Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE)
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their
content. You can update or correct this page, and/ or send graphs to the Facebook page, Indpaedia.com. All information used will be duly acknowledged. |
Growth in affiliations: 1996-2013
No. of CBSE schools triple in 17 yrs
Hemali Chhapia Shah & Vinamrata Borwankar
Mumbai:
TNN The Times of India Jun 18 2014
Almost half-a-dozen school boards—local, national and international—offer Indian students a choice of academic algorithms for careers ahead. The landscape of school education has for long promised a variety of options.
But of them all, CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education), which was largely designed for those who moved home and could not be loyal to a state board, is picking up popularity across the nation.
In 1996-97, there were 4,843 affiliated schools to the CBSE board, which has grown to
15,000 institutes now, with most of the growth attributed to independent private schools, indicating the way the wind is blowing. While every year thousands of Indian parents find it tough to decide which board their child must sign up for, new school managements too face the same quandary when they start operations.
CBSE officials and school principals attribute the board’s popularity to its academic and administrative reforms which are student and school friendly. “Close to 98% of the schools that apply for affiliation are new institutes,” said an officer. Since 2005, the affiliation process is online and information at every stage is sent via electronic mail. “Also, the board is a national board, allowing parents to shift to just about anywhere in the country. The NCERT syllabus is also the most modern and wholesome one which is in tune with the times,” said a
CBSE administrative officer.
Little wonder then that in 2001-02 there were 6,293 affiliated schools, a number which increased to 13,898 in March 2012-13. Most of the growth came from independent institutes, the count of which went up from 3,483 in 2001-02 to 10,290 by the end of 2013.
Delhi has the largest number of CBSE schools, followed by UP, Haryana and Kerala.
Maharashtra, which has seen a 67% increase in the number of CBSE schools in the last three years, is home to over 500 institutes. “We have introduced and successfully implemented the continuous comprehensive evaluation system.
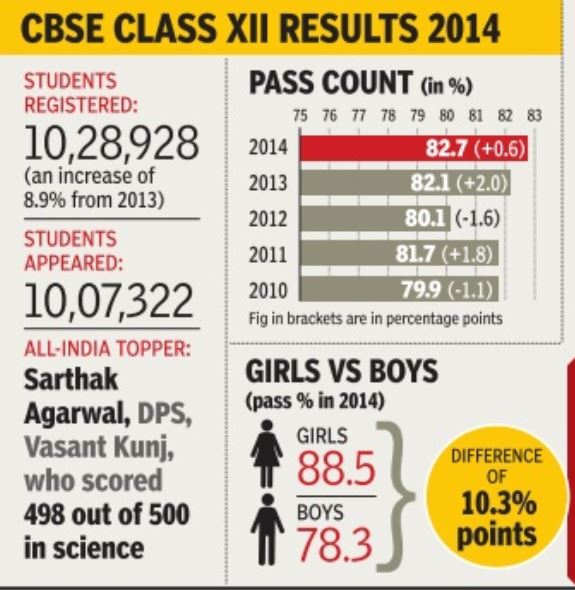
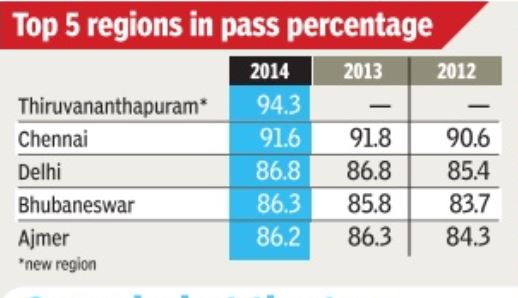
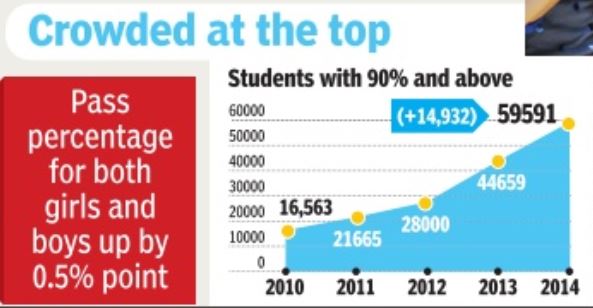
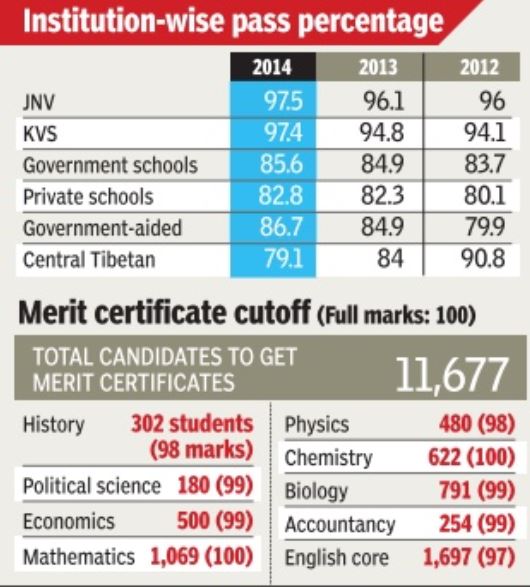
Class XII results: historical trends
CBSE is India's Central Board of Secondary Education