Economy, India: international comparisons
(Created page with "=The Indian economy: international comparisons= {| class="wikitable" |- |colspan="0"|<div style="font-size:100%"> This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence ...") |
(→2009-16) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 9: | Line 8: | ||
See [[examples]] and a tutorial.</div> | See [[examples]] and a tutorial.</div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | =Comparisons on multiple-indicators= | |
| + | ==1991-21: trade, FDI, foreign funds, Indians abroad== | ||
| + | [[File: The Indian economy vis-à-vis the world, 1991-21, trade, FDI, foreign funds, Indians abroad.jpg| The Indian economy vis-à-vis the world, 1991-21: trade, FDI, foreign funds, Indians abroad <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2021%2F02%2F02&entity=Ar00703&sk=F7D23A54&mode=image February 2, 2021: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''See graphic''': | |
| − | + | '' The Indian economy vis-à-vis the world, 1991-21: trade, FDI, foreign funds, Indians abroad '' | |
| − | + | ==1991-21: GDP, Poverty, life expectancy, literacy, urban population== | |
| + | [[File: 1991-21, GDP, Poverty, life expectancy, literacy, urban population and power consumption in India and South Asia.jpg| 1991-21: GDP, Poverty, life expectancy, literacy, urban population and power consumption in India and South Asia <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2021%2F02%2F02&entity=Ar01209&sk=EC5480F6&mode=image February 2, 2021: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''See graphic''': | |
| − | + | '' 1991-21: GDP, Poverty, life expectancy, literacy, urban population and power consumption in India and South Asia ''' | |
| − | + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | |
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| − | India, | + | =Economic growth= |
| + | == 2007> 2017: India 5th fastest, behind Ethiopia== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2018%2F02%2F04&entity=Ar02305&sk=5E7C7301&mode=text February 5, 2018: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| − | + | [[File: State of the world's wealth, biggest gainers and top losers, February 2018.jpg|State of the world's wealth, biggest gainers and top losers, February 2018 <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2018%2F02%2F04&entity=Ar02305&sk=5E7C7301&mode=text February 5, 2018: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Vietnam grew rich the fastest in the past 10 years, India finished fifth behind Ethiopia'' | |
| − | + | The combined wealth of people across the world is $215 trillion now — more than 11 times the US GDP. But some countries have grown richer much faster than others. Vietnam added wealth the fastest between 2007 and 2017, although China, a close second, impressed more by continuing to accelerate hard over its already impressive wealth base. India was a distant fifth, behind Ethiopia, while many European countries ended the decade poorer than they were before the start of the financial crisis in 2007. Among rich nations, Australia and New Zealand performed best, almost doubling their wealth in the period. | |
| − | The | + | ==2014-17== |
| + | [[File: 2014- Q3 of 2017- The growth rate of the Indian economy vis-à-vis China, OECD and the USA.jpg|2014- Q3 of 2017: The growth rate of the Indian economy vis-à-vis China, OECD and the USA <br/> From [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2018%2F01%2F30&entity=Ar02611&sk=AB92F888&mode=text '' The Times of India ''] |frame|500px]] | ||
| − | + | '''See graphic:''' | |
| − | The | + | ''2014- Q3 of 2017: The growth rate of the Indian economy vis-à-vis China, OECD and the USA'' |
| − | The | + | =Economic influence= |
| + | ==2016== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2018%2F09%2F19&entity=Ar00200&sk=A07D5091&mode=text September 19, 2018: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: GDP (in PPP) and working population of India and comparable countries (China, USA, Japan, Russia) in 2016.jpg|i) GDP (in PPP) and working population of India and comparable countries (China, USA, Japan, Russia) in 2016; <br/> ii) The ‘power’ and influence (in the Asia-Pacific region) of the above countries, as well as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Nepal. <br/> iii) Productivity and spending on R&D in India, China, USA, Japan, Singapore. <br/> iv) Exports from India, China, USA, Japan, Russia: globally and with Asia-Pacific countries. <br/> All presumably as in 2016. <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2018%2F09%2F19&entity=Ar00200&sk=A07D5091&mode=text September 19, 2018: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''See graphic''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''i) GDP (in PPP) and working population of India and comparable countries (China, USA, Japan, Russia) in 2016; <br/> ii) The ‘power’ and influence (in the Asia-Pacific region) of the above countries, as well as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Nepal. <br/> iii) Productivity and spending on R&D in India, China, USA, Japan, Singapore. <br/> iv) Exports from India, China, USA, Japan, Russia: globally and with Asia-Pacific countries. <br/> All presumably as in 2016.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Global power, economic and strategic, is shifting eastwards. The Asia-Pacific region is home to three of the world’s four largest economies and by 2025 two-thirds of the global population will live here. Despite the US’s waning power, with its diplomatic ties and economic strength, it beats all other Asia-Pacific nations on influence held in the region. A Lowy Institute report on 25 Asia-Pacific countries shows the most influential nations in the region. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =External debt in foreign and domestic currencies= | ||
| + | ==External debt: its size in rupees== | ||
| + | ===2009-16=== | ||
| + | [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=STATOISTICS-A-debt-of-Rs-54000-hangs-over-23122016008034 ''The Times of India''], Dec 23, 2016 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: External debt of the Government of India, March 31, 2016 and interest paid on debt, 2009-16, year-wise.jpg|External debt of the Government of India, March 31, 2016 and interest paid on debt, 2009-16, year-wise; [http://epaperbeta.timesofindia.com/Article.aspx?eid=31808&articlexml=STATOISTICS-A-debt-of-Rs-54000-hangs-over-23122016008034 ''The Times of India''], Dec 23 2016|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''A debt of Rs 54,000 hangs over every Indian's head''': as on '''31 March, 2016''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Apart from all the EMI payments and other personal loans that each Indian may have availed, he or she also has another big, if notional, debt burden. This is the onus of paying back the loans and commercial borrowings of the Union government, money taken from external agencies primarily for developmental expenditure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===2017-2025=== | ||
| + | [https://epaper.indiatimes.com/article-share?article=28_08_2025_018_001_cap_TOI Aug 28, 2025: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' External Debt and Debt-to-GDP Ratio ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! <br>Year<br> !! <br>External Debt ($bn)<br> !! <br>Debt-to-GDP Ratio (%)<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2017<br> || <br>~470<br> || <br>~20.0<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2018<br> || <br>~510<br> || <br>~20.5<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2019<br> || <br>~490<br> || <br>~19.8<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2020<br> || <br>~560<br> || <br>~21.0<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2021<br> || <br>~570<br> || <br>~21.5<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2022<br> || <br>~610<br> || <br>~20.5<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2023 R<br> || <br>~630<br> || <br>~19.0<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2024 PR<br> || <br>~690<br> || <br>~18.0<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>2025 P<br> || <br>736.3<br> || <br>19.1<br> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''' External Debt Currency Profile (end-March 2025) ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! <br>Currency<br> !! <br>Share (%)<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>US Dollar<br> || <br>54.2<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>Indian Rupee<br> || <br>31.1<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>Japanese Yen<br> || <br>6.2<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>SDR<br> || <br>4.6<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>Euro<br> || <br>3.2<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <br>Others<br> || <br>0.7<br> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==2024: India vis-à-vis the world== | ||
| + | [[File: The relative proportions of foreign vs domestic currency-denominated external debt in India and comparable countries, in Q3 2024.jpg| The relative proportions of foreign vs domestic currency-denominated external debt in India and comparable countries, in Q3 2024 <br/> From: [https://epaper.indiatimes.com/article-share?article=22_04_2025_021_002_cap_TOI April 22, 2025: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''See graphic''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | '' The relative proportions of foreign vs domestic currency-denominated external debt in India and comparable countries, in Q3 2024 '' | ||
| + | |||
| + | See also [[ Economic Affairs: India]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = External debt to GDP ratio= | ||
| + | ==2024== | ||
| + | Source: The Times of India 21 April 2025, citing Moody’s ratings | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Chile | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~80% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Malaysia | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~70% | ||
| + | |||
| + | UAE | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~65% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Romania | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~60% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nigeria | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~60% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hungary | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~50% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Poland | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~50% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~45% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Colombia | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~45% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Argentina | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~40% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vietnam | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~40% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Peru | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~40% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thailand | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~35% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Indonesia | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~30% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mexico | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~25% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Philippines | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~25% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Turkiye | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~25% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Brazil | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~20% | ||
| + | |||
| + | India | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~15% | ||
| + | |||
| + | China | ||
| + | External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~10% | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = External Vulnerability Indicator= | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==As of 2023== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is a text representation of a chart from The Times of India, New Delhi, dated Saturday, April 19, 2025, showing the External Vulnerability Indicator (%) by country: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | External Vulnerability Indicator (%) by Country (Data as of 2023, Source: Moody’s Ratings) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Turkey: ~300% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Argentina: ~280% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hungary: ~250% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chile: ~200% | ||
| + | |||
| + | UAE: ~180% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt: ~150% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Malaysia: ~130% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Romania: ~120% | ||
| + | |||
| + | South Africa: ~110% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nigeria: ~100% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Poland: ~90% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Colombia: ~80% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vietnam: ~70% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Brazil: ~60% | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' India: ~50% ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Indonesia: ~40% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thailand: ~30% | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' China: ~25% ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mexico: ~20% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Philippines: ~15% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Peru: ~10% | ||
| + | |||
| + | Saudi Arabia: ~5% | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =GDP growth= | ||
| + | ==As in 2018== | ||
| + | [[File: GDP growth in India vis-à-vis other major economies, 2018; China’s growth rate, 1961-2018.jpg| GDP growth in India vis-à-vis other major economies, 2018 <br/> China’s growth rate, 1961-2018 <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/Olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2019%2F09%2F05&entity=Ar00400&sk=14372EB1&mode=image Sep 5, 2019: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''' See graphic ''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | '' GDP growth in India vis-à-vis other major economies, 2018 <br/> China’s growth rate, 1961-2018 '' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONSECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Prosperity Index = | ||
| + | ==2016> 2017: Legatum == | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/india-reduces-gap-with-china-on-prosperity-study/articleshow/62031094.cms December 12, 2017: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: Score in Legatum Prosperity Index, India, Pakistan, and other countries.jpg|Score in Legatum Prosperity Index, India, Pakistan, and other countries <br/> From: [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/india-reduces-gap-with-china-on-prosperity-study/articleshow/62031094.cms December 12, 2017: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''HIGHLIGHTS''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The gap between China and India's prosperity has narrowed by four ranks since 2016. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Legatum Prosperity Index is an annual ranking developed by the London-based Legatum Institute. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The gap between China and India's prosperity+ has narrowed by four ranks since 2016 and to a quarter of what it was in 2012, according to the latest Legatum Prosperity Index, an annual ranking developed by the London-based Legatum Institute. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The upward trend in India's prosperity is significant in view of the fact that India registered lower GDP growth following demonetisation and implementation of the GST reform in 2017. India closed in on China+ through gains in business environment, economic quality and governance, the report said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Legatum Institute applauded India for improving governance by legislation "that increased the ability to challenge regulation in the legal system". The report attributed the gains in business environment and economic quality to improvement in intellectual property rights and massive rise in bank account holders. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Prosperity Index determined by nine sub-indices — business environment, governance, education, health, safety and security, personal freedom, social capital and natural environment — is reviewed by a panel of academics from various disciplines and reputed schools like London School of Economics, Tufts University, Brookings Institution and University of California, San Diego. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the 2017 Legatum Prosperity Index, based on 104 different variables analysed across 149 nations, India has significantly improved in the economic quality and education pillars. "More people are now satisfied with their standard of living and household incomes," the report said. | ||
| + | |||
| + | China, according to the report, has lost out "economically as people perceived greater barriers to trade and less encouragement of competition; and educationally through a falling primary school completion rate". | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overall, world prosperity increased in 2017 and now sits at its highest level in the last decade even as the world went through turbulence due to terrorism, war against Islamic State and displacement of massive number of people in West Asia and North Africa. The global prosperity is now 2.6% higher than in 2007. While prosperity improved around the world in 2017, no region grew as fast as Asia-Pacific. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Asia-Pacific region, which includes China and India, registered greatest improvement in business environment and worst performance towards natural environment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Trade= | ||
| + | ==1990-2016: Trade as percentage of GDP- India, China and the USA== | ||
| + | [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/toi-budget-2018-special-indias-economy-is-more-globalised-than-china-us/articleshow/62600713.cms January 22, 2018: ''The Times of India''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: Trade as percentage of GDP, India, China and the USA, 1990-2016.jpg|Trade as percentage of GDP, India, China and the USA, 1990-2016 <br/> From: [https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/toi-budget-2018-special-indias-economy-is-more-globalised-than-china-us/articleshow/62600713.cms January 22, 2018: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''See graphic''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Trade as percentage of GDP, India, China and the USA, 1990-2016'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | One of the measures of globalisation is trade (export and import) as percentage of GDP. In 1990, trade accounted for only 15 per cent of India's GDP, nearly half of China's trade-GDP ratio. But the picture now is very different. In 2016, India's trade had risen to nearly 40 per cent of GDP, whereas it was only 37.05 per cent in the case of China, and this despite a slight drop in trade. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Of course, in the case of China, trade peaked at 63 per cent of GDP before falling again, reflecting a change in the structure of the economy towards being more driven by domestic demand. Wonder what finance minister Arun Jaitley has in store in Budget 2018 to give a leg up to both trade and domestic consumption? | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Trillion dollar economies= | ||
| + | == Add a trillion dollars to the economy== | ||
| + | [[File: The number of years it took the USA, China, India and Brazil to add every trillion dollars to their economies.jpg|The number of years it took the USA, China, India and Brazil to add every trillion dollars to their economies <br/> From: [https://epaper.timesgroup.com/olive/ODN/TimesOfIndia/shared/ShowArticle.aspx?doc=TOIDEL%2F2019%2F07%2F10&entity=Ar00603&sk=D353D67B&mode=image July 10, 2019: ''The Times of India'']|frame|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | See graphic, 'The number of years it took the USA, China, India and Brazil to add every trillion dollars to their economies ' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|E | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|E | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|E | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|E | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|E | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:China|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Development|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Economy-Industry-Resources|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages with broken file links|ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pakistan|EECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS | ||
| + | ECONOMY, INDIA: INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 22 September 2025
This is a collection of articles archived for the excellence of their content. Readers will be able to edit existing articles and post new articles directly |
Contents |
[edit] Comparisons on multiple-indicators
[edit] 1991-21: trade, FDI, foreign funds, Indians abroad

From: February 2, 2021: The Times of India
See graphic:
The Indian economy vis-à-vis the world, 1991-21: trade, FDI, foreign funds, Indians abroad
[edit] 1991-21: GDP, Poverty, life expectancy, literacy, urban population
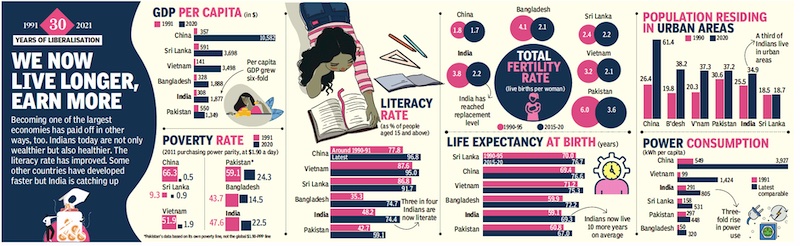
From: February 2, 2021: The Times of India
See graphic:
1991-21: GDP, Poverty, life expectancy, literacy, urban population and power consumption in India and South Asia '
[edit] Economic growth
[edit] 2007> 2017: India 5th fastest, behind Ethiopia
February 5, 2018: The Times of India

From: February 5, 2018: The Times of India
Vietnam grew rich the fastest in the past 10 years, India finished fifth behind Ethiopia
The combined wealth of people across the world is $215 trillion now — more than 11 times the US GDP. But some countries have grown richer much faster than others. Vietnam added wealth the fastest between 2007 and 2017, although China, a close second, impressed more by continuing to accelerate hard over its already impressive wealth base. India was a distant fifth, behind Ethiopia, while many European countries ended the decade poorer than they were before the start of the financial crisis in 2007. Among rich nations, Australia and New Zealand performed best, almost doubling their wealth in the period.
[edit] 2014-17

From The Times of India
See graphic:
2014- Q3 of 2017: The growth rate of the Indian economy vis-à-vis China, OECD and the USA
[edit] Economic influence
[edit] 2016
September 19, 2018: The Times of India

ii) The ‘power’ and influence (in the Asia-Pacific region) of the above countries, as well as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Nepal.
iii) Productivity and spending on R&D in India, China, USA, Japan, Singapore.
iv) Exports from India, China, USA, Japan, Russia: globally and with Asia-Pacific countries.
All presumably as in 2016.
From: September 19, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
i) GDP (in PPP) and working population of India and comparable countries (China, USA, Japan, Russia) in 2016;
ii) The ‘power’ and influence (in the Asia-Pacific region) of the above countries, as well as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Nepal.
iii) Productivity and spending on R&D in India, China, USA, Japan, Singapore.
iv) Exports from India, China, USA, Japan, Russia: globally and with Asia-Pacific countries.
All presumably as in 2016.
Global power, economic and strategic, is shifting eastwards. The Asia-Pacific region is home to three of the world’s four largest economies and by 2025 two-thirds of the global population will live here. Despite the US’s waning power, with its diplomatic ties and economic strength, it beats all other Asia-Pacific nations on influence held in the region. A Lowy Institute report on 25 Asia-Pacific countries shows the most influential nations in the region.
[edit] External debt in foreign and domestic currencies
[edit] External debt: its size in rupees
[edit] 2009-16
The Times of India, Dec 23, 2016

A debt of Rs 54,000 hangs over every Indian's head: as on 31 March, 2016
Apart from all the EMI payments and other personal loans that each Indian may have availed, he or she also has another big, if notional, debt burden. This is the onus of paying back the loans and commercial borrowings of the Union government, money taken from external agencies primarily for developmental expenditure.
[edit] 2017-2025
Aug 28, 2025: The Times of India
External Debt and Debt-to-GDP Ratio
| Year |
External Debt ($bn) |
Debt-to-GDP Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 |
~470 |
~20.0 |
| 2018 |
~510 |
~20.5 |
| 2019 |
~490 |
~19.8 |
| 2020 |
~560 |
~21.0 |
| 2021 |
~570 |
~21.5 |
| 2022 |
~610 |
~20.5 |
| 2023 R |
~630 |
~19.0 |
| 2024 PR |
~690 |
~18.0 |
| 2025 P |
736.3 |
19.1 |
External Debt Currency Profile (end-March 2025)
| Currency |
Share (%) |
|---|---|
| US Dollar |
54.2 |
| Indian Rupee |
31.1 |
| Japanese Yen |
6.2 |
| SDR |
4.6 |
| Euro |
3.2 |
| Others |
0.7 |
[edit] 2024: India vis-à-vis the world

From: April 22, 2025: The Times of India
See graphic:
The relative proportions of foreign vs domestic currency-denominated external debt in India and comparable countries, in Q3 2024
See also Economic Affairs: India
[edit] External debt to GDP ratio
[edit] 2024
Source: The Times of India 21 April 2025, citing Moody’s ratings
Chile
External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~80%
Malaysia External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~70%
UAE External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~65%
Romania External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~60%
Nigeria External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~60%
Hungary External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~50%
Poland External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~50%
Egypt External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~45%
Colombia External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~45%
Argentina External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~40%
Vietnam External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~40%
Peru External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~40%
Thailand External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~35%
Indonesia External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~30%
Mexico External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~25%
Philippines External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~25%
Turkiye External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~25%
Brazil External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~20%
India External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~15%
China External debt by place of issue as a percentage of GDP: ~10%
[edit] External Vulnerability Indicator
[edit] As of 2023
This is a text representation of a chart from The Times of India, New Delhi, dated Saturday, April 19, 2025, showing the External Vulnerability Indicator (%) by country:
External Vulnerability Indicator (%) by Country (Data as of 2023, Source: Moody’s Ratings)
Turkey: ~300%
Argentina: ~280%
Hungary: ~250%
Chile: ~200%
UAE: ~180%
Egypt: ~150%
Malaysia: ~130%
Romania: ~120%
South Africa: ~110%
Nigeria: ~100%
Poland: ~90%
Colombia: ~80%
Vietnam: ~70%
Brazil: ~60%
India: ~50%
Indonesia: ~40%
Thailand: ~30%
China: ~25%
Mexico: ~20%
Philippines: ~15%
Peru: ~10%
Saudi Arabia: ~5%
[edit] GDP growth
[edit] As in 2018

China’s growth rate, 1961-2018
From: Sep 5, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic :
GDP growth in India vis-à-vis other major economies, 2018
China’s growth rate, 1961-2018
[edit] Prosperity Index
[edit] 2016> 2017: Legatum
December 12, 2017: The Times of India

From: December 12, 2017: The Times of India
HIGHLIGHTS
The gap between China and India's prosperity has narrowed by four ranks since 2016.
The Legatum Prosperity Index is an annual ranking developed by the London-based Legatum Institute.
The gap between China and India's prosperity+ has narrowed by four ranks since 2016 and to a quarter of what it was in 2012, according to the latest Legatum Prosperity Index, an annual ranking developed by the London-based Legatum Institute.
The upward trend in India's prosperity is significant in view of the fact that India registered lower GDP growth following demonetisation and implementation of the GST reform in 2017. India closed in on China+ through gains in business environment, economic quality and governance, the report said.
The Legatum Institute applauded India for improving governance by legislation "that increased the ability to challenge regulation in the legal system". The report attributed the gains in business environment and economic quality to improvement in intellectual property rights and massive rise in bank account holders.
The Prosperity Index determined by nine sub-indices — business environment, governance, education, health, safety and security, personal freedom, social capital and natural environment — is reviewed by a panel of academics from various disciplines and reputed schools like London School of Economics, Tufts University, Brookings Institution and University of California, San Diego.
In the 2017 Legatum Prosperity Index, based on 104 different variables analysed across 149 nations, India has significantly improved in the economic quality and education pillars. "More people are now satisfied with their standard of living and household incomes," the report said.
China, according to the report, has lost out "economically as people perceived greater barriers to trade and less encouragement of competition; and educationally through a falling primary school completion rate".
Overall, world prosperity increased in 2017 and now sits at its highest level in the last decade even as the world went through turbulence due to terrorism, war against Islamic State and displacement of massive number of people in West Asia and North Africa. The global prosperity is now 2.6% higher than in 2007. While prosperity improved around the world in 2017, no region grew as fast as Asia-Pacific.
The Asia-Pacific region, which includes China and India, registered greatest improvement in business environment and worst performance towards natural environment.
[edit] Trade
[edit] 1990-2016: Trade as percentage of GDP- India, China and the USA
January 22, 2018: The Times of India
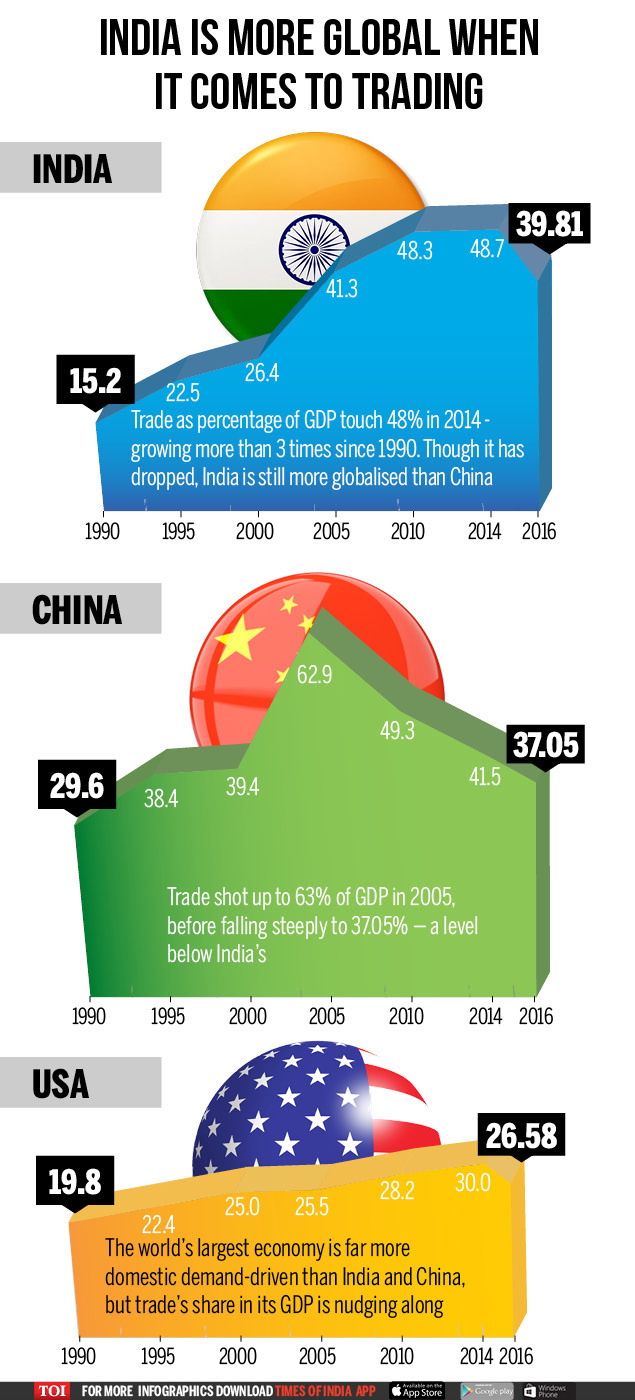
From: January 22, 2018: The Times of India
See graphic:
Trade as percentage of GDP, India, China and the USA, 1990-2016
One of the measures of globalisation is trade (export and import) as percentage of GDP. In 1990, trade accounted for only 15 per cent of India's GDP, nearly half of China's trade-GDP ratio. But the picture now is very different. In 2016, India's trade had risen to nearly 40 per cent of GDP, whereas it was only 37.05 per cent in the case of China, and this despite a slight drop in trade.
Of course, in the case of China, trade peaked at 63 per cent of GDP before falling again, reflecting a change in the structure of the economy towards being more driven by domestic demand. Wonder what finance minister Arun Jaitley has in store in Budget 2018 to give a leg up to both trade and domestic consumption?
[edit] Trillion dollar economies
[edit] Add a trillion dollars to the economy

From: July 10, 2019: The Times of India
See graphic, 'The number of years it took the USA, China, India and Brazil to add every trillion dollars to their economies '