Antiques, antiquities, artefacts stolen from India
(→India Pride Project (IPP)) |
(→2022) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Category:India |A ]] | [[Category:India |A ]] | ||
[[Category:History |A ]] | [[Category:History |A ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Jahangir’s 12kg gold coin= | ||
| + | ==A== | ||
| + | [[File: Jahangir 12kg gold coin1.png| Jahangir’s 12kg gold coin <br/> Graphic courtesy: [ ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=27_06_2022_008_004_cap_TOI Syed.Akbar , Govt renews its hunt for world’s biggest gold coin, ''The Times of India'', 27 Jun. 22] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Former joint director of CBI, Shantonu Sen, in his book said that CBI officials found that Jahangir had minted two 12kg gold coins; while one was presented to Yadgar Ali, ambassador of the Shah of Iran, the other had become the property of the Nizams of Hyderabad. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It was last seen in the possession of the titular Nizam VIII of Hyderabad, Mukarram Jah, who purportedly tried to auction the coin at a Swiss bank, but India’s CBI failed to locate the coin that was passed on to Jah through his grandfather and last Nizam of Hyderabad, Mir Osman Ali Khan. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The last Nizam had inherited the coin minted by emperor Jahangir. Eminent historian Salma Ahmed Farooqui of HK Sherwani Centre for Deccan Studies, Maulana Azad National Urdu University, who conducted research on the history and inheritance of the world’s biggest gold coin, said it is priceless and Hyderabad’s pride. | ||
| + | |||
| + | “In 1987, when Indian officials in Europe alerted the central government about the world-famous auctioneer Habsburg Feldman SA auctioning the 11,935. 8gm gold coin in Geneva at Hotel Moga on November 9, through Paris-based Indosuez Bank’s Geneva branch, CBI came into the picture. Investigations started and much information was unearthed,” Farooqui told TOI. She said CBI officials donned the role of historians, building up on the history of the | ||
| + | coin. Many CBI officials, who were part of the probes are not in office anymore, so the search remained inconclusive. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Salma said CBI special investigation unit XI headed by a superintendent-rank officer in 1987 registered an FIR under the Antique and Art Treasures Act, 1972. “Further investigations revealed that Mukarram Jah was trying to auction two gold mohurs in 1987 at the Swiss auction, one of which was supposedly the 1,000 tola coin. It was valued at $16million in 1987,” she said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==B== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=29_06_2022_020_007_cap_TOI Salma Ahmed Farooqui, June 29, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Two special coins minted during the Mughal period are back in the limelight with the Centre renewing its efforts to trace them. One of them weighing about 12 kg is the biggest and heaviest gold coin ever minted in the world, and it was minted during the reign of Emperor Jahangir, who referred to it as Kaukab-iTali. The other one weighing a kilo belonged to Emperor Shahjahan. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ’’’ Act 1 involves the Asaf Jahi dynasty: ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Both of these were last seen with the Asaf Jahi dynasty. Since then historians and CBI officers have together tried to piece together the jigsaw puzzle of how the coins went from the Great Mughals to the Nizams of Hyderabad and maybe together they will be able to also track down where the coins are today. | ||
| + |
The last century saw the 12-kg coin being inherited by Mukarram Jah, the titular Nizam VIII of Hyderabad. It was last seen in a bank in Europe in 1987. It made news at that time because Mukarram Jah was trying to sell it along with the 1-kg coin at a Swiss auction. Its valuation then was $16 million. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Starring also the Shah of Iran: ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The metrology of coins of Jahangir’s reign shows that in the early 17th century, gigantic coins and zodiacal coins had started to be minted. Such gigantic pieces were also mentioned by foreign travellers like the Venetian Niccolao Manucci and the English Captain Hawkins in their travelogues. | ||
| + | ● Manucci wrote that such coins were not currency; rather the Mughal emperors gave them as presents to ambassadors and special guests, and they appear to have been significant valuables in their collection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ● Jahangir in his autobiography, Tuzuk-i- Jahangiri, tells us of a gold mohur weighing 1,000 tolas which he presented to Yadgar Ali, the ambassador of the Shah of Iran who visited his court on 19 Farwardin, the emperor’s eighth regnal year, by the Persian calendar. This equates to April 10, 1612. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ● Ali was there to pay homage, carrying gifts for Jahangir and a letter of condolence for Akbar’s death. The stunning Kaukab-i-Tali he mentions was 20. 3 cm in diameter, weighed 11,935. 8 grams, and was minted in Agra. | ||
| + | Two authorities on the subject of Mughal gigantic coins, SH Hodivala and PL Gupta, have described how difficult was the craft of engraving legends on these coins. The craftsmen at the mint were paid highly, because they were not only making these coins but afterwards hammering upon them the Persian script in different calligraphic styles too. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' Act 2 is about a grateful Aurangzeb: ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we have an account of the coin’s journey to Persia, we also have another of it making its way to Hyderabad. | ||
| + |
● Ishwardas Nagaur’s Fatuhat-iAlamgiritells of Emperor Aurangzeb arranging to send relief to the tired and hungry Mughal soldiers when Bijapur was being captured. Banjaras with 5,000 oxen laden with wheat, rice and other grains and some treasure then reached the camp of Prince Muhammad Azam under the escort of Ghaziuddin Khan Bahadur, Ranmast Khan, Amanullah Khan and others. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ● It is said that in gratitude, Aurangzeb presented the 1,000-tola gigantic gold coin to Ghaziuddin Khan Feroz Jung I from whom it passed down to his son Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jah I. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ● The coin continued to remain in the possession of the Asaf Jahis until Independence. For this reason, when the Hyderabad Mint in Saifabad held an exhibition of coins earlier this month, it included a big image of Jahangir’s 1,000-tola coin, describing it as the pride of Hyderabad. | ||
| + | What the above details suggest is that one coin weighing 1,000 tolas found its way to Persia and another coin of the same weight remained with the Asaf Jahis in Hyderabad. So, did Jahangir mint two such coins? But even when it comes to the big gold coin of Jahangir that was stationed in Hyderabad, nobody knows what has happened to that either. So our sleuthing continues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The writer is Director of HK Sherwani Centre for Deccan Studies, Maulana Azad National Urdu University, Hyderabad | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Crime|AANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:History|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFA | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
=Theft of antiquities= | =Theft of antiquities= | ||
| Line 56: | Line 122: | ||
As the antiquities law is now reconsidered, perhaps the answer would be to work with the world, not against it. | As the antiquities law is now reconsidered, perhaps the answer would be to work with the world, not against it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Crime|AANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:History|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFA | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
=1913: Statue stolen from Kashi= | =1913: Statue stolen from Kashi= | ||
| Line 148: | Line 227: | ||
It's work that has gained them the respect of enforcement agencies around the world. US Homeland Security Investigations special agent Brenton Easter told TOI: “They have been helpful as have other academics and institutions, like the French Institute of Pondicherry . Without the record keeping and image recognitions done by these individuals and entities many of our recoveries would take much longer.“ | It's work that has gained them the respect of enforcement agencies around the world. US Homeland Security Investigations special agent Brenton Easter told TOI: “They have been helpful as have other academics and institutions, like the French Institute of Pondicherry . Without the record keeping and image recognitions done by these individuals and entities many of our recoveries would take much longer.“ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==As in 2022== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=27_02_2022_023_017_cap_TOI Himanshi Dhawan, February 27, 2022: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: DEITY RETURNS- An Italian collector returned this Buddha idol to India last week, 22 years after it was stolen from Bihar.jpg|DEITY RETURNS- An Italian collector returned this Buddha idol to India last week, 22 years after it was stolen from Bihar <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=27_02_2022_023_017_cap_TOI Himanshi Dhawan, February 27, 2022: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | It was 3am on a February morning in 2018 when pictures of a Buddha statue seated in bhumisparsha mudra (earth-touching gesture) landed from the Netherlands on S Vijay Kumar’s phone. At 3:48 am, he WhatsApped his friend, “It is a match. ” The ‘match’ was to a 12th century bronze stolen from a Buddhist monastery in Bihar’s Nalanda in 1961. It had finally surfaced 57 years later. With that began a six-month chase involving the Indian government, Scotland Yard and scores of anonymous volunteers. The effort was a success and the beautiful bronze was back where it belonged — in India. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Getting back stolen antiquities is an uphill task but members of the India Pride Project (IPP) have turned it into a fine art. Helmed by Kumar, the IPP has helped bring over 300 antiquities back to India since 2008. It was slow at first but since December last year, India has received several precious pieces of its tangible heritage including an 8th-century goat head Yogini statue looted from Uttar Pradesh’s Lokhari village and an 8th-9th century Avalokiteshwara Padamapani idol stolen from Bihar. Sculptures and idols have also been returned from museums, private collectors and art dealers in Australia, the UK, US and Singapore. Quite a few of these were allegedly trafficked by a notorious Manhattan art dealer called Subhash Kapoor who has since been arrested. But the grey market in precious Indian antiquities flourishes, with idols being plundered from village temples or illegal digs and sold to international collectors and museums by a nexus of middlemen that includes so-called experts, greedy art dealers and lax law enforcement authorities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To identify stolen Indian artefacts, the eight-member team of IPP has painstakingly created a database of thousands of images. They work with researchers, NGOs, law enforcement authorities to verify, collect evidence and help bring Indian idols back. The team is supported by 40 volunteers that spread awareness, run campaigns and travel to heritage sites to photograph and catalogue temple idols, statues and art. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Born in Chennai, Kumar, 49, was working in a shipping company in Singapore when he started a blog on Indian temples in 2006. This slowly brought him in touch with a network of like-minded people who started documenting heritage sites. “Over time we found idols missing in many temples. This led us on a trail to international markets where stolen Indian art pieces landed up,” he says. In 2011, journalist Peter Watson’s book and a TV series exposing the systemic plunder of Indian antiquities brought global attention to the problem. In 2014, IPP was born but hit a wall with experts, scholars and Archaeological Survey of India. | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, their persistence has paid off. In the last couple of years, Kumar has expanded his volunteer network to nearly every Indian state and several countries. “I tell people, don’t send us money or give us awards. Go through catalogues and brochures and if you feel there is an artwork that might be stolen, take a picture and send it to us,” he says. Of course, not every tip turns to gold but the anonymous army has helped make selling stolen goods more difficult. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Typically, temples across the country have weak or no security systems. India has no separate law for stolen antiquities so the police often resort to the IPC section for a house burglary that invites a mere seven-year imprisonment and fine. Police complaints are often carelessly written and hastily closed. But it is signatory to the 1970 UN convention that bans the trafficking of cultural heritage and provides legal ground for restitution | ||
| + | of stolen objects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In some cases, precious sculptures or statues that were buried decades ago to prevent their loot by village priests are dug up by robbers. These statues are given a green pati- na (to give an appearance of never having been worshipped) or mutilated, its hands, or head broken, before it is packaged and couriered off to international markets with fake paperwork. “Customs staff is either unable to recognise a real from a fake or paid well to turn a blind eye,” says Kumar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The artwork is usually fenced or hidden till it is forgotten in public memory. It resurfaces years, or even decades, later with fake provenance papers that disguise its history. Sometimes like the goat head Yogini, it is found moss-covered in an English garden or adorning the mansion of a wealthy collector. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Christopher A Marinello, a lawyer and founder of Art Recovery International who has collaborated with Kumar on several cases, says that is where the work done by IPP is crucial. “In many cases, buyers do not know that the gods and goddesses they have bought are venerated and not for display on a shelf,” Marinello says. When an art work “reappears” the group works to prove that it is indeed the stolen one. Any significant markings, defects, dents can help in identification. Kumar goes through his database that is often like looking for a needle in a haystack. They work with law enforcement authorities to check the antecedents of the owner or dealer before giving them a chance to return it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some do like the Italian collector who returned a stolen Buddha statue last week. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The statue had been looted from the Devisthan Kundalpur Temple in Kurkihar, Bihar. Kumar had been tracking the statue for over eight years and was close to securing it when it was consigned for sale by a French dealer. Marinello managed to locate the object in an Italian collection. The owner of the Buddha voluntarily gave it up as soon as he understood that it had been stolen. But for every conscientious owner, there are many unscrupulous ones who stonewall investigations or deny information about stolen objects. But Kumar and his IPP team seldom give up. | ||
[[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | [[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| Line 156: | Line 265: | ||
]] | ]] | ||
[[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | [[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFA | ||
]] | ]] | ||
[[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | [[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| Line 334: | Line 445: | ||
According to sources in Dharohar Bhawan, these artefacts were stolen at different times though several of them were smuggled into the US by jailed art dealer Subhash Kapoor, who was charged by prosecutors in Manhattan in 2019 with stealing and possessing artefacts worth millions of dollars. Kapoor is currently in an Indian jail awaiting trial. Over the years, several international museums have voluntarily shared information with India about antiquities they procured from Kapoor that they were unaware were illegally being traded. | According to sources in Dharohar Bhawan, these artefacts were stolen at different times though several of them were smuggled into the US by jailed art dealer Subhash Kapoor, who was charged by prosecutors in Manhattan in 2019 with stealing and possessing artefacts worth millions of dollars. Kapoor is currently in an Indian jail awaiting trial. Over the years, several international museums have voluntarily shared information with India about antiquities they procured from Kapoor that they were unaware were illegally being traded. | ||
| − | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA]] | + | [[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA |
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Crime|AANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:History|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFA | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM | + | =2022= |
| − | + | ==Glasgow museum== | |
| − | [[Category:Crime|AANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM | + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=20_08_2022_028_007_cap_TOI August 20, 2022: ''The Times of India''] |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Category:History|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM | + | [[File: Museum conservator Stephanie De Roemer holds a ceremonial Indo-Persian sword during a transfer-of-ownership ceremony at Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum in Glasgow.jpg|Museum conservator Stephanie De Roemer holds a ceremonial Indo-Persian sword during a transfer-of-ownership ceremony at Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum in Glasgow <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/article-share?article=20_08_2022_028_007_cap_TOI August 20, 2022: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM | + | Glasgow: Glasgow held a ceremony on Friday to officially repatriate seven Indian cultural artefacts looted during British colonial rule, calling it a first for a UK museum service.
|
| − | + | Dignitaries from the high commission of India joined members of Glasgow Life, the charity that manages the Scottish city’s museum collections, at the transfer of ownership ceremony, following more than 18 months of talks. | |
| − | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM | + |
Six of the items were stolen from northern India in the 1800s, and a seventh was illegally purchased after being stolen from its original owners. All seven objects were looted from sacred places such as temples and shrines and given as gifts to the Scottish city’s museum collections. “Glasgow has led repatriation efforts in the UK since 1998,” said Duncan Dornan, head of Museums and Collections at Glasgow Life. “We look forward to continuing our work with the Indian authorities to deliver the safe return of these artefacts. ” In all, Glasgow is set to return 51 items to the descendants of their rightful owners from India and Nigeria as well as the Cheyenne River and Oglala Sioux tribes in the US state of South Dakota. |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM | + | Glasgow’s repatriation commitment is part of a wider reassessment of the provenance of items in Western museums, in the wake of global anti-racism movements. Earlier this year, two British universities returned two Benin bronzes looted by British colonialists in the 19th century to Nigeria. |
| − | + | AFP | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Yale Museum== | ||
| + | [https://www.nytimes.com/2022/04/01/arts/design/yale-art-looting-investigation.html?campaign_id=2&emc=edit_th_20220403&instance_id=57492&nl=todaysheadlines®i_id=30033251&segment_id=87380&user_id=5702604d9dc5e777f99c5676cb366aeb April 3, 2022: ‘'The New York Times''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Law enforcement officials have seized 13 artifacts from the Yale University Art Gallery that they say were looted. Many of those, the authorities said, are part of an ongoing investigation into Subhash Kapoor, a former Madison Avenue art dealer accused of being one of the world’s most prolific antiquities smugglers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Arts|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Crime|AANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
| + | [[Category:History|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|A ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTE | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFA | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Sculpture|SANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIAANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEFACTS STOLEN FROM INDIA | ||
| + | ANTIQUES, ANTIQUITIES, ARTEF]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:19, 11 September 2022

This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. |
Contents |
[edit] Jahangir’s 12kg gold coin
[edit] A
Syed.Akbar , Govt renews its hunt for world’s biggest gold coin, The Times of India, 27 Jun. 22
Former joint director of CBI, Shantonu Sen, in his book said that CBI officials found that Jahangir had minted two 12kg gold coins; while one was presented to Yadgar Ali, ambassador of the Shah of Iran, the other had become the property of the Nizams of Hyderabad.
It was last seen in the possession of the titular Nizam VIII of Hyderabad, Mukarram Jah, who purportedly tried to auction the coin at a Swiss bank, but India’s CBI failed to locate the coin that was passed on to Jah through his grandfather and last Nizam of Hyderabad, Mir Osman Ali Khan.
The last Nizam had inherited the coin minted by emperor Jahangir. Eminent historian Salma Ahmed Farooqui of HK Sherwani Centre for Deccan Studies, Maulana Azad National Urdu University, who conducted research on the history and inheritance of the world’s biggest gold coin, said it is priceless and Hyderabad’s pride.
“In 1987, when Indian officials in Europe alerted the central government about the world-famous auctioneer Habsburg Feldman SA auctioning the 11,935. 8gm gold coin in Geneva at Hotel Moga on November 9, through Paris-based Indosuez Bank’s Geneva branch, CBI came into the picture. Investigations started and much information was unearthed,” Farooqui told TOI. She said CBI officials donned the role of historians, building up on the history of the coin. Many CBI officials, who were part of the probes are not in office anymore, so the search remained inconclusive.
Salma said CBI special investigation unit XI headed by a superintendent-rank officer in 1987 registered an FIR under the Antique and Art Treasures Act, 1972. “Further investigations revealed that Mukarram Jah was trying to auction two gold mohurs in 1987 at the Swiss auction, one of which was supposedly the 1,000 tola coin. It was valued at $16million in 1987,” she said.
[edit] B
Salma Ahmed Farooqui, June 29, 2022: The Times of India
Two special coins minted during the Mughal period are back in the limelight with the Centre renewing its efforts to trace them. One of them weighing about 12 kg is the biggest and heaviest gold coin ever minted in the world, and it was minted during the reign of Emperor Jahangir, who referred to it as Kaukab-iTali. The other one weighing a kilo belonged to Emperor Shahjahan.
’’’ Act 1 involves the Asaf Jahi dynasty:
Both of these were last seen with the Asaf Jahi dynasty. Since then historians and CBI officers have together tried to piece together the jigsaw puzzle of how the coins went from the Great Mughals to the Nizams of Hyderabad and maybe together they will be able to also track down where the coins are today. The last century saw the 12-kg coin being inherited by Mukarram Jah, the titular Nizam VIII of Hyderabad. It was last seen in a bank in Europe in 1987. It made news at that time because Mukarram Jah was trying to sell it along with the 1-kg coin at a Swiss auction. Its valuation then was $16 million.
Starring also the Shah of Iran:
The metrology of coins of Jahangir’s reign shows that in the early 17th century, gigantic coins and zodiacal coins had started to be minted. Such gigantic pieces were also mentioned by foreign travellers like the Venetian Niccolao Manucci and the English Captain Hawkins in their travelogues. ● Manucci wrote that such coins were not currency; rather the Mughal emperors gave them as presents to ambassadors and special guests, and they appear to have been significant valuables in their collection.
● Jahangir in his autobiography, Tuzuk-i- Jahangiri, tells us of a gold mohur weighing 1,000 tolas which he presented to Yadgar Ali, the ambassador of the Shah of Iran who visited his court on 19 Farwardin, the emperor’s eighth regnal year, by the Persian calendar. This equates to April 10, 1612.
● Ali was there to pay homage, carrying gifts for Jahangir and a letter of condolence for Akbar’s death. The stunning Kaukab-i-Tali he mentions was 20. 3 cm in diameter, weighed 11,935. 8 grams, and was minted in Agra. Two authorities on the subject of Mughal gigantic coins, SH Hodivala and PL Gupta, have described how difficult was the craft of engraving legends on these coins. The craftsmen at the mint were paid highly, because they were not only making these coins but afterwards hammering upon them the Persian script in different calligraphic styles too.
Act 2 is about a grateful Aurangzeb:
If we have an account of the coin’s journey to Persia, we also have another of it making its way to Hyderabad. ● Ishwardas Nagaur’s Fatuhat-iAlamgiritells of Emperor Aurangzeb arranging to send relief to the tired and hungry Mughal soldiers when Bijapur was being captured. Banjaras with 5,000 oxen laden with wheat, rice and other grains and some treasure then reached the camp of Prince Muhammad Azam under the escort of Ghaziuddin Khan Bahadur, Ranmast Khan, Amanullah Khan and others.
● It is said that in gratitude, Aurangzeb presented the 1,000-tola gigantic gold coin to Ghaziuddin Khan Feroz Jung I from whom it passed down to his son Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jah I.
● The coin continued to remain in the possession of the Asaf Jahis until Independence. For this reason, when the Hyderabad Mint in Saifabad held an exhibition of coins earlier this month, it included a big image of Jahangir’s 1,000-tola coin, describing it as the pride of Hyderabad. What the above details suggest is that one coin weighing 1,000 tolas found its way to Persia and another coin of the same weight remained with the Asaf Jahis in Hyderabad. So, did Jahangir mint two such coins? But even when it comes to the big gold coin of Jahangir that was stationed in Hyderabad, nobody knows what has happened to that either. So our sleuthing continues.
The writer is Director of HK Sherwani Centre for Deccan Studies, Maulana Azad National Urdu University, Hyderabad
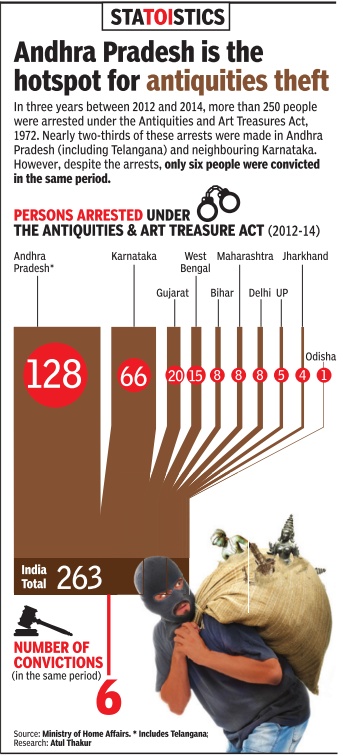
[edit] Theft of antiquities
The Times of India, Aug 16 2015
Amulya Gopalakrishnan
Will reworking the Antiquities Act stamp out the illicit trade in cultural artefacts? Sunday Times examines both sides of the debate What is anantiquity? Itcould be an idol in a shrine, a piece of jewellery passed on from your grandmother, or a casually bought souvenir that is much older than you realize. These are all covered under the Antiquities Act of 1972, but the ethics of owning and circulating them are not the same. Despite a stringent law, antiquities continually stream out of India. Their owners secretly sell them abroad, flouting export restrictions. The ongoing Chennai trial of Manhattan-based art dealer Subhash Kapoor, reveals how antiquities are spirited across the border by a network of smugglers and dealers, sold to museums, galleries and collectors.
Recently, Union culture minister Mahesh Sharma told Parliament about the theft of eight antiquities in the last year. As a remedy , he has spoken of liberalizing the Antiquities and Art Treasures Act of 1972, to create a more open market in India that might deter smuggling.
While the details are still being worked out, it is expected to involve a measure of selfcertification, electronic registration, and easier internal trade in antiquities. “We have invited comments, and will amend the law very soon,“ said Rakesh Tiwari, director-general of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
Flaw in the law?
The antiquities law covers objects over a 100 years old, forbids their export by citizens, and allows them to be sold within India only with a licence. Owners of an antique item must register it with the ASI. The state can also compulsorily acquire an object from its owners, without any reliable valuation of a fair price.
According to art historian Naman Ahuja, its chief flaw is the broad and meaningless definition of antiquities. A Chola bronze of inestimable historical value is treated the same way as a flea market idol that just happens to be a hundred years old, and may be personally valuable to a col ector, but is not worth the government's attention. “The state cannot possibly defend so much material; the law's only use is to harass middleclass citizens,“ he says. “What s the need for this elaborate registration, treating us like children?“ says Dadiba Pundole of the Pundole Art Gal ery that acquired a licence to sell in 2011.
And despite the punitive strength of the law, it hasn't been able to stem the illicit low of antiquities out of India. “That only one Subhash Kapoor has been caught in so many years only shows how neffective the law has been,“ says Ahuja.
In his view, this repressive legal regime has discouraged Indians from buying and selling antiques, recognizing special pieces, producing scholarship and images. A thriving internal market, he says, would be the best safeguard against smuggling.
“Without an open market, nobody knows where things are, and fakes circulate with ease,“ says art historian Kavita Singh. In her view, this law speaks of the anxiety of a decolonized nation, and the political situation of the 1970s, where the government and erstwhile royal families who held large art collections were suspicious of each other.
She points to laws in the UK and Canada that balance the owners' right to their property and the nation's investment in important cultural objects -you can place your object for sale in the international market, and the state is given time to match the highest bid.
Can selling within India discourage smuggling? Opinion is divided. Singaporebased S Vijay Kumar, a heritage enthusiast who runs the website Poetry in Stone, disagrees with Ahuja and fears that any dilution in the law would give a free run to underhand dealers, given the more lucrative market abroad. “We have a handful of corporate buyers in India, who can't compete with the billionaires and museums of the West,“ he says. ASI officials also privately say that this loosening of the law will only benefit wealthy lobbies.
Kirit Mankodi, an archaeology professor who posts information and photographs about stolen antiquities on his website, Plundered Past, says that India's real problem is the inability to prove provenance.Photographs and dated documents are essential to tell a looted object apart from a legitimately owned one. And yet, “there is no public register to report losses, or for buyers to check out an object,“ he says. The National Mission for Monuments and Antiquities was set up in 2007 with a fiveyear plan to create an exhaustive database, say ASI officials.In 2015, it remains far away from the goal.
Whose patrimony is it?
While there is growing consciousness about looted antiquities, there is also a charged debate over whether nations are right to be so possessive about their heritage.Many source nations demand repatriation of objects taken away long ago -whether Greece's Elgin marbles, Egypt's Rosetta Stone or India's Koh-i-Noor diamond.
Some in the museum world, like Getty Trust president and provocateur James Cuno, disagree with these “nationalist-retentionist“ arguments, arguing that the great cosmopolitan museums (that happen to be in the West) are better equipped to preserve and display previous antiquities to the world, whose collective heritage they are.Others say that national cultures are complicated affairs, made by chance encounters and unforeseen circumstances, and that there must be a cut-off point to correcting historical wrongs.
“But as things are, for some of these global museums to display our antiquities, Indian laws may have been broken, violence committed on the monument, a sculpture wrenched from its niche, the context destroyed. When the sculpture was exported, Indian laws were broken again,“ says Mankodi.
Singh points out that it's often the museums still on the make -in Australia, Singapore and other locations -that are fed by the illicit supply of antiquities, and have had to return several artefacts bought at a high price. A much better strategy for India, says Singh, would be for Indian museums to capitalize on their vast stores, and loan pieces to museums in other nations.
As the antiquities law is now reconsidered, perhaps the answer would be to work with the world, not against it.
[edit] 1913: Statue stolen from Kashi
Binay Singh, November 21, 2020: The Times of India

From: Binay Singh, November 21, 2020: The Times of India
Kashi will soon get back an antique idol of Goddess Annapoorna, which was stolen over a century ago from a Varanasi ghat and found its way to University of Regina, Canada. And it’s a coincidence that the beginning of World Heritage Week from November 19 to 25, is witnessing the repatriation of the statue from an art gallery in the Canadian varsity.
The Annapoorna statue from University of Regina’s collection at the MacKenzie Art Gallery will soon begin its journey home following a virtual repatriation ceremony between interim president and vice-chancellor of the university Thomas Chase and India’s high commissioner to Canada, Ajay Bisaria on November 19, a press statement from the university said. Representatives from MacKenzie Art Gallery, Global Affairs Canada, and Canada Border Services Agency also attended the ceremony.
Artist Divya Mehra drew attention to the fact that the statue had been wrongfully taken over a century ago, while going through MacKenzie’s permanent collection. The statue was part of the original 1936 bequest by Norman MacKenzie, the gallery’s namesake.
Upon research Mehra stumbled upon the fact that a stranger overheard MacKenzie talking about his desire to possess the idol during his trip to India in 1913, and stole the idol from a temple on the stone steps along the Ganga and gave it to the Canadian art patron.
[edit] Antiques stolen, state-wise
[edit] Karnataka
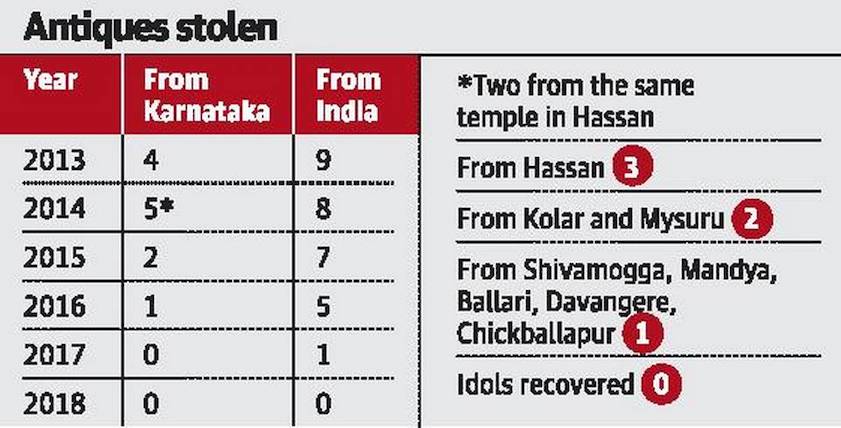
[edit] 2013-18/ Antiques stolen in Karnataka
From: Sathish G.T., 30 whisked away from ASI sites, reveals written answer in Lok Sabha, March 14, 2019: The Hindu
At least 12 idols have been stolen from protected monuments in Karnataka in the past six years, and none of them has been recovered by the police.
Karnataka tops the list in the country that has seen 30 idols or artefacts being stolen from Archaeology Survey of India (ASI) sites, reveals the Ministry of Culture in a written answer to a Lok Sabha question last week.
In a span of three years, a stone Nandi and a stone Ganesha were stolen from the Ramalingaswara temple complex at Avani in Kolar district.
A stone Shivalinga was stolen from a Shiva temple in Thimalapura in Ballari district; while, the eight-armed goddess Mahishamardini was stolen from the Panchalingeswara Temple in Mandya is yet to be recovered.
Tracing problem
“The demand for these Hoysala and Chalukya idols exist and the three southern States are susceptible as there are hundreds of unprotected or State-protected sites,” said T. Arun Raj, Superintending Archaeologist (Museum), ASI, New Delhi, and who was in-charge of Karnataka till recently.
In Hassan district, three sculptures of Hoysala period were stolen.
A seated Chaturbhuja Ganesha sculpture from Bucheshwara Temple at Koravangala near Hassan was stolen on the night of October 11, 2013.
ASI officers had filed the complaint with Dudda Police in Hassan taluk.
Within a year, two schist stone sculptures were stolen from Nageshwara Temple at Mosale in Hassan taluk.
A case was filed at Gorur Police Station. “In both the cases, the police have reported that the stolen sculptures were not traceable (C-report). I recently visited both the police stations and spoke to the officers concerned. They have not been able to trace them so far,” said L.B. Kamath, Junior Conservation Assistant of ASI posted in Hassan.
Lack of sufficient staff to guard the monuments is said to be one of the reasons for the thefts. H.N. Nagaraj, district general secretary of Temporary Workers Union of ASI, said the sculptures were stolen from a place that had no night watchmen.
[edit] India Pride Project (IPP)
[edit] 2008-16
The Times of India, June 12, 2016

Debayan Tewari
Chasing Ganeshas: Meet the art sleuths bringing India's stolen heritage home When Prime Minister Narendra Modi re turned from his foreign travels, in his luggage was a consignment of 200 antiquities, including a beautiful 1,000-year-old Ganesha bronze, that the US government handed over to him. What few know that is behind the goodwill gestures and photo-ops highlighting cultural cooperation is a group of very committed idol chasers who helped investigative agencies in the US crack the cases of stolen antiquities. In March, when special agents in the US seized two stolen Indian artefacts -a sandstone stele of Rishabhanata and a panel with Revanta and his entourage -from an auction in New York as part of the ongoing decade-long Operation Hidden Idol, among the first to identify the 10th century Rishabhanata was Vijay Kumar, an accountant working for a shipping company in Singapore.
Kumar has been photographing and documenting Indian antiquities for the past 12 years, trying -in his own way -to prevent their theft and ensure the return of stolen artefacts to India.In 2014, he and fellow heritage lover and art enthusiast Anuraag Saxena began the India Pride Project (IPP) to “restore the nation's pride through restoring its culture“.
IPP began with 20 members and has since grown to 4,000, including researchers, art-loversturned-private-investigators, bloggers, freelance photographers and journalists. It is managed by a core team of 40 people.
Except for Kumar and Sax ena, the rest have chosen to stay anonymous, providing expertise and inside information to the group. “Our members are heritage enthusiasts, scholars, archaeologists... many help but want to keep their identity private,“ says Kumar, who grew up in Chennai and was drawn to heritage conservation after reading `Ponniyin Selvan', a Tamil historical novel based in the Chola period. “My whole sense of cultural pride comes from the book,“ he says.
IPP helps track and restore stolen artefacts by contradicting the provenance that museums are provided by not-so-legitimate art dealers. Volunteers use photographs of the artefact in its original site from the IPP database or from archives to prove that it was stolen. For example, in the case of a Nataraja idol that Australia returned to India in September 2014, IPP volunteers matched photographs taken by the French Institute Pondicherry (IFP) in November 1994, frameby-frame, to prove that the idol on display at the National Gallery of Australia (NGA) was stolen from Sripuranthan in Tamil Nadu.
Saxena, a banker-turned-education executive who is also based in Singapore, says IPP depends on a network of volunteers. “We are spread across the world and are from various background and professions. It is very normal for a volunteer who is a CEO in Singapore to work with another who runs a cloth-shop in a small village in Tamil Nadu,“ he says.
IPP also scans catalogues of art galleries to track down looted antiquities. Kumar used a print cata logue from in ternational art thief Subhash Kapoor's Art of the Past gallery to match a stat ue of Uma Parameshwari in Singapore's Asian Civilizations Museum with a photograph of a stolen idol from Ariyalur that the Tamil Nadu police's idol wing released.
It's a long, slow process to prove that the idols were stolen and then get them back. The latest seizures in New York came after three years of work, while proving that the Uma Parameshwari statue was the same one stolen from Ariyalur took five years with valuable time being lost mostly due to red tape in India, explains Kumar.
Kumar began photographing temple architecture and idols in Tamil Nadu as a hobby . These photographs have become a part of the database IPP volunteers are building to compensate for the lack of an official database. “We do documenting missions twice a year for two weeks,“ he says.
Besides field work, IPP also uses social media, encouraging members and volunteers to contribute photos to its archive.
After the arrest of Kapoor and his deportation to India in 2012, Kumar reached out to Jason Felch, an investigative journalist based in the US, who published a story about objects smuggled by Kapoor on display at NGA. “Vijay immediately began supplying me with detailed information about other objects in the NGA's collection and possible links to objects stolen from Indian temples,“ Felch told TOI in an email interview. “Soon, we developed a collaborative relationship with journalists in Australia and India, each of us working our sources and sharing information to advance the story .“
While Kumar leads research and analysis, Saxena handles coordination with government agencies and the media.
But Saxena does not want IPP to be seen as police informers.“People are interested in the whodunit stuff, and we are often seen as khabris (informers). But our work is more than that,“ he says.
IPP's website has detailed information about how it helped to identify the Sripuranthan Nataraja, Vriddhachalam Shiva Ardhanari and sandstone Yakshi seized from Kapoor's warehouse in the US, a bronze Ganesha in Toledo Museum, and the Uma Parameshwari statue in Singapore. Vijay says they are currently tracking more 4,000 antiquities.
It's work that has gained them the respect of enforcement agencies around the world. US Homeland Security Investigations special agent Brenton Easter told TOI: “They have been helpful as have other academics and institutions, like the French Institute of Pondicherry . Without the record keeping and image recognitions done by these individuals and entities many of our recoveries would take much longer.“
[edit] As in 2022
Himanshi Dhawan, February 27, 2022: The Times of India

From: Himanshi Dhawan, February 27, 2022: The Times of India
It was 3am on a February morning in 2018 when pictures of a Buddha statue seated in bhumisparsha mudra (earth-touching gesture) landed from the Netherlands on S Vijay Kumar’s phone. At 3:48 am, he WhatsApped his friend, “It is a match. ” The ‘match’ was to a 12th century bronze stolen from a Buddhist monastery in Bihar’s Nalanda in 1961. It had finally surfaced 57 years later. With that began a six-month chase involving the Indian government, Scotland Yard and scores of anonymous volunteers. The effort was a success and the beautiful bronze was back where it belonged — in India.
Getting back stolen antiquities is an uphill task but members of the India Pride Project (IPP) have turned it into a fine art. Helmed by Kumar, the IPP has helped bring over 300 antiquities back to India since 2008. It was slow at first but since December last year, India has received several precious pieces of its tangible heritage including an 8th-century goat head Yogini statue looted from Uttar Pradesh’s Lokhari village and an 8th-9th century Avalokiteshwara Padamapani idol stolen from Bihar. Sculptures and idols have also been returned from museums, private collectors and art dealers in Australia, the UK, US and Singapore. Quite a few of these were allegedly trafficked by a notorious Manhattan art dealer called Subhash Kapoor who has since been arrested. But the grey market in precious Indian antiquities flourishes, with idols being plundered from village temples or illegal digs and sold to international collectors and museums by a nexus of middlemen that includes so-called experts, greedy art dealers and lax law enforcement authorities.
To identify stolen Indian artefacts, the eight-member team of IPP has painstakingly created a database of thousands of images. They work with researchers, NGOs, law enforcement authorities to verify, collect evidence and help bring Indian idols back. The team is supported by 40 volunteers that spread awareness, run campaigns and travel to heritage sites to photograph and catalogue temple idols, statues and art.
Born in Chennai, Kumar, 49, was working in a shipping company in Singapore when he started a blog on Indian temples in 2006. This slowly brought him in touch with a network of like-minded people who started documenting heritage sites. “Over time we found idols missing in many temples. This led us on a trail to international markets where stolen Indian art pieces landed up,” he says. In 2011, journalist Peter Watson’s book and a TV series exposing the systemic plunder of Indian antiquities brought global attention to the problem. In 2014, IPP was born but hit a wall with experts, scholars and Archaeological Survey of India.
However, their persistence has paid off. In the last couple of years, Kumar has expanded his volunteer network to nearly every Indian state and several countries. “I tell people, don’t send us money or give us awards. Go through catalogues and brochures and if you feel there is an artwork that might be stolen, take a picture and send it to us,” he says. Of course, not every tip turns to gold but the anonymous army has helped make selling stolen goods more difficult.
Typically, temples across the country have weak or no security systems. India has no separate law for stolen antiquities so the police often resort to the IPC section for a house burglary that invites a mere seven-year imprisonment and fine. Police complaints are often carelessly written and hastily closed. But it is signatory to the 1970 UN convention that bans the trafficking of cultural heritage and provides legal ground for restitution of stolen objects.
In some cases, precious sculptures or statues that were buried decades ago to prevent their loot by village priests are dug up by robbers. These statues are given a green pati- na (to give an appearance of never having been worshipped) or mutilated, its hands, or head broken, before it is packaged and couriered off to international markets with fake paperwork. “Customs staff is either unable to recognise a real from a fake or paid well to turn a blind eye,” says Kumar.
The artwork is usually fenced or hidden till it is forgotten in public memory. It resurfaces years, or even decades, later with fake provenance papers that disguise its history. Sometimes like the goat head Yogini, it is found moss-covered in an English garden or adorning the mansion of a wealthy collector.
Christopher A Marinello, a lawyer and founder of Art Recovery International who has collaborated with Kumar on several cases, says that is where the work done by IPP is crucial. “In many cases, buyers do not know that the gods and goddesses they have bought are venerated and not for display on a shelf,” Marinello says. When an art work “reappears” the group works to prove that it is indeed the stolen one. Any significant markings, defects, dents can help in identification. Kumar goes through his database that is often like looking for a needle in a haystack. They work with law enforcement authorities to check the antecedents of the owner or dealer before giving them a chance to return it.
Some do like the Italian collector who returned a stolen Buddha statue last week.
The statue had been looted from the Devisthan Kundalpur Temple in Kurkihar, Bihar. Kumar had been tracking the statue for over eight years and was close to securing it when it was consigned for sale by a French dealer. Marinello managed to locate the object in an Italian collection. The owner of the Buddha voluntarily gave it up as soon as he understood that it had been stolen. But for every conscientious owner, there are many unscrupulous ones who stonewall investigations or deny information about stolen objects. But Kumar and his IPP team seldom give up.
[edit] YEAR-WISE
[edit] 2014
[edit] Recovery of artefacts from Australia
The Indian Express, October 11, 2015
During his visit to India in 2014, the then Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott had handed over to his Indian counterpart Narendra Modi two antique statues of Hindu deities which had been stolen from temples in Tamil Nadu before being bought by art galleries in Australia. Abbott returned the idols, one of which was a Nataraja –the dancing Shiva– belonging to the Chola period 11th-12th century. The other was Ardhanariswara dating to 10th century. Ardhnariswara, the androgynous form of Shiva and his consort Parvati, is depicted as half male and half female, split down the middle.
The Nataraja statue, cast in bronze, was purchased by the National Gallery of Australia (NGA) in February 2008 from Subhash Kapoor who was then based in New York.
In 2012,Subhash Kapoor, owner of the “Art of the Past” gallery in New York, was arrested in Germany and subsequently extradited to India. He has been accused of conspiracy to commit burglary and smuggling from Tamil Nadu of antique idols of Hindu deities belonging to Chola dynasty. German Chancellor Angela Merkel had on October 6 handed over to Prime Minister Narendra Modi a 10th century Durga idol which had gone missing from a temple in Kashmir over two decades back and was later found in a museum in that country.
[edit] 2016
[edit] June 2016: Recovery of artefacts from the US
The Hindu, September 24, 2016
In June 2016, the United States formally returned to India about 200 stolen cultural objects, which include 2,000-year-old artefacts, part of a $100 million trove unearthed by an investigation of Subhash Kapoor’s art business. What emerges from these long battles to reclaim articles that constitute cultural heritage is the insight that a dedicated national agency with State government support would be better equipped to fight the scourge of theft and illicit transfer. With trained personnel, it could devote itself to the task of documenting antiquities and ensuring that the country’s ports are sealed against smuggling.
[edit] September 2016: Recovery of artefacts from Australia
The Hindu, September 24, 2016


The return to India of three ancient sculptures from the National Gallery of Australia is another milestone in the long and difficult campaign waged by several countries to repossess their cultural treasures, which have often been bought by museums from idol smugglers. As the provenance of the artefacts — the 900-year old statues of Goddess Pratyangira and Seated Buddha, and the third century Worshippers of Buddha — became clear, the only ethical course open to the Australian gallery was to restore the sculptures, which it must be commended for pursuing. Evidently, the two icons other than the sandstone Seated Buddha were acquired from a New York-based art dealer, Subhash Kapoor, for about $840,000 on the strength of fake documentation.
The National Gallery of Australia’s inquiry into the status of its Asian art objects conducted by a retired judge, Susan Crennan, has had the positive outcome of identifying 22 articles that have questionable or doubtful credentials, 14 of which were purchased from Kapoor. Many of the findings in the Australian review underscore the importance of creating a strong repository of information of all Indian antiquities, backed up by unimpeachable forensic records, so that they may be claimed without difficulty at a future date. A lot of the illicit trade has been carried out by smugglers who have laundered the provenance of idols using fake documentation designed to overcome the prohibition imposed by the Antiquities and Art Treasures Act, 1972 on non-governmental exports. Providentially, it is the records of a research institution such as the French Institute of Pondicherry that helped establish the claim to the 11th-12th century Nataraja idol stolen from Tamil Nadu in 2006. Documentation of antiquities using public and private records should become a national mission. These treasures could then be put on display in national museums.
[edit] 2019
[edit] US returns two rare artefacts
Jaya Menon, August 15, 2019: The Times of India

From: Jaya Menon, August 15, 2019: The Times of India
UK returns two rare artifacts to India
CHENNAI: A limestone carved relief estimated to be dated from 1st century BC to 1st century AD from Andhra Pradesh and a 17th century Nayaka-period Navaneetha Krishna Bronze from Tamil Nadu were handed over to the Indian high commissioner in London on Thursday.
The two artifacts are “linked to one of the most prolific art smugglers in the world” who were recently charged in Manhattan, New York, said a Homeland Security Investigations (HSI) release. “An individual in the UK, who possessed the items came forward to HSI (US Department of Homeland Security), expressing a desire to surrender the pieces,” said the release. Both items would be physically examined by domain experts at a later date to establish their exact period and original location.
“The repatriated artifacts are just two of more than 2,600 antiquities that have been recovered around the world. The investigation remains ongoing,” said the release.
“The cultural significance of artifacts looted from regions around the world extends beyond a monetary value. The pieces, like those recovered through this operation, are stolen fragments of history; and it is an honour to return them to their rightful home country,” said Peter C Fitzhugh, special agent in charge for HSI New York.
“HSI recognises the importance of both international and local partnerships in locating pilfered antiquities and cultural property, and it is through these repatriations that new generations are able to experience a part of their nation’s story,” Fitzhugh said.
[edit] 12th-century stolen bronze Buddha idol returned by UK
Sep 18, 2019: The Times of India

From: Sep 18, 2019: The Times of India
A 12th -century bronze idol stolen from Nalanda Museum in 1961 and returned to India by the UK last year was formally handed over to the Archaeological Survey of India on Tuesday evening. It was formally presented by finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman to Union culture minister Prahlad Singh Patel at her residence. Director general of ASI and other staff were also present on the occasion, said a source.
The idol had been stolen along with 13 other antiquities from ASI’s site museum. It changed several hands before surfacing at a London trade fair in March 2018. There, it was identified by Lynda Albertson of Association for Research into Crimes Against Art and S Vijay Kumar of India Pride Project, who then alerted the Metropolitan Police. Once it was verified, the Scotland Yard returned it to the Indian high commissioner on Independence Day last year.
After India received it, the artefact lay in the custody of the Department of Revenue Intelligence. Now, ASI will hold it in Delhi for a while before it is returned to Nalanda Museum. The idol is made of bronze with silver inlay work and has a seated Buddha in the ‘bhumisparsha mudra’ or ‘earth witness’ gesture. The idol is six and a half inches in length and was found during a dig at the ruins of the ancient university at Nalanda or the Nalanda Mahavihara.
[edit] 2020
[edit] Idols stolen from TN return after 42 years
Manimugdha Sharma, November 19, 2020: The Times of India

From: Manimugdha Sharma, November 19, 2020: The Times of India
Three medieval-era bronze idols of Ram, Lakshman and Sita, stolen from a Tamil Nadu temple in the 1970s before surfacing in Britain recently, were handed over to the Tamil Nadu government on Wednesday, ending a quest that began 42 years ago.
These idols along with a fourth of Hanuman, belonging to the Sri Rajagopalaswamy Temple in Anandamangalam, Nagapattinam, were photographed and documented in 1958, and their record remained with the French Institute of Pondicherry since. But between November 23 and 24, 1978, all four idols were stolen.
The thieves were later caught, but by then the idols had changed hands and left the country. The Hanuman idol was traced to a museum in a Southeast Asian country, but the whereabout of the rest was unknown until three years ago when a private initiative called India Pride Project spotted the Ram statue while going through the website of British Association of Antique Dealers.
Inquiries were made in India and Britain, and an important tip from the UK boosted the search. In August 2019, after receiving the information, the Indian high commission contacted the Idol Wing of Tamil Nadu Police. The details matched, so the high commission contacted the Art and Antiques unit of Scotland Yard. The British police met the owner of the idols and he agreed to hand them back.
On September 15, Metropolitan Police, London, which had taken custody of the statues, gave them to the high commission. On Wednesday, Union minister Prahlad Singh Patel, flanked by Abhay Kumar Singh, ADGP of Tamil Nadu Police’s Idol Wing, and other ASI officials, were present at an event where the recovered idols were unveiled.
The Ram, Lakshman and Sita statues measure, respectively, 90.5cm, 78cm and 74.5cm. They are in the Vijaynagar style, distinguished by the tall headgear or kulavi, derived from the Persian kula or cap.
The culture ministry said at the event that since 2014, 40 artefacts stolen from India had been returned, many of which are now in the museum at Purana Qila. But the battle to stop theft of antiquities, their documentation and streamlining channels of return is still a continuing process.
Art historian and museum expert Deepthi Sasidharan said that while the government made efforts, “the robust trade of antiquities across borders is proof of the basic weaknesses”. Sasidharan said, “I am unaware of any public portal where you can submit a query and an agency speedily responds. The National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities exists but the site lists 12,61,982 registered antiquities, but there’s no way to monitor the movement of these antiquities. Quick superficial changes can quickly obliterate their identities.” While gratified to see national treasures returned, she was insistent that “a robust national registry is imperative”.
Another expert, choosing to remain anonymous, also wondered what happened to the retrieved artefacts away from the media glare. “In museums abroad, at least, they are well taken care of and preserved in temperature-controlled environments. What happens once such objects are back in India is anybody’s guess,” the expert said. “There’s a need to build good mechanisms, but these occasional returns shouldn’t be the only way for us to take notice of the bigger problem of theft, and in some cases, retheft after artefacts are recovered.”
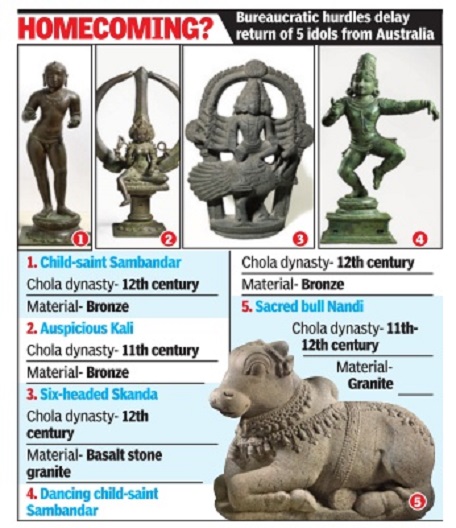
[edit] 2021
[edit] Indian antiques in other countries

From: Aug 8, 2021: The Times of India
See graphic:
Indian antiques in other countries, As in 2021
[edit] Kashi temple idol stolen in 1913 back from Canada
Zumbish, Nov 12, 2021: The Times of India
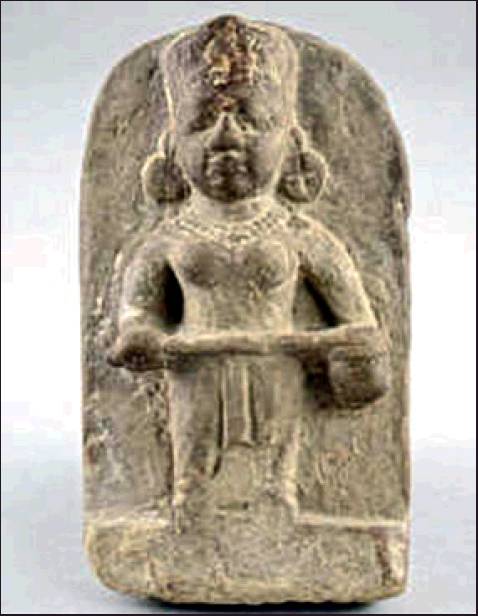

From: Zumbish, Nov 12, 2021: The Times of India
After a wait of over100 years, an18th century idol of Goddess Annapurna stolen from Varanasi and illegally taken to Canada was returned to the Uttar Pradesh government. To mark the moment, an event was organised at National Gallery of Modern Art.
Brought back with the help of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), the idol would be placed inside Kashi Vishwanath temple. After crossing Aligarh on November 11, Kannauj on November 12 and Ayodhya on November 14, it would finally reach Varanasi on November 15.
“The idol, illegally lifted by Canadian art collector and lawyer Norman MacKenzie from a Kashi temple 108 years ago, was returned to India on October 15,” a senior official at ASI’s headquarters Dharohar Bhavan at Tilak Marg, where the idol was kept before being returned to UP, told TOI.
ASI said the statue was returned with the help of the Consulate General office in Canada. Prime Minister Narendra Modi had announced the return of this idol from Canada in his “Mann Ki Baat” on November 29, 2020. Two years ago, Canada-based artist Divya Mehra noticed a sculpture at MacKenzie Art Gallery at University of Regina represented as Lord Vishnu while researching on the collection and it struck her as a female, holding a bowl of rice. When she checked the records, she found that the same sculpture was stolen from a temple in Kashi in 1913.
Union culture minister G Kishan Reddy applauded ASI for the feat and said, “Soon, the central government will hand over two idols to Tamil Nadu, one to Andhra Pradesh and one to Rajasthan.” MoS for external affairs and culture Meenakshi Lekhi and ASI officials were also present at the event to officially hand over the statue to UP.
Meanwhile, of the 157 Indian heritage artefacts and antiquities handed over to the PM during his recent visit to the US, 63 were returned to India late on Tuesday. ASI officials told TOI that the artefacts would stay in their custody unless some would need to be returned to the states from where they were stolen. They added that 94 other artefacts handed over to the PM by the US government would return to India within a month.
Sources said the stolen or smuggled artefacts and antiquities included a 10th century 1.5m bas relief panel of Revanta in sandstone, a 12th century bronze Nataraj figure, 56 terracotta pieces, bronze figurines and copper objects, and an 18th century sword in its sheath.
[edit] 63 Antiques back from the USA
Zumbish, Dec 2, 2021: The Times of India
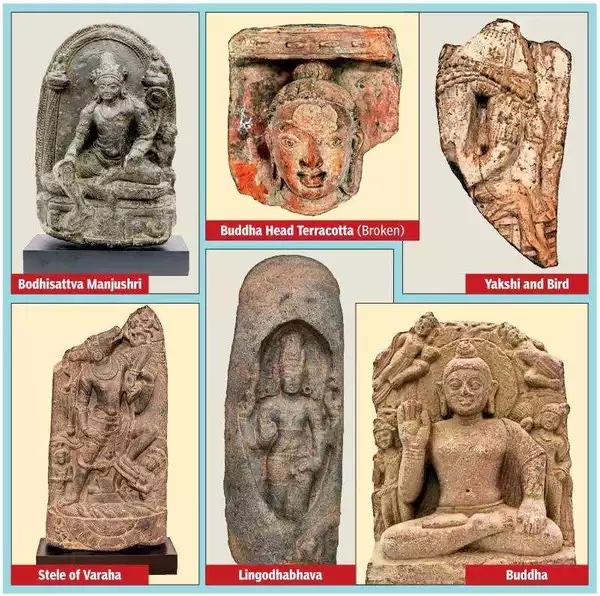

From: Zumbish, Dec 2, 2021: The Times of India
The Archaeological Survey of India has received 63 of the 157 antiques that were repatriated to India after decades of stay in the US, either smuggled into that country or stolen from India.
The articles that came home on November 9 include figurines in metal, stone and terracotta and paintings. “A consignment of the remaining artefacts will arrive in India from the US next month,” said Anil Tiwari, director of antiquities, ASI. An official at Dharohar Bhawan added on Tuesday, “ASI had been constantly communicating with the Indian embassy in the US and the Indian consulate in New York on the repatriation of the artefacts.”
Tiwari spent a fortnight in the US prior to the PM’s visit inspecting the retrieved historic objects. Lingodhbhava, a black stone sculpture, was on display at the Birmingham Museum in Alabama. Another sculpture depicting Bodhisattva Manjushri, the embodiment of wisdom holding a sword and painted in gold leaf, was found at Ackland Art Museum of the University of North Carolina.
Lingodhbhava dates to the late Chola period between the 12th and 13th centuries CE and depicts Lord Shiva as a four-armed god. At the bottom of the sculpture, Vishnu is depicted as a boar digging deep into the earth. Brahma is represented by a swan soaring into the sky. This antiquity’s state of origin has been traced by Dharohar Bhawan to Tamil Nadu.
Bodhisattva Manjushri depicts the most significant Bodhisattva in Mahayana literature. The statute shows the left hand holding a lotus on which Buddha is seen seated. The Bodhisattva is seen wearing beautiful ornaments. A lion's image is carved on both sides of the pedestal. The artefact dates back to the Pala empire around the 10th century CE. According to ASI officials, its origin is either West Bengal or Odisha.
There is also a paper painting on a copper sheet that depicts Rasikapriya from Samdehi Ragini. The painting by an anonymous painter has a scene possibly influenced by the famed Rasikapriya, a poetic work written by Keshava Das in 1555-1617. The painting’s reverse bears a rubber stamp marking that puts its provenance in the personal collection of the Maharaja of Bikaner.
Among other repatriated items are Torso of a Woman from a period between the 1st century BCE and 1st century CE, Standing Monkey dating to the Gupta period, a beautifully carved statue of Buddha in red sandstone from around 7th-8th century CE, its origin, according to ASI, being probably Mathura in UP.
The origin state of the other artefacts is yet to be determined by ASI. Buddha Head in terracotta probably from the Gupta period, Bull probably from the Harappa civilisation of 5th-3rd millennium BCE, a beautifully carved Yakshi and Bird from 1st century BCE-1st century CE and the stele of Varaha, dated 8th-11th century CE.
“The Buddha Head seems to have its origin in central India and Yakshi and Bird in West Bengal,” surmised D N Dimri, retired director of antiquities, ASI. “The stele of Varaha, in which Varaha is the boar incarnation of Lord Vishnu, comes from an area ruled by the Palas and today comprises parts of the states of Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal.”
According to sources in Dharohar Bhawan, these artefacts were stolen at different times though several of them were smuggled into the US by jailed art dealer Subhash Kapoor, who was charged by prosecutors in Manhattan in 2019 with stealing and possessing artefacts worth millions of dollars. Kapoor is currently in an Indian jail awaiting trial. Over the years, several international museums have voluntarily shared information with India about antiquities they procured from Kapoor that they were unaware were illegally being traded.
[edit] 2022
[edit] Glasgow museum
August 20, 2022: The Times of India

From: August 20, 2022: The Times of India
Glasgow: Glasgow held a ceremony on Friday to officially repatriate seven Indian cultural artefacts looted during British colonial rule, calling it a first for a UK museum service. Dignitaries from the high commission of India joined members of Glasgow Life, the charity that manages the Scottish city’s museum collections, at the transfer of ownership ceremony, following more than 18 months of talks. Six of the items were stolen from northern India in the 1800s, and a seventh was illegally purchased after being stolen from its original owners. All seven objects were looted from sacred places such as temples and shrines and given as gifts to the Scottish city’s museum collections. “Glasgow has led repatriation efforts in the UK since 1998,” said Duncan Dornan, head of Museums and Collections at Glasgow Life. “We look forward to continuing our work with the Indian authorities to deliver the safe return of these artefacts. ” In all, Glasgow is set to return 51 items to the descendants of their rightful owners from India and Nigeria as well as the Cheyenne River and Oglala Sioux tribes in the US state of South Dakota.
Glasgow’s repatriation commitment is part of a wider reassessment of the provenance of items in Western museums, in the wake of global anti-racism movements. Earlier this year, two British universities returned two Benin bronzes looted by British colonialists in the 19th century to Nigeria. AFP
[edit] Yale Museum
April 3, 2022: ‘'The New York Times
Law enforcement officials have seized 13 artifacts from the Yale University Art Gallery that they say were looted. Many of those, the authorities said, are part of an ongoing investigation into Subhash Kapoor, a former Madison Avenue art dealer accused of being one of the world’s most prolific antiquities smugglers.

