband in July after she deposed during the divorce trial that she had consummated the marriage with him in 2011 multiple times immediately after their marriage. His plea for divorce, filed five years ago, was on the grounds that she had not, and was "incapable of". The couple married in December 2010. She was 33 years old and he, 38. It was a second marriage for both.
The family court had directed the medical board to "report whether she is impotent (sic) as alleged". Aggrieved at the order, which had even set a date in August for her medical examination, the wife moved the HC and her lawyer Mandar Limaye argued that the husband had made his plea, impermissibly, at a belated stage, and that the trial was almost over and only arguments remained to be heard. Besides, he submitted a medical certificate by a private doctor who she had visited. The certificate was adequate, the wife argued. Her lawyer pointed to a Supreme Court ruling which said family courts cannot order "roving enquiries" without specific grounds being made out by the other side.
The HC accepted the husband's counsel Ramesh Lalwani's submission that the plea was not belated as it was made within three months of the wife's deposition. It noted that "to prove non-consummation of marriage, medical examination was required". It also noted that the wife had in her cross-examination before the family court said she was "ready to undergo any kind of physical examination". Relying on the same SC ruling, Lalwani argued that the family court has powers to direct a party to undergo a medical test and such an order is no violation of personal liberty under right to life. If, despite the order, the husband or wife, against whom such order is made, refuses to submit to a test, the court is entitled to draw an adverse inference, the SC had held. The HC thus found no merit in the wife's plea.
Residing with husband till divorce
‘Until divorce, wife can stay with hubby’
TIMES NEWS NETWORK
New Delhi: A trial court has said that a woman and her child have every right to reside in the household she shared with her husband after marriage, till the disposal of any matrimonial dispute between them.
Metropolitan magistrate Rachna Lakhanpal made these observations while passing interim residence order in favour of a woman who had moved the court seeking directions to her estranged husband to allow her to live in the matrimonial house till a dispute concerning domestic violence was decided.
“Complainant (woman) and her child have every right to reside in the shared household till final disposal of the case and the respondents (estranged husband and his mother) are restrained from dispossessing her from the shared household till final disposal of the case without due process of law,” the court said.
While passing the order, the court held the man’s household is to be shared with the complainant since they resided there together after marriage.
The court also said that the husband and his mother, residing in northwest Delhi, would not create any hindrance to the woman using the facilities of kitchen and toilet or interfere with the supply of water and electricity to the portion of the household she would stay.
The magistrate also directed a protection officer to facilitate the woman’s peaceful entrance in the house while the SHO concerned was asked to provide necessary assistance if required. The court also directed the man to provide a maintenance amount of Rs 4,000 to his estranged wife and Rs 1,500 to the child per month.
In her plea for interim maintenance and residence order, the woman had alleged cruel treatment by her husband, whom she married in 2000, and told the court that she was thrown out of the matrimonial house. The allegations were denied by the husband. The court, however, said allegations of cruelty or counter allegations cannot be decided with the application for interim maintenance and interim residence.
Hindus get 90 days to appeal divorce decree
A warring Hindu couple now has 90 days, not 30, to file an appeal against a divorce decree granted by a family court, a full bench of the Bombay high court has held.The court ruling lays to rest divided verdicts, and means that a Hindu man or woman would now have to wait three months after a divorce decree to remarry . Provided, of course, that within this time, the losing spouse has not already challenged the dissolution of marriage and the appeal is pending.
The three-judge bench comprising Justices Naresh Patel, R D Dhanuka and Sadhana Jadhav held that time to file an appeal has to read harmoniously when provisions in two different laws were different and conflicting. The two different laws here were the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA) of 1955, which provided for 90 days to file an appeal, as amended in 2003, and the Family Courts Act of 1984 that provides only 30 days. In 2014, the HC had, in a divorce appeal filed in 2013, referred to the larger bench the issue of fixing the appeal deadline, after different benches gave conflicting findings on which law would prevail.
The bench held that the Family Courts Act was a procedural law and that its provisions were not intended to “impliedly“ repeal provisions of the HMA.
Six-month wait for divorce can be waived: SC
`Can Be Granted A Week After Filing Petition'
A Hindu couple need not wait six months for a separation order if the divorce is by mutual consent and the marriage can be legally terminated in a week. The Supreme Court ruled on Tuesday that the “cooling-off “ period is not mandatory and can be waived.
The court ruled that the stipulation under the Hindu Marriage Act for a six-month wait could be done away with if all efforts for mediation and conciliation had failed. The waiver can be considered if the parties had already lived separately for at least a year. In such situations, the court could take a view that delay in proceedings would only prolong subsequent resettlement.
“The object of the provision is to enable the parties to dissolve a marriage by consent if the marriage has irretrievably broken down and to enable them to rehabilitate them as per available options.The amendment was inspired by the thought that forcible perpetuation of status of matrimony between unwilling partners did not serve any purpose. The object of the cooling-off period was to safeguard against a hurried decision if there was otherwise a possi bility of differences being reconciled,“ a bench of Justices A K Goel and U U Lalit said.
The bench said the period can be waived if reconciliation fails and the parties have settled differences relating to alimony , custody of child, etc. Section 13B(2) of the Hindu Marriage Act says that if both parties do not change their pleas for divorce in a time period not less than six months and not later than 18 months, the court shall pass a decree declaring the marriage to be dissolved. The period of six to 18 months provided in Section 13B is an interregnum to give time and opportunity to the couple to reflect on their move.
“Though every effort has to be made to save a mar riage, if there are no chances of reunion and there are chances of fresh rehabilitation, the court should not be powerless in en abling the parties to have a better option,“ the bench said. The court passed the order on a petition filed by a couple seeking direction to waive the cool-off period as they'd been living separately for eight years and had settled all issues pertaining to custody of kids and alimony .
Senior advocate K V Vishwanathan, who was assisting the court in adjudicating the case, said the waiting period under the Act was directory and could be waived if the parties have been living separately for a period of one year or more and agreed that the marriage be dissolved.
The bench concluded that Section 13B(2) is not mandatory but directory . It said the court concerned could waive off the six-month period after being satisfied that the parties were living separately for over a year with no chance of reconciliation. It said parties can file waiver application just one week after the divorce petition is filed and the court will take a call on waiving off the period.
Statistics of divorce, widowhood
Childhood divorce (10-14 years)
Amarjeet Singh, Census: Over 12,000 kids are divorced, The Times of India (Delhi) Sep 15 2016
Nearly 12,105 children aged between 10 and 14 years were identified as divorcees in Census 2011, 53.67% or 6,497 of them girls. However, the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India fails to explain the legal basis of categorising underage individuals as `divorcees' when child marriage itself is unlawful.
The data stands testimony to the fact that child marriage remains fairly common.
As regards the overall number of minor divorces, that is people whose marriage ended before adulthood, Maharashtra accounts for the highest share of all states (1,984), followed by Uttar Pradesh (1,875), Gujarat (1,638), West Bengal (1,286) and Bihar (801). Rajasthan, considered to be the child marriage capital of the country, only has 366 such minors.
A K Saxena, joint director, Directorate of Census (Madhya Pradesh), said, “These are exact field data from our enumerators who go house-tohouse to collect and record information as given to them.“
Religion-wise likelihood of divorce, 2016
The Times of India, Aug 24 2016
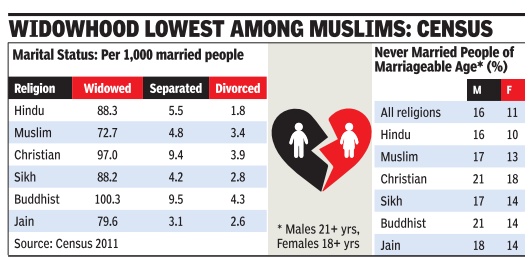
Subodh Varma
Divorce and separation rates are higher among Christians and Budd hists, and lowest among Jains, according to freshly released Census 2011 data. Although separation rates are higher for Hindus than Muslims, divorce is more prevalant among the latter. The share of those who have lost a spouse to death is the highest among Buddhists, followed by Christians. Widowhood rates are much higher among Hindus and Sikhs than Muslims. A complex web of religious and social factors is responsible for these trends, which are similar to those discovered in the previous Census. Although divorce is legally allowed for Hindus, it may still carry social stigma. This could be the reason why the separation rate for Hindus was 5.5 per thousand married people, while the divorce rate was pegged at just 1.8 per thousand.Separation includes wives abandoned by husbands.
Among Muslims, it seems the triple talaq provision pushed up the share of female divorcees to five per thousand, against 2-3 per thousand for Hindus, Sikhs and Jains. However, Christians and Buddhists have similar rates of women divorcees. The rate of widowhood is directly linked to the wellknown demographic fact that women live longer than men.This results in two to three times the number of widows compared to widowers across all communities. Another factor at work is life expectancy.Muslims have the lowest average life expectancy of all communities and this results in the least number of widowed people, at about 73 per thou sand married persons. Among Hindus and Sikhs, the share is about 88 per thousand, while it is higher for Christians (97) and Buddhists (100).
An interesting dimension of the marital status details released by the Census relates to never-married persons across different communities. Among those who have attained the marriageable age, that is, 21 years for men and 18 years for women, Hindus have the lowest share, at 16% unmarried men and just 10% unmarried women.This indicates a very high drive towards early marriage, with many tying the knot before attaining the legal marriage age.
Christians have the highest rate of unmarried persons of marriageable age, at 21% among men and 18% among women.
But across all communities, a smaller share of women are still unmarried after the legal age than men, indicating the relentless pressure on women to get married.
Statistics of separation, not divorce
2001-2011, an analysis
While there is no denying that the regressive practice of triple talaq needs to end, just how prevalent is it in the Muslim community and how are divorce and separation handled in other religious communities? The share of divorced women is indeed high among Muslims -5 for every 1,000 ever married women, according to Census 2011. This is twice the rate among Hindus, but almost the same as Christians and less than that among Buddhists.
But a different picture emerges when one looks at separation, another common way in which legally married couples split up. This may or may not be followed by divorce.In our male-dominated society , it often means abandonment by the husband. The share of separated women among Muslims is 6.7 per 1,000 ever married women. This is less than the rate among Hindu women (6.9) and almost half the rate for Christian and Buddhist women.
Combined, separated and divorced women make up 9.1of every 1,000 ever married women among Hindus and 11.7 among Muslims. This gap has shrunk as it appears that among Hindus, separation is more easily embraced and socially acceptable than a complicated legal battle. For those concerned about injustice to women, this too needs to be considered.Among Christians and Buddhists, the combined rate of separation and divorce is 16.6 and 17.6 -almost 50% more than Hindus and Muslims. Among the six major religious communities in India, Jain and Sikh women have the lowest separation or divorce rates at 6.3 per 1,000 ever married women.
This could be because of higher educational levels and better income among families of these two communities, or it could be the result of more social control.
Comparing 2011 with 2001 shows that in Buddhist communities, the increase in share of separated and divorced women is the least at 34%, followed closely by Muslims with 39% and then Hindus at 40%.
The most dramatic rise is shown in the Sikh community (108%), possibly due to breakdown or abandonment after marriages with partners settled abroad.
From this decadal change, it does not appear that triple talaq is pushing an increasing number of Muslim women into divorce.
Another dimension evident from Census data is that the total number of separated and divorced women among Hindus is almost five times that among Muslims.
This is not really surprising because the population of Hindus is about five times that of Muslims.
However, it highlights the need for better laws across all religious communities for separatedabandoned women who get no maintenance or support from husbands.
Women more likely to be widowed|divorced | separated: 2014
See graphic.
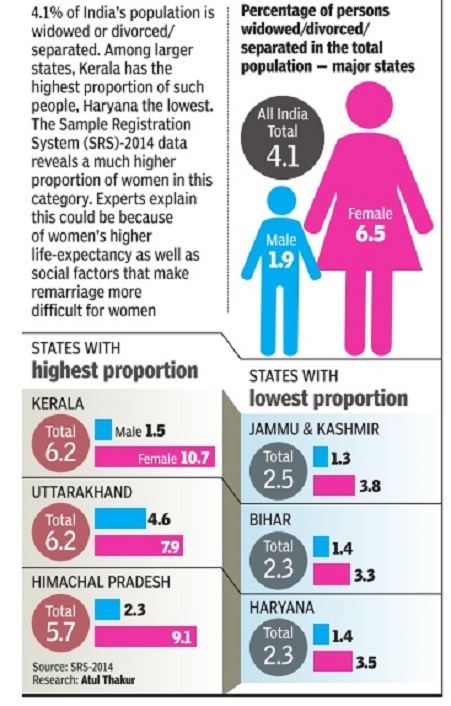
The Times of India
Streedhan
SC ruling of 2015
Sources: The Times of India
1. The Times of India, Nov 22 2015, AmitAnand Choudhary
2. The Times of India, November 22, 2015, Amit Anand Choudhary
Streedhan can be claimed even after separation
Matters temporal & spiritual before Supreme Court
A woman has an inalienable right to ‘streedhan’ and can claim it even after her separation from her husband, the Supreme Court has said in a ruling that makes it clear that denial of her claims can amount to domestic violence, making her husband and in-laws liable to face criminal prosecution. As per Hindu Law, ‘streedhan’ refers to all valuables — movable and immovable property and gifts — a woman receives in her lifetime, prior to and after marriage. This is quite different from dowry, the demand of which by the husband or his family is illegal.
A bench of Justices Dipak Misra and Prafulla C Pant quashed the order of a trial court and Tripura high court which had held that a woman cannot claim her ‘streedhan’ after separation and ruled out criminal proceedings against the husband and in-laws for not handing over the properties. The Supreme Court has pulled up a trial court and the Tripura high court for dismissing the plea of a woman for `streedhan' on the ground that she lost the right over it after judicial separation from her husband. The court said the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act was meant to provide an effective protection to a woman and the court should adopt a sensitive approach towards such complaints.
The bench clarified that separation under court orders is different from divorce and the couple remains as husband and wife, though living separately . It said under judicial separation, a couple can keep their status as wife and husband till their lifetime and a wife is entitled to invoke the Act during that period if her rights are violated. “It is quite clear that there is a distinction between a decree for divorce and decree of judicial separation; in the former, there is a severance of status and the parties do not remain as husband and wife, whereas in the later, the relationship between husband and wife continues and the legal relationship continues as it has not been snapped,“ the bench said.
“Thus the findings recorded by the courts and concurred by HC that the parties having been judicially separated, the wife has ceased to be an aggrieved person is wholly unsustainable,“ it said.
In this case, the woman had got married in 2005. Five years later, her husband sought and the court passed the order in his favour. Alleging that her husband and inlaws were not handing over jewellery and other assets gifted to her by family and friends, she approached the trial court which dismissed her plea. The HC also upheld the order.
Quashing the order of trial court and HC, the apex court said the woman has inalienable right over streedhan and neither the husband nor any other family members can have any right over it.
“We are of the considered opinion that as long as the status of the aggrieved person remains and streedhan remains in the custody of the husband, the wife can always put forth her claim under Section 12 of the Act. We are disposed to think so as the status between the parties is not severed because of the decree of dissolution of marriage,“ it said.
“A decree or an order for judicial separation permits the parties to live apart. Mutual rights and obligations arising out of a marriage are suspended. The decree however, does not sever or dissolve the marriage,“ the bench said and directed the trial court hear her plea on merit.
Surname of ex-husband: Using it after divorce
From the archives of The Times of India 2010
Divorced woman can’t use ex’s name’
Swati Deshpande | TNN
Mumbai: ‘‘What’s in a name...’’ The famous Shakespearean line from Romeo and Juliet popped up during an acrimonious divorce proceedings on Wednesday. ‘‘A lot,’’ said an aggrieved man, ‘‘especially when my ex-wife is misusing it’’. The Bombay high court concurred and in a rare order that might make divorced men smile, directed the divorced woman to stop using her former husband’s name and surname.
The HC further clarified: ‘‘ex-wife cannot use the husband’s name anywhere, including in her bank account’’. The landmark judgment was passed by Justice Roshan Dalvi as she dismissed a petition filed by a woman challenging an interim order of the family court in Bandra.
The Ex Files
Granted divorce in 2006, but woman uses surname of ex-husband, a police inspector Man alleges ex-wife misuses his name after getting into arguments and fights in public HC says woman can’t use ex-husband’s name or surname, including in bank account
‘People may be misled’
The Bombay high court on Wednesday upheld a lower court ruling restraining a divorced woman from using her husband’s name and surname. R R Vachha, principal judge of the family court in Mumbai, had in September last year adjudicated in favour of the ex-husband as the marriage had ended four years ago.
‘‘By using the exhusband’s name or surname, there is always a possibility of people being misled that she is still the wife, when in fact she is not,’’ said Vachha. The HC upheld the family court order and said it need not be interfered with but should be given effect to ‘‘for all purposes’’. The battle over names between the couple arose a year after the family court granted them divorce in February 2006 and the HC finalized it the same year. TNN
Which Act will apply?
Same act as married under
Divorce only under Hindu Act if married under it: HC
Shibu Thomas Mumbai:
The Times of India Sep 01 2014
Once a couple marries under the Hindu Marriage Act, they can only get a divorce under the same law even if they are no longer Indian citizens, the Bombay high court has held.
Hearing a petition filed by a man against his wife, both British nationals of Indian origin and doctors, a division bench of Justices Vijaya Kapse Tahilramani and V L Achliya recently upheld a family court order granting interim custody of the couple's 3.5year-old daughter to the woman. The daughter too is a UK citizen. “The Court at London is not the competent court of jurisdiction to decide the issue of dissolution of marriage between two Hindus married in India as per the Hindu Vedic rites,“ observed the judges.
“Once provisions of Hindu Marriage Act apply , they would continue to apply as long as the marriage exists and even for the marriage's dissolution. The Hindu marriage gives rise to a bundle of rights and obligations between the parties to the marriage and their progeny ,“ said the HC.
PART III
Divorce and family finances
Investments, streedhan, regular alimony vs. lump sum
Know your rights
The law says any investments made in the name of the woman will be a part of her wealth in the event of divorce. Earlier, the woman would be the sole beneficiary of such an investment under the Prevention of Benami Property Act. Now, after a recent Delhi HC order on the Benami Act, a purchase made by the husband from his known sources of income in his wife’s name will no longer be considered benami and he can claim a share in it. But, any gift received by the woman at the time of marriage and during the time she remains married is her property. This is known as streedhan.
Alimony and maintenance
Besides streedhan, a woman is also entitled to alimony. Mrunalini Deshmukh, a Mumbai-based lawyer says the court decides the alimony amount after considering the wife’s working status and family’s overall financial status. She adds that alimony should not be confused with child support. Take the case of Chennai-based Sandhya Natarajan, who got custody of her son after divorce. She did not demand alimony for herself hoping to get maintenance for her son although she qualified for both as her salary was very little compared to her husband’s and she had no savings. Natarajan did not start a legal fight for what was due to her either as she did not have enough money to engage a lawyer. Deshmukh says in such a situation, the wife can ask for interim maintenance from her husband till the divorce is finalised.
After the divorce
Once the dust settles, it is important for the affected parties to rejig their financial plans. Experts say the first step is to determine the new net income and expenses. At this point, one should not lose sight of long and short-term goals.
Suresh Sadagopan, Founder, Ladder7 Advisories, says building an emergency fund is priority. While most financial goals may change, there could be some goals that may remain entangled with one’s former partner like child’s education or marriage. Experts suggest that it is better to get a lump sum for child support and invest it in proper instruments to avoid any future conflicts.
Budgeting for the alimony
Alimony can affect the budget of both the parties and their respective tax outgoes. For the receiver, regular alimony may constitute a great portion of the monthly income. So taxes on alimony should be carefully understood to estimate the net cash flow.
In a one-time settlement, the lump sum can feel like a windfall. Experts suggest that lump sum alimony is better than regular payouts as the the lump sum can be utilised better for future needs. For the spouse paying regular alimony, no deductions can be claimed on it.
See also
Divorce: India